![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
125 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Which generation scanner has Fan beam geometry and a detector array arranged in a curved arc? |
3rd Generation Scanner. |
|
|
|
The abdominal aorta bifurcates at what level? |
L4 |
|
|
|
What is a normal platelet count? |
150,000-400,000/mm3 |
|
|
|
Quantitative CT is used to measure what? |
The mineral content of bone. |
|
|
|
What is the average osmolality of high osmolar contrast? |
1000-2400 mOsm/kg water |
|
|
|
What is the density of a mass of fat cells in HU numbers? |
-50 to -100 HU |
|
|
|
A CT of the abdomen should be done during what kind of breathing? |
Full expiration. (Holding breath) |
|
|
|
What can be given to reduce peristalsis and distend the colon for a CT of the abdomen pelvis? |
Glucagon ( 1 mg. by I.V.) |
|
|
|
What is the term used to describe a radio density similar to that of another or adjacent tissue? |
Isodense. (Hemangiomas enhance from periphery in word until they become isodense.) |
|
|
|
Common areas of calcifications within the brain? |
Choroid Plexus and Pineal gland. |
|
|
|
Angle of the gantry during a CT of the brain? |
15° above orbitomeatal line |
|
|
|
What happens when you increase the average photon energy of a heterogeneous x-ray beam? |
Beam Hardening. |
|
|
|
Increased aperture size (slice thickness) will increase what? |
Signal to noise ratio. |
Pixel x Matrix size= DFOV |
|
|
Calculate DFOV with a 320 Matrix and pixel dimension of 0.75x0.75 mm. |
0.75mmx320= 240 mm (24cm) |
|
|
|
The full width at half - maximum of the CT scanner describes? |
Spatial resolution. |
|
|
|
The average photon energy of the primary beam of a CT scanner with the tube potential of 120 KVP. |
70 KeV (average photon energy is 30-40% of applied kilo volts) |
|
|
|
How to reduce streak artifacts from edge gradient effect? |
Increase filtration, increase KVP |
|
|
|
What is statistical noise? (Static) |
Quantum mottle\graininess. |
|
|
|
Causes of low contrast resolution on scanner and the result to the patient? |
Increased electronic noise and decreased patient dose. |
|
|
|
The value of a pixel in H.U. Is calculated by? |
Comparison of linear attenuation. Coefficient of a voxel of tissue to that of water. |
|
|
|
Explain what contrast resolution is? |
The ability of scanner to differentiate objects with minimal differences in attenuation coefficients. |
|
|
|
What does dynamic scanning involve? |
Bolus of IV contrast, rapid scanning with minimal interscan delays. |
|
|
|
How will an acute subdural hematoma appear on a scan? |
Hyperdense. |
|
|
|
Benign pulmonary nodules will have a CT H.U. # of? |
+164 H.U. |
|
|
|
What area of the brain is not enhanced on the CT scan ? |
Posterior horn of the lateral ventricle. (Because it contains spinal fluid) |
|
|
|
What is interpolation used for? |
Mathematical technique used in reconstruction process of a spiral CT. |
|
|
|
A CT produces diagnostic images with improved_____? |
contrast resolution. |
|
|
|
What is the primary interaction between x-ray photons and tissue? |
Compton. |
|
|
|
Parental injection of medicine into the body? Name the different routes. (4) |
Intramuscular, intravenous, intradermal, subcutaneous. |
|
|
|
What is osmolality? |
The number of particles\ions formed when a substance dissociates in a given solution. |
|
|
|
The term used to describe systemic hypertension often leading to cerebral ischemia? |
Vasovagal. |
|
|
|
The interaction between x-ray beam and matter? (Also has the largest amount of patient dose.) |
Photoelectric effect. |
|
|
|
A common and effective sedative for children? |
Choral Hydrate. |
|
|
|
The portion of the nephron (kidney) that filters on wanted substances from blood plasma? |
Renal glomerulus. |
|
|
|
The adult spinal cord and at what level? |
L1-L2 |
|
|
|
Body part that stores most of the mature sperm? |
Vas deferns. |
|
|
|
Which sinuses are absent at birth and do not fully develope until after puberty? |
Frontal sinus. |
|
|
|
A condition of excess nitrogenous material in blood? |
Axotemia, uremia. |
|
|
|
Partial voluming average can be decreased by________? |
Decreasing slice thickness. |
|
|
|
The artifact that occurs when the patient suspends respiration at different depths during scanning? |
Misregistration. |
|
|
|
Most common type of noise found in CT image? |
Statistical noise. |
|
|
|
CT window controls _______on the CT image? |
Contrast and brightness. |
|
|
|
What is the relationship between the CT number and actual linear attenuation coefficients of an object? |
Linearity. |
|
|
|
What is responsible for the math calculations of the image reconstruction process? |
Array Processor. |
|
|
|
What would decrease noise on a CT image? |
Decreasing the matrix size. |
|
|
|
What is the CT number for blood? |
+42 - +58 H.U. |
|
|
|
The math technique used exclusively for image reconstruction with spiral CT? |
Interpolation. |
|
|
|
A contrast material that may be described as one that does not dissociate into charged particles in a solution? |
Non-ionic contrast. |
|
|
|
What are the advantages of auto power injectors over manual bolus of contrast injection? |
Increased tissue enhancement due to faster injection time. And uniform administration over entire length of the scan. |
|
|
|
The third ventricle of the brain communicates with the fourth ventricle through the________? |
Cerebral Aqueduct. |
|
|
|
To differentiate between the duodenum and the head of the Pancrease what is the best way to scan. And what type of contrast to use, and timing of? |
Use oral contrast 30 to 45 minutes before the scan. It is best if patient is placed in right lateral decubitus while scanning. |
|
|
|
What is a glioma and where would it be found? |
It is found in the brain. It is a general term to describe a group of primary tumor's consisting of malignant glial cells. |
|
|
|
Does decreasing the matrix size decrease the noise on a CT image? |
Yes !!! |
|
|
|
Increasing the pitch during a spiral CT exam adversely affects the _______along with which axis? |
The spatial resolution. The Z axis. |
|
|
|
Pre-patient collimation directly controls________? |
Slice thickness. |
|
|
|
What reduces scatter radiation from reaching the detectors? |
Post patient collimation and pre-detector collimation. |
|
|
|
Name a type of iso-osmolar contrast media? |
Iodixanal (Visipaque) |
|
|
|
What are three types of non-ionic contrast media (low osmolar)? |
(Omnipaque 350) Iohexol (Isovue 370) Lopamidol (Visipaque 320) Iodixanol (Ultravist 370) Iopromide (Oxilan 350) Ioxilan |
|
|
|
Name two types of high osmolar contrast media? (Ionic contrast) |
(Hypaque 50) Diatrizoate (Isopaque 370) Metrizoate (Hexabrix) Ioxaglate (Conray) |
|
|
|
Explain, what is window width? |
Ranges of shades of gray on CT image. It is controlled by contrast. |
|
|
|
Explain what window level is? |
It's the H.U. at the center of window width. It controls density or brightness of the image. |
|
|
|
What is photon fluence? |
The quantity of x-ray photons passing through a specific area. |
|
|
|
What is photon flux? |
The rate at which the quantity of x-ray photons (fluence) passes through a unit area over time. |
|
|
|
What is Aliasing? |
A streaking artifact caused by insufficient number of views (data samples) obtained during data acquisition. |
|
|
|
Low energy photons are absorbed as x-ray beam passes through an object resulting in an increase of the average photon energy of the beam. This is called_________? |
Beam Hardening. |
|
|
|
What is binning? |
Electronically combining signal from adjacent detector elements to produce reconstructed CT image that is thicker than the detector width. |
|
|
|
What streak artifact occurs at the interface between a high density object and a lower attenuation material surrounding it? |
Edge gradient. |
|
|
|
What is M I P? |
Maximum intensity Projection. (Multiplanar Reformation) Displays maximum pixel value along Ray traced through viewer. |
|
|
|
Define temporal resolution? |
Ability of CT to freeze motion and provide blur free images. |
|
|
|
What is linear attenuation coefficient? |
Is a constant that describes the rate of energy loss by a photon beam per cm. within a medium. |
|
|
|
Describe what a step artifact is? |
In multiplane or or 3-D reformats the stair step artifacts produces loss of sharpness and loss of detail. Misalignment of the tube can cause these artifacts. |
|
|
|
Explain hyper dense? |
Attenuation values are greater than the surrounding tissues. |
|
|
|
Explain Hypo dense? |
Attenuation values are less than the values of the surrounding tissues |
|
|
|
What is iso-dense? |
The attenuation values are equal to the values of the surrounding tissues. |
|
|
|
What is iso-tropic? |
Equal dimensions along the X, Y, and Z axis. |
|
|
|
What is insufflation? |
The introduction of air into an organ or cavity for distention and improving visualization. |
|
|
|
Describe volume rendering? |
Is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set. Adjusting opacity of Voxel's according to tissue type. |
|
|
|
What is convolution? |
Mathematical Filtration used by CT to remove blurring artifacts during back projection method of image reconstruction. |
|
|
|
Define what a kernel is? |
Mathematical filter applied to Raw data to remove the "blurring" artifact. A.k.a. algorithm. |
|
|
|
What is retrospective reconstruction? |
Reconstruction done after the initial re-cons are done. Using raw data to change DFOV, image center, etc..... |
|
|
|
What is considered the normal range for cerebral blood flow through the brain? |
50-60 ml./100g. Brain tissue/minute. |
|
|
|
What is considered a normal range of cerebral blood volume/100g. Of brain tissue? |
4-5 ml./100g. Brain tissue |
|
|
|
What is cerebral perfusion? |
The level of blood flow throughout the brain tissue. |
|
|
|
Define data acquisition system.(DAS) ? |
It is responsible for measuring the transmitted x-radiation absorbed by the detectors. |
|
|
|
The component of the CT system that receives raw data, performs all major re-cons and returns the recon images to storage memory to the host computer? |
Array processor. |
|
|
|
What are 10 organs that make up the retroperitoneum? |
Duodenum, pancreas, prostate, uterus, kidneys, ureter's, bladder, aorta, IVC, adrenal gland's. |
|
|
|
What is a normal BUN level (Blood Urea Nitrogen) and a normal creatinine level for adults? |
BUN: 7-25 mg/dl. Creatinine: 0.5-1.5 mg/dl. |
|
|
|
What is a normal PT? (Prothrombin Time) |
12-15 sec. |
|
|
|
What is a normal PTT ? (Partial Thromboplastin Time) |
25-35 sec. |
|
|
|
What is the normal range for a platelet count? |
140,000-440,000 |
|
|
|
What is the parameter that is responsible for partial volume averaging? |
Slice Thickness. |
|
|
|
What is a single 2-D picture element within the image plane? |
Pixel. |
|
|
|
Define spatial resolution? |
The ability of CT to display fine details. (Units: line pairs/cm.)
