![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Measures and controls that ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information system assets including hardware, software, firmware, and information being processed, stored, and communicated. |
Computer Security |
|
|
Two concepts of Confidentiality |
Data confidentiality Privacy |
|
|
Two features of Integrity |
Data integrity System integrity |
|
|
What makes up CIA Triad |
Confidentiality Integrity Availability |
|
|
Essential Network and Computer Security Requirements |
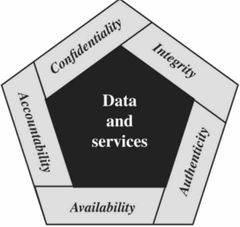
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Individual, group, organization, or government that conducts or has the intent to conduct detrimental activities. |
Adversary |
|
|
3 classifications of hackers |
Cyber Criminals Hacktivists State Sponsored |
|
|
Any kind of malicious activity that attempts to collect, disrupt, deny, degrade, or destroy information system resources or the information itself. |
Attack
|
|
|
A device or techniques that has as its objective the impairment of the operational effectiveness of undesirable or adversarial activity, or the prevention of espionage, sabotage, theft, or unauthorized access to or use of sensitive information or information systems. |
Countermeasure |
|
|
A measure of the extent to which an entity is threatened by a potential circumstance or event, and typically a function of 1) the adverse impacts that would arise if the circumstance or event occurs; and 2) the likelihood of occurrence. |
Risk |
|
|
A set of criteria for the provision of security services. It defines and constrains the activities of a data processing facility in order to maintain a condition of security for systems and data. |
Security Policy |
|
|
A major application, general support system, high impact program, physical plant, mission critical system, personnel, equipment, or a logically related group of systems.
|
System Resource (Asset)
|
|
|
Any circumstance or event with the potential to adversely impact organizational operations (including mission, functions, image, or reputation), organizational assets, individuals, other organizations, or the Nation through an information system via unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of information, and/or denial of service. |
Threat
|
|
|
The 4 main things that need protecting |
Hardware Software Data Networks |
|
|
3 types of Vulnerability |
Corruption Leaky Unavailable |
|
|
Two types of attacks |
Active Passive |
|
|
4 stages of Countermeasures |
Prevent Detect Response Recover |
|
|
4 types of unauthorized Disclosure |
Exposure Interception Inference Intrusion
|
|
|
3 types of Deception |
Masquerade Falsification Repudiation |
|
|
3 types of Disruption |
Incapacitation Corruption Obstruction |
|
|
3 types of Disruption |
Incapacitation Corruption Obstruction |
|
|
2 types of Usurpation |
Misappropriation Misuse |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states the design of security measures embodied in both hardware and software should be as simple and small as possible. |
Economy of mechanism |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept statesaccess decisions should be based on permission rather than exclusion. |
Fail-safe default |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states every access must be checked against the access control mechanism. |
Complete mediation |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states the design of a security mechanism should be open rather than secret. |
Open design |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states as a practice in which multiple privilege attributes are required to achieve access to a restricted resource. |
Separation of privilege |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states every process and every user of the system should operate using the least set of privileges necessary to perform the task |
Least privilege |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states the design should minimize the functions shared by different users, providing mutual security. |
Least common mechanism |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states the security mechanisms should not interfere unduly with the work of users, and at the same time meet the needs of those who authorize access. |
Psychological acceptability |
|
|
Isolation 3 parts |
Process isolation Physical/Network isolation Subject/Object isolation |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states in the context of security refers both to the development of security functions as separate, protected modules, and to the use of a modular architecture for mechanism design and implementation. |
Encapsulation |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states in the context of security refers both to the development of security functions as separate, protected modules, and to the use of a modular architecture for mechanism design and implementation. |
Modularity |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept refers to the use of multiple, overlapping protection approaches addressing the people, technology, and operational aspects of information systems. |
Layering |
|
|
This fundamental security design concept states a program or user interface should always respond in the way that is least likely to astonish the user. |
Least astonishment |
|
|
List the three attack surface: |
Network attack surface Software attack surface Human attack surface |
|
|
What 3 factors does a Security manager need to consider when creating security |
The value of the assets being protected The vulnerabilities of the system Potential threats and the likelihood of attacks |
|
|
Additional Considerations for any security mechanism |
Ease of use versus security Cost of security versus cost of failure and recovery |
|
|
an attribute of an information system that provides grounds for having confidence that the system operates such that the system’s security policy is enforced. |
Assurance |
|
|
the process of examining a computer product or system with respect to certain criteria. |
Evaluation |

