![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Responsibility of the nervous system
|
To initiate and modify the activation of the muscles
|
|
|
Three types of muscle
|
Smooth, cardiac and skeletal
|
|
|
What is the Epimysium?
|
A layer of connective tissue surrounding each skeletal muscle
|
|
|
What is a fascicle or fasciculus?
|
A bundle of muscle fibers
|
|
|
What is the perimysium?
|
A layer if connective tissue surrounding each fasciculus.
|
|
|
What is the endomysium?
|
A layer of connective tissue surrounding each muscle fiber, separating it from adjacent fibers.
|
|
|
What is the sarcolemma?
|
The plasma membrane surrounding each muscle fiber. It encloses the contents of the cell and regulates the passages of materials such as glucose in and out of the cell. It also receives and conducts stimuli in the form of electrical impulses or action potentials.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Where if the cytoplasm located?
|
Within the boundary of the sarcolemma but outside the nuclei.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Where if the cytoplasm located?
|
Within the boundary of the sarcolemma but outside the nuclei.
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm referred to as?
|
The sarcoplasm of the muscle.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Where if the cytoplasm located?
|
Within the boundary of the sarcolemma but outside the nuclei.
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm referred to as?
|
The sarcoplasm of the muscle.
|
|
|
What does the watery solution of the cytoplasm contain?
|
The cell's energy resources: ATP, phosphocreatine, glycogen, and fat droplets.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Where if the cytoplasm located?
|
Within the boundary of the sarcolemma but outside the nuclei.
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm referred to as?
|
The sarcoplasm of the muscle.
|
|
|
What does the watery solution of the cytoplasm contain?
|
The cell's energy resources: ATP, phosphocreatine, glycogen, and fat droplets.
|
|
|
What organelles can be found suspended in the sarcoplasm?
|
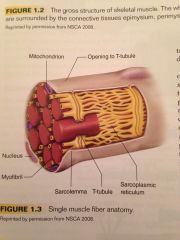
The mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Where if the cytoplasm located?
|
Within the boundary of the sarcolemma but outside the nuclei.
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm referred to as?
|
The sarcoplasm of the muscle.
|
|
|
What does the watery solution of the cytoplasm contain?
|
The cell's energy resources: ATP, phosphocreatine, glycogen, and fat droplets.
|
|
|
What organelles can be found suspended in the sarcoplasm?
|
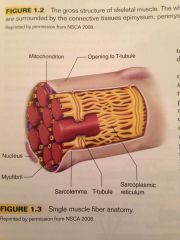
The mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
|
|
|
What is the mitochondria?
|
The sites of aerobic ATP production within the cell.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Where if the cytoplasm located?
|
Within the boundary of the sarcolemma but outside the nuclei.
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm referred to as?
|
The sarcoplasm of the muscle.
|
|
|
What does the watery solution of the cytoplasm contain?
|
The cell's energy resources: ATP, phosphocreatine, glycogen, and fat droplets.
|
|
|
What organelles can be found suspended in the sarcoplasm?
|
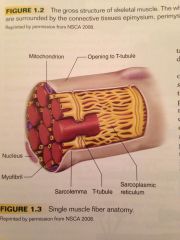
The mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
|
|
|
What is the mitochondria?
|
The sites of aerobic ATP production within the cell.
|
|
|
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
|
This is an organelle which stores calcium and regulates the muscle action process by alternating the intercellular calcium concentration.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Where if the cytoplasm located?
|
Within the boundary of the sarcolemma but outside the nuclei.
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm referred to as?
|
The sarcoplasm of the muscle.
|
|
|
What does the watery solution of the cytoplasm contain?
|
The cell's energy resources: ATP, phosphocreatine, glycogen, and fat droplets.
|
|
|
What organelles can be found suspended in the sarcoplasm?
|
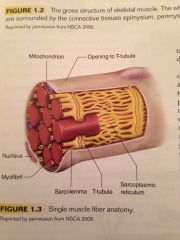
The mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
|
|
|
What is the mitochondria?
|
The sites of aerobic ATP production within the cell.
|
|
|
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
|
This is an organelle which stores calcium and regulates the muscle action process by alternating the intercellular calcium concentration.
|
|
|
What are t-tubules?
|
Channels that form from openings in the sarcolemma of the cell muscle.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Where if the cytoplasm located?
|
Within the boundary of the sarcolemma but outside the nuclei.
