![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Abiotic factor |

a nonliving condition or thing, as climate or habitat, that influences or affects an ecosystem and the organisms in it |
|
|
Adaption |

a change or the process of change by which an organism or species becomes better suited to its environment |
|
|
Altitude |
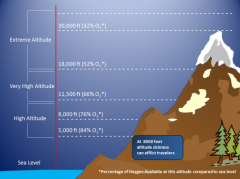
the apparent height of a celestial object above the horizon, measured as an angle |
|
|
Atmosphere
|
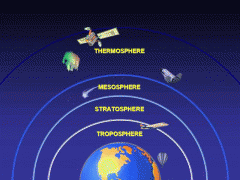
the envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet
|
|
|
Atom
|
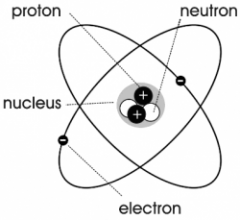
the basic unit of a chemical element
|
|
|
Biodiversity
|

the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
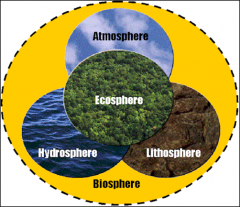
the regions of the surface, atmosphere, and hydrosphere of the earth (or analogous parts of other planets) occupied by living organisms
|
|
|
Biotic factor
|

any living component that affects another organism, including animals that consume the organism in question, and the living food that the organism consumes
|
|
|
Carnivore
|

an animal that feeds on flesh
|
|
|
Carrying capacity
|
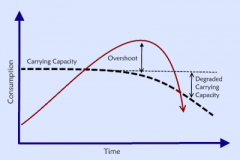
the number of people, other living organisms, or crops that a region can support without environmental degradation
|
|
|
Cinder cone
|
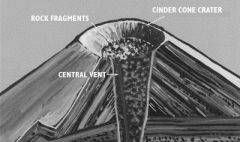
a cone formed around a volcanic vent by fragments of lava thrown out during eruptions
|
|
|
Climate
|
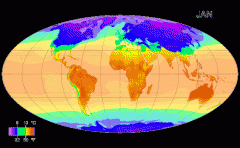
the weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period
|
|
|
Commensalisms
|

an association between two organisms in which one benefits and the other derives neither benefit nor harm
|
|
|
Community
|

a group of people living in the same place or having a particular characteristic in common
|
|
|
Compound
|
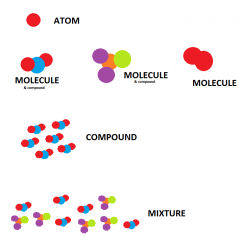
a thing that is composed of two or more separate elements; a mixture
|
|
|
Concentration
|
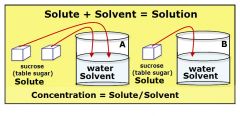
the number of molecules or ions in a given volume of a substance, expressed as moles of solute per litre of solution (molarity)
|
|
|
Condensation
|

the process by which water vapor in the air is changed into liquid water
|
|
|
Coniferous trees
|

a type of tree that produces cones and evergreen needles
|
|
|
Conservation
|

the act of conserving; prevention of injury, decay, waste, or loss; preservation: conservation of wildlife or conservation of human rights
|
|
|
Consumer
|
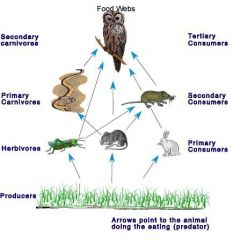
defined as 'one who acquires goods and services'
|
|
|
Continental drift
|
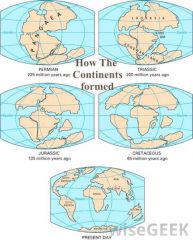
the Earth's continents have been joined together and have moved away from each other at different times in the Earth's history; this theory might've been first proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912
|
|
|
Contour interval
|
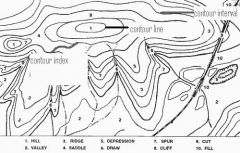
the difference in elevation represented by each contour line on a topographic map
|
|
|
Control
|
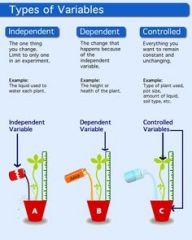
a standard of comparison for checking or verifying the results of an experiment
|
|
|
Convection current
|
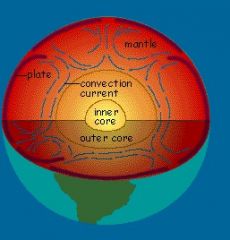
a major factor in weather
|
|
|
Coriolis effect
|
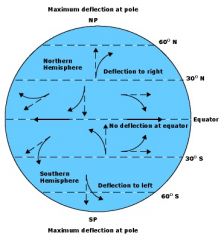
describes the turn of the wind to the right in the Northern Hemisphere caused by earth's rotation
|
|
|
Crater
|

