![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of Skin Cancer |
- Basal Cell Carcinoma - Squamous Cell Carcinoma - Melanoma - Merkel Cell Carcinoma - Eccrine Carcinoma - Sebaceous Gland Carcinoma - Dermatofibrosarcomaprotuberans |
|

|
Actinic Keratosis - Intraepithelial keratinocyte neoplasia - Precursor to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) (about 1% per lesion per year) - Found on sun-exposed skin - Thin pink or red papillose with adherent scale - Often can be noticed by palpation before visual inspection Treatment : - Liquid nitrogen - Topical therapies: - 5-fluorouracil (Efudex, Carac) - imiquimod (Aldara) - Photodynamic therapy: 5-ALA and blue light |
|
|
Actinic Keratosis - Intraepithelial keratinocyte neoplasia - Precursor to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)(about 1% per lesion per year) - Found on sun-exposed skin - Thin pink or red papillose with adherent scale- Often can be noticed by palpation before visualinspection Treatment : - Liquid nitrogen - Topical therapies: - 5-fluorouracil (Efudex, Carac) - imiquimod (Aldara) - Photodynamic therapy: 5-ALA and blue light |
|

|
Actinic Keratosis |
|

|
Actinic Cheilitis - Usually affects lower lip |
|

|
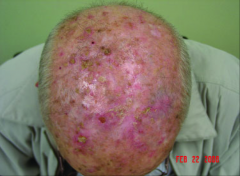
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) - Second most common type of skin cancer - Hyperkeratotic,scaly, flesh-colored to pink papules - Typically arises on sun-damaged skin (can occur on lips, genitals, non-exposed skin) Treatment for SCCIS (in-situ) - Liquid nitrogen (2 cycles of 30second freeze thaw) –Electrodessication and Curettage –Topical imiquimod(Aldara)cream Treatment for SCC - Liquid nitrogen or ED&C (destruction) - Surgery (excision vs. Mohs Micrographic) - Radiation therapy (for older people) |
|

|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
|

|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
|

|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
|

|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma - Second most common type of skin cancer - Hyperkeratotic, scaly, flesh-colored to pink papules - Typically arises on sun-damaged skin(can occur on lips, genitals, non-exposed skin) Treatment for SCCIS (in-situ) - Liquid nitrogen (2 cycles of 30 second freeze thaw) –Electrodessication and Curettage –Topical imiquimod (Aldara) cream Treatment for SCC - Liquid nitrogen or ED&C (destruction) - Surgery (excision vs. Mohs Micrographic) - Radiation therapy (for older people) |
|

|
Basal Cell Carcinoma - Most common skin cancer and most common malignancy in humans - Slightly more common in males - Usually arises on head and neck - Variants: - Nodular, Superficial, Morpheaform, Recurrent Treatment for superficial BCC: - Liquid nitrogen - Electrodessication and Curettage - Topical imiquimod cream Treatment for other BCCs: - Liquid nitrogen or ED&C - Surgery (excision vs. Mohs Micrographic) - Radiation therapy |
|

|
Basal Cell Carcinoma (Nodular) - Most common BCC - Can be pigmented |
|

|
Basal Cell Carcinoma |
|

|
Basal Cell Carcinoma (Morpheaform) - Scar-like; poorly defined margins; aggressive Treatment - Mohs Micrographic Surgery |
|

|
Basal Cell Carcinoma |
|

|
Basal Cell Carcinoma (pigmented) |
|

|
Basal Cell Carcinoma |
|

|
Basal Cell Carcinoma (Mohs Surgery) |
|

|
Basal Cell Carcinoma |
|

|
Malignant Melanoma - Malignancy arising from melanocytes - High metastatic potential leads to >75% skin cancer death - Most common cancer in young adults Melanoma Variants - Superficial Spreading Melanoma (60%) - Nodular Melanoma - Lentigo Maligna Melanoma - Acral Lentiginous Melanoma - Amelanotic Melanoma - Occular Melanoma - Mucosal Melanoma Treatment - Excision - Interferon alpha - Melanoma vaccines - Palliative Surgery - Chemotherapy: BRAF or CTLA-4 inhibitors |
|
|
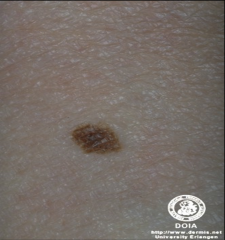
ABC's of Melanoma |
Asymmetry irregular Borders Colors Diameter: > 5mm Evolution (changing lesion) |
|
|
Benign Nevus |
|

|
Superficial Spreading Melanoma - Most common (60%) - Slow horizontal growth then rapid vertical growth - Men: Trunk - Women: Legs |
|

|
Superficial Spreading Melanoma |
|

|
Superficial Spreading Melanoma |
|

|
Superficial Spreading Melanoma |
|

|
Superficial Spreading Melanoma |
|

|
Nodular Melanoma - Second most common type (15-30%) - Usually diagnosed in 6th decade - Commonly on trunk, head, neck - More common in men - Blue to black noodle that grows rapidly/months - Poorer diagnosis |
|

|
Nodular Melanoma |
|

|
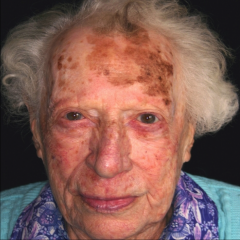
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma - 15% of Melanomas - Usually diagnosed in 7th decade - Slowlygrowing, asymmetric black macule/patch - InvasiveLMM arises in a precursor lesion termed lentigo maligna - SLOW EVOLUTION |
|

|
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma |
|
|
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma |
|

|
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma - Relatively uncommon - Occurs on palms, soles or around nails - 70% of melanomas in DARKLY PIGMENTED - Fast progression than other types - Mutation in c-kit gene |
|

|
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma |
|

|
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma (Hutchinson Sign) |
|

|
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma |

