![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Evolution |
gradual change of entire species over many generations through a process of natural selection. |
|
|
Natural Selection |
inherited traits and mutations that are favorable to the survival of the organisms become more prevalent as these traits are passed to offspring. These are actual changes in the DNA over time and are the result of the modification of previous forms. |
|
|
Life Cycle Diagram of Butterfly |
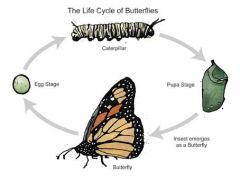
|
|
|
Life cycle diagram of frog |
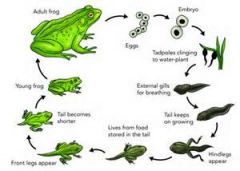
|
|
|
Factors that affect growth and development of plants |
light gravity stress |
|
|
Gravity (plant growth) aka Geotropism |
The force of gravity acting upon plant cells gives them directional information. Root tissue responds to gravity by growing downward into the soil (positive response). In response to the same stimulus the shoot is programmed to grow upward (negative response).
|
|
|
Light (plant growth) |
Light regulates the elongation process in stems so that the stem can develop the necessary strength to support itself above the ground.
Light striking one side of a stem causes less growth hormone on that side and a concentration on the darker side. This results in increased growth on the darker side, curving the tip toward the light. This response is called Photo-tropism. |
|
|
Sexual reproduction and Asexual Reproduction |
asexual reproduction requires only one parent, whereas sexual reproduction generally requires two. Asexual reproduction does not involve meiosis or fertilization. However, in sexual reproduction meiosis is essential for gametogenesis and fertilization for zygote formation |
|
|
Fossil Record |
Preserved impressions or remains in rocks of living organisms from the past. The most direct evidence of evolutionary change and are generally found in sedimentary rock. |
|
|
Comparative Anatomy |
a way to find evolutionary relationships between organisms. animals that evolved from common ancestor might be expected to have similar anatomical features as their ancestors. when we compare the anatomies we can form hypothesis about common ancestors and shed light on pressures that led to certain abilities. ex. ability to fly |
|
|
DNA sequences |
The closer the genetic sequences of organism are to each other, the more closely related they are in evolution. |
|
|
Sexual reproduction in Plants
` |
most plants are able to reproduce both sexually and asexually, some do both in the course of their life |
|
|
Angiosperms |
flowering plants |
|
|
Auxins |
an important class of plant hormones associated with growth patterns |
|
|
Eukaryotic Cells |
multicellular ogranisms whose cells contain organelles |
|
|
Gametes |
sex cells produced through meiosis in males and females |
|
|
Haploid cells |
gametes that ,when joined, produce diploid offspring |
|
|
Meiosis |
a specialized form of eukaryotic cell division involving male and female gametes |
|
|
Mitosis |
an asexual reproductive process of eukaryotic cells in which cells divide to form two daughter cells with the same genetic makeup as the parent cell. |