the bowl-shaped depression around the orifice of a volcano
|
|
|
Crust
|
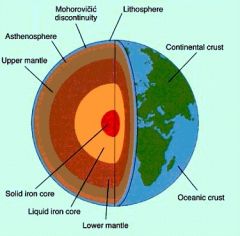
the outer layer of the Earth, between the surface and the mantle, which is up to 40 miles deep
|
|
|
Crystal
|

based on the microscopic arrangement of atoms inside it, called the crystal structure, a crystal is a solid where the atoms form a periodic arrangement
|
|
|
Cumulus
|

clouds generally associated with fair weather but can also bring rain when they expand to higher levels
|
|
|
Cyclone
|

a large-scale, atmospheric wind-and-pressure system characterized by low pressure at its center and by circular wind motion, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere
|
|
|
Deciduous trees
|

oak, maple, and elm are examples of deciduous trees; they lose their foliage in the fall and grow new leaves in the spring
|
|
|
Decomposer
|

an organism, often a bacterium or fungus, that feeds on and breaks down dead plant or animal matter, thus making organic nutrients available to the ecosystem |
|
|
Deep-ocean trench
|
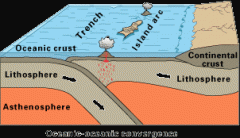
oceanic crust is formed at an oceanic ridge, while the lithosphere is sub-ducted back into the atmosphere at trenches; the oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor and are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor
|
|
|
Delta
|
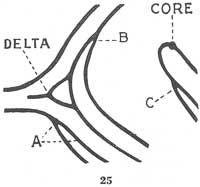
a nearly flat plain of alluvial deposit between diverging branches of the mouth of a river, often, though not necessarily, triangular
|
|
|
Density
|

a measure of mass per volume
|
|
|
Deposition
|
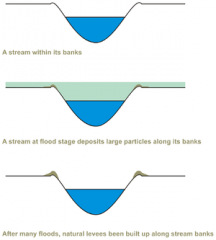
the geological process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to a landform or land mass
|
|
|
Earthquake
|
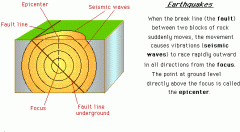
a sudden release of energy in the earth's crust or upper mantle, usually caused by movement along a fault plane or by volcanic activity and resulting in the generation of seismic waves which can be destructive related adjective seismic
|
|
|
Ecology
|
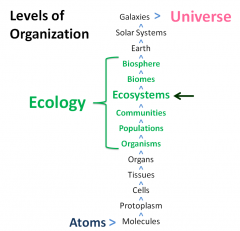
the scientific study of the processes influencing the distribution and abundance of organisms, the interactions between organisms and the transformation and flux of energy and matter
|
|
|
Element
|
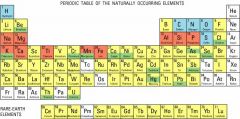
any material (such as carbon, hydrogen, iron, or oxygen) that cannot be broken down into more fundamental substances
|
|
|
Endangered species
|

a species of animal or plant that is seriously at risk of extinction
|
|
|
Epicenter
|
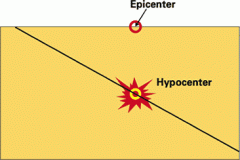
the point on the Earth's surface that is directly above the focus (the point of origin) of an earthquake; the epicenter is usually the location where the greatest damage associated with an earthquake occurs
|
|
|
Erosion
|
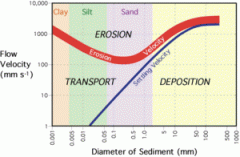
a type of weathering in which surface soil and rock are worn away through the action of glaciers, water, and wind
|
|
|
Extinct
|