Small detector size, small pixel, thin slice, small focal spot. *To get better spatial resolution. |
|
|
|
What is partial volume artifact? |
The error occurs when structure only partly positioned within the voxel and attenuation is not accurately represented. |
|
|
|
What is partial volume effect/averaging? |
Distortion in signal intensity from object because it partially extends into the Adjacent slice thickness. Inaccuracy in pixel values.
Values will average together to attempt to yield a single pixel value. |
|
|
|
What are the main components of a typical CT scanner and the path they are used starting with the console. |
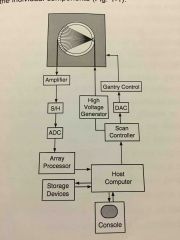
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What year was the first CT scanner introduced for general clinical use? |
1973 |
|
|
|
What type of scanner Incorporated an x-ray tube which generated a thin focused x-ray beam called a pencil beam through the patient to a single detector? Both the tube and the detector were part of an Assembly which moved or translated across the gantry while the patient remained stationary between them. |
First-generation scanners. |
|
|
|
What was the total scan time per image for a first generation scanner? |
5 minutes |
|
|
|
The tube and detector assembly moved across the patient then rotated by 1°. Which generation scanner is this? |
First generation scanner. |
|
|
|
What type of scanner had a "pencil beam" and a single detector? |
First generation scanner. |
|
|
|
Which generation scanner used a series of translate -rotate procedures covering an arc of 180° around the patient? |
First generation scanner. |
|
|
|
Which generation scanner incorporated and x-ray tube which generated an x-ray beam that had a shape similar to an open paper fan? |
Second generation scanner. |
|
|
|
Which type of scanner had a fan beam geometry and a group of detectors referred to as a detector array? |
Second generation scanner. |
|
|
|
About how many detectors were used in the second-generation scanners? |
30 |
|
|
|
Which type of scanner utilize the tube/detector assembly moving across the patient and then rotating by 5°? Multiple detectors in a straight line. |
Second-generation scanner. |
|
|
|
What was the total scan time per image for second-generation scanners? |
20 seconds |
|
|
|
What were the two most important additions to the second-generation scanners? |
The fan beam geometry and introduction of the detector array. |
|
|
|
When were the third generation scanners first introduced? |
1975 |
|
|
|
Which generation scanner has Fan beam geometry and a detector array arranged in a curved arc? |
3rd Generation Scanner. |
|
|
|
What is the scan time for the third generation scanners? |
Less than 1 second per image. |
|
|
|
Most scanners today are based off of which generation scanner? |
3rd Generation Scanner |
|
|
|
What is the primary difference between the third and fourth generation scanners relating to the detectors? |
In the fourth generation scanners the detectors do not travel with the tube they form a complete circle around the gantry in a ring configuration. |
|
|
|
With a continuous rotation scanner what piece of equipment is used to supply electrical power, accept scanning instructions, convey information concerning the measured attenuation data from the patient to the computer and array processor to facilitate image construction? |
The slip ring. |
|
|
|
In what year was the multi-row detector scanners offered? |
1998 |
|
|
|
What type of scanner collects information from multiple anatomical slices in each rotation of the x-ray tube? |
Multi-row detector scanners. |
|
|
|
What are some benefits of the multi-row detector CT? |
Faster scans, increased anatomical coverage, and scanning with thinner slices to improve resolution along the slice direction. |
|
|
|
What type of CT is used for oncology? |
Cone beam CT |
|
|
|
What is the primary link between the technologist and the other components of the imaging system? |
The Host Computer. |
|
|
|
The axis which extends along the patient table or the long axis of the body is called what? |
Z axis. |
|
|
|
If the patient is lying supine on the table, the axis that extends from the patients left to right sided is called what? |
X axis. |
|
|
|
The axis that extends anterior to posterior through the patient is called? |
Y axis. |
|
|
|
An atomic particle with a negative electrical charge is called? |
Electron. |
|
|
|
When an electron collides with the nucleus of an Atom or enters the vicinity of the nucleus what happens to the electrons? |
They lose energy in the form of x-ray photons. |
|
|
|
Electrons losing their energy and slowing down forming x-ray photons is a phenomenon called what? |
Bremsstrahlung or braking radiation. |
|