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm referred to as?
|
The sarcoplasm of the muscle.
|
|
|
What does the watery solution of the cytoplasm contain?
|
The cell's energy resources: ATP, phosphocreatine, glycogen, and fat droplets.
|
|
|
What organelles can be found suspended in the sarcoplasm?
|
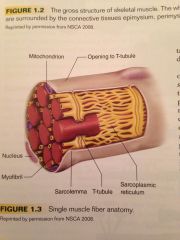
The mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
|
|
|
What is the mitochondria?
|
The sites of aerobic ATP production within the cell.
|
|
|
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
|
This is an organelle which stores calcium and regulates the muscle action process by alternating the intercellular calcium concentration.
|
|
|
What are t-tubules?
|
Channels that form from openings in the sarcolemma of the cell muscle.
|
|
|
What is a muscle fiber?
|
A cell specialized to contract and generate force.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscles multinucleated?
|
Yes
|
|
|
What are myofibrils?
|
A columnar protein structure that run parallel to the length of the muscle fiber. They are also the elements of a muscle fiber that primarily consist of actin and myosin.
|
|
|
The nuclei of skeletal muscles contains what and is responsible for what?
|
Skeletal muscle contains DNA and is largely responsible for initiating the processes associates with adaptations to exercise (ie muscle cell enlargement or hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Where if the cytoplasm located?
|
Within the boundary of the sarcolemma but outside the nuclei.
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm referred to as?
|
The sarcoplasm of the muscle.
|
|
|
What organelles can be found suspended in the sarcoplasm?
|
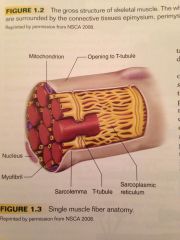
The mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
|
|
|
What organelles can be found suspended in the sarcoplasm?
|
The mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
|
|
|
What is the mitochondria?
|
The sites of aerobic ATP production within the cell.
|
|
|
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
|
This is an organelle which stores calcium and regulates the muscle action process by alternating the intercellular calcium concentration.
|
|
|
What are t-tubules?
|
Channels that form from openings in the sarcolemma of the cell muscle.
|
|
|
What is a muscle fiber?
|
A cell specialized to contract and generate force.
|
|
|
What are myofilaments?
|
The two primary proteins in a myofibril (ie actin and myosin)
|
|
|
The arrangement of actin and myosin along the length of the myofibril give it what kind of appearance?
|
Striated or striped.
|
|
|
The arrangement of actin and myosin along the length of the myofibril give it what kind of appearance?
|
Striated or striped.
|
|
|
What are myosin filaments?
|
Thick proteins that contain a head, neck and tail. The head is capable of attaching to and pulling on actin called a power stroke.
|
|
|
The arrangement of actin and myosin along the length of the myofibril give it what kind of appearance?
|
Striated or striped.
|
|
|
What are myosin filaments?
|
Thick proteins that contain a head, neck and tail. The head is capable of attaching to and pulling on actin called a power stroke.
|
|
|
What is the protein tutti in responsible for?
|
Maintaining the position of the myosin filament relative to actin.
|
|
|
The arrangement of actin and myosin along the length of the myofibril give it what kind of appearance?
|
Striated or striped.
|
|
|
What are myosin filaments?
|
Thick proteins that contain a head, neck and tail. The head is capable of attaching to and pulling on actin called a power stroke.
|
|
|
What is the protein tutti in responsible for?
|
Maintaining the position of the myosin filament relative to actin.
|
|
|
What is actin?
|
Actin is a protein formed from individual globular or G-actin proteins. It contains 3 proteins: actin, tropomyosin and troponin.
|
|
|
The arrangement of actin and myosin along the length of the myofibril give it what kind of appearance?
|
Striated or striped.
|
|
|
What are myosin filaments?
|
Thick proteins that contain a head, neck and tail. The head is capable of attaching to and pulling on actin called a power stroke.
|
|
|
What is the protein tutti in responsible for?
|
Maintaining the position of the myosin filament relative to actin.
|
|
|
What is actin?
|
Actin is a protein formed from individual globular or G-actin proteins. It contains 3 proteins: actin, tropomyosin and troponin.
|
|
|
What is the protein nebulin responsible for?
|
Ensuring the correct length of actin filaments.
|
|
|
The arrangement of actin and myosin along the length of the myofibril give it what kind of appearance?
|
Striated or striped.
|
|
|
What are myosin filaments?
|
Thick proteins that contain a head, neck and tail. The head is capable of attaching to and pulling on actin called a power stroke.
|
|
|
What is the protein tutti in responsible for?
|
Maintaining the position of the myosin filament relative to actin.
|
|
|
What is actin?
|
Actin is a protein formed from individual globular or G-actin proteins. It contains 3 proteins: actin, tropomyosin and troponin.
|
|
|
What is the protein nebulin responsible for?
|
Ensuring the correct length of actin filaments.
|
|
|
What is a sacromere?
|
The most basic contractile unit of the muscle.
|