(of a species, family, or other larger group) having no living members
|
|
|
Fault
|
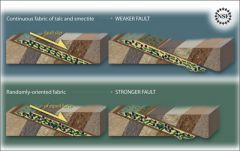
a fault is a crack in a rock along which slippage has occurred but most faults are small, even microscopic; only the large ones get names, like the San Andreas Fault
|
|
|
Flood plain
|
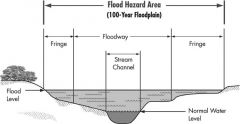
a nearly flat plain along the course of a stream or river that is naturally subject to flooding
|
|
|
Food chain
|
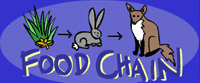
a diagram that shows how food energy moves from one organism to another in a given environment because food energy moves along the food chain when one organism eats another
|
|
|
Food web
|
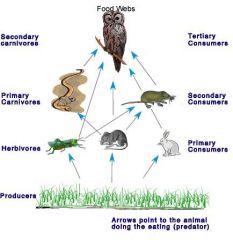
a series of organisms related by predator-prey and consumer-resource interactions; the entirely of interrelated food chains in an ecological community
|
|
|
Fossil
|

the preserved remains of a prehistoric organism or is slang for someone or something that is old and outdated; an example of a fossil is the preserved remains from a prehistoric organism that have been preserved inside rock
|
|
|
Geologist
|
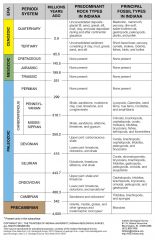
the science devoted to the study of the Earth, particularly the solid Earth and the rocks that compose it
|
|
|
Global warming
|
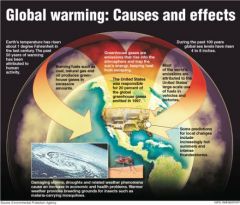
the increase in Earth's average surface temperature due to rising levels of greenhouse gases
|
|
|
Greenhouse effect
|
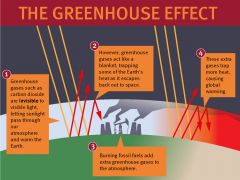
a phenomenon in which the atmosphere of a planet traps radiation emitted by its sun, caused by gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane that allow incoming sunlight to pass through but retain heat radiated back from the planet's surface
|
|
|
Groundwater
|
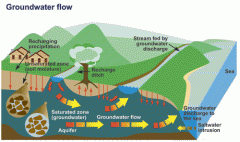
water that collects or flows beneath the Earth's surface, filling the porous spaces in soil, sediment, and rocks
|
|
|
Habitat
|

the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism
|
|
|
Hot spot
|
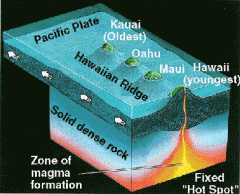
a place deep within the Earth where hot magma rises to just underneath the surface, creating a bulge and volcanic activity; the chain of Hawaiian Islands is thought to have been created by the movement of a tectonic plate over a hot spot
|
|
|
Humidity
|
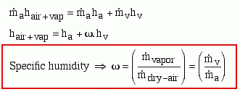
the state or quality of being humid
|
|
|
Hypothesis
|
a hypothesis is an idea or explanation that you then test through study and experimentation
|
|
|
Igneous rock
|
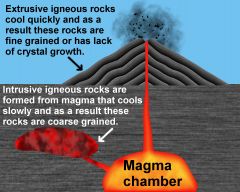
formed by the cooling and solidifying of molten materials
|
|
|
Landform
|

a recognizable, naturally formed feature on the Earth's surface
|
|
|
Lava
|
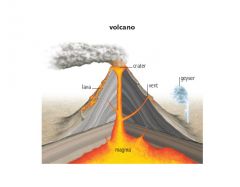
a type of igneous rock that is formed when molten magma from a volcano hardens
|
|
|
Magma
|
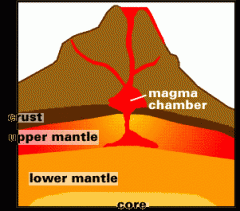
molten rock usually located deep within the mantle of the Earth that occasionally comes to the surface through cracks in the mantle or through the eruption of volcanoes
|
|
|
Metamorphic
|

denoting rock that has undergone transformation by heat, pressure, or other natural agencies in the folding of strata or the nearby intrusion of igneous rocks
|
|
|
Niche
|

the function or position of a species within an ecological community; a species niche includes the physical environment to which it has become adapted as well as its role as producer and consumer of food resources
|
|
|
Omnivore
|

an organism that eats both plants and animals
|
|
|
Plate tectonics
|
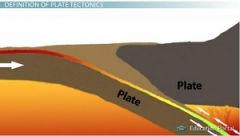
a theory in geology: the lithosphere of the Earth is divided into a small number of plates which float on and travel independently over the mantle and much of the Earth's seismic activity occurs at the boundaries of these plates
|
|
|
Rain forest
|

a dense evergreen forest with a minimum annual rainfall of approximately 180 centimeters (71 inches). Rainforests are found chiefly in the tropics but also occur in temperate regions, where the rainfall amount is somewhat lower
|
|
|
Sediment
|
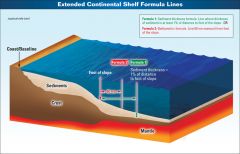
any particulate matter that can be transported by fluid flow and which eventually is deposited as a layer of solid particles on the bed or bottom of a body of water or other liquid; sedimentation is the deposition by settling of a suspended material
|
|
|
Sedimentary rock
|

rock that has formed through the deposition and solidification of sediment, especially sediment transported by water (rivers, lakes, and oceans), ice (glaciers), and wind; sedimentary rocks are often deposited in layers, and frequently contain fossils
|
|
|
Topographic map
|
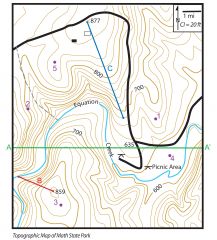
maps that are detailed, accurate graphic representations of features that appear on the Earth's surface
|
|
|
Variable
|
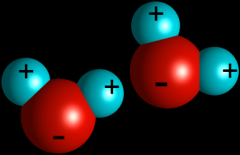
any factor, trait, or condition that can exist in differing amounts or types
|
|
|
Volcano
|

a rupture in the Earth's crust where molten lava, hot ash, and gases from below the Earth's crust escape into the air
|
|
|
Water cycle
|
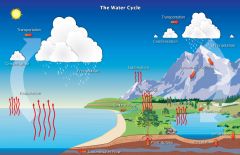
the continuous process by which water is circulated throughout the Earth and the atmosphere through evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and the transpiration of plants and animals; also called hydrologic cycle
|
|
|
Weather
|
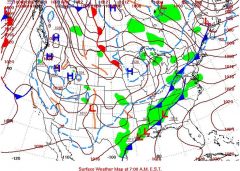
the daily conditions of the atmosphere in terms of temperature, atmospheric pressure, wind, and moisture
|
|
|
Weathering |

any of the chemical or mechanical processes by which rocks exposed to the weather undergo chemical decomposition and physical disintegration
|
|
|
Wetland |

land consisting of marshes or swamps; saturated land
|
|
|
Wind
|
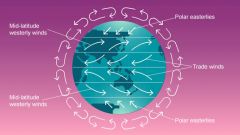
a current of air, especially a natural one that moves along or parallel to the ground, moving from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure; surface wind is measured by anemometers or its effect on objects, such as trees
|

