![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
139 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
IA = policies, procedures and mechanisms are employed to protect the ___ of info
|
Triad
|
|
|
The CIA triad refers to:
|
- Confidentiality
- Integrity - Availability |
|
|
What is confidentiality?
|
Assurance that information is not disclosed to unauthorized individuals, processes, or devices.
|
|
|
What is Integrity?
|
Condition existing when data is unchanged from its source and has not been accidentally or maliciously modified, altered, or destroyed
|
|
|
What is Availability?
|
Timely, reliable access to data and information services for authorized users
|
|
|
Information Assurance is not about "perfect security" it is about ____?
|
Risk Management
|
|
|
What is the IA equation?
|
Residual Risk=Threats x Vulnerabilities x impact/Security Controls
|
|
|
What part of the IA equation is the least controllable, addresses the malicious ones with laws and other deterrence measures?
|
Threats
|
|
|
What part of the IA equation deals with attributes of a system's design (or humans) that result in the potential for intentional or accidental problems?
|
Vulnerabilities
|
|
|
What part of the IA equation deals with how bad it will hurt if you suffer a failure or attack?
|
Impact
|
|
|
What are security controls in the IA equation?
|
Policies, operations, procedures, devices, put in place and managed so as to mitigate risk.
|
|
|
What things can you do to decrease vulnerability?
|
- Build secure systems to begin with.
- Apply all patches...quickly - Principle of Least Privilege (PLOP) |
|
|
What things can be done to maximize Security Controls?
|
- Identify, and obtain good security products.
- Install, configure, and implement correctly. - Pursue/apply defense-in-depth - Stay "rationally paranoid" |
|
|
The DoD approach for establishing an adequate IA posture in a shared-risk environment that allows for shared mitigation through: the integration of people, technology, and operations; the layering of IA solutions within and among IT assets; and, the selection of IA solutions based on their relative level of robustness.
|
Defense-in-depth
|
|
|
Defense-in-Depth has several dimensions (T/F)
|
True
|
|
|
Defense-in-Depth exhorts that we not put all of our eggs in one basket (T/F)
|
True
|
|
|
D-I-D doesn't use technical controls, or operational and personnel controls (T/F)
|
False
|
|
|
In D-I-D, each _______ _______ is likely to have it's own flaws and or limitations
|
protection mechanism
|
|
|
Together the mechanisms provide _____ to make the attacker's job much harder in a D-I-D
|
mutual support
|
|
|
What is the IA Matrix
|
Grid that combines the CIA Triad with the controllable terms of the IA equation
|
|
|
What are the three categories that the IA Matrix fall into?
|
Technology, Operations, People
|
|
|
What are the rows of the IA Matrix?
|
Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability
|
|
|
What are the columns on the IA Matrix?
|
Threats, Vulnerabilities, Security Controls
|
|
|
Forging a signature belongs where in the IA Matrix?
|
People, Integrity, Threat
|
|
|
What agencies are devoted to finding and disseminating information about vulnerabilities?
|
www.cert.org, www.securityfocus.com, xforce.iss.net
|
|
|
What are the two classes of threats?
|
- Human
- Natural |
|
|
What are the two subcategories of Human threats?
|
- Unintentional
- Intentional |
|
|
Intentional Human threats have two categories, what are they?
|
- Insider (Trusted)
- Outsider (Untrusted) |
|
|
Natural threats have two categories, what are they?
|
- System failure (wiring, power, cooling)
- Nature (fire, flood, tornado) |
|
|
What are the general protections to defend against threats?
|
- Policy
- Training and Awareness - Install the latest patches - PLOP - Regular backups - Auditing mechanisms - Integrity checks - Access Control |
|
|
What are the two major changes in the past 4-5 decades that exacerbates problems with threats?
|
1- New Information Storage Medium
- Old - paper, protected in safes etc - New - data, easily replicated and disseminated 2 - Distributed Systems - inter-networked for easier distribution. |
|
|
What part of Network Security is protecting the good bits while in transit
|
Network
|
|
|
What part of Network Security is identifying and blocking bad bits?
|
Security
|
|
|
What are examples of bad bits in place
|
- malware
- virus - worms - buggy code ridden with security flaws |
|
|
What are examples of bad bits in transit?
|
- malformed packets
- worm - spoofed packet - malicious payload - reconnaissance/scan |
|

|
Observation (Sniffing)
Confidentiality |
|

|
Redirect
Confidentiality |
|
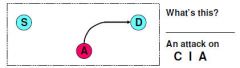
|
Impersonation (Spoofing)
Integrity |
|

|
Modification
Integrity |
|

|
Hijack
Confidentiality, Integrity |
|
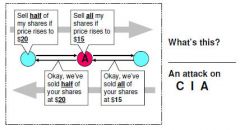
|
Man in the middle
Confidentiality, Integrity |
|
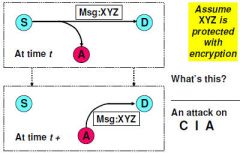
|
Replay
Integrity |
|
|
Cryptography ensures the _______ of good bits while in transit
|
Confidentiality and Integrity
|
|
|
Bad bits are blocked and identified by ____
|
Firewalls, Filters, Cryto to check integrity
|
|
|
DES is an example of what type of encryption
|
Block
|
|
|
Block encryption is more efficient without chaining because of ____, but also provides the cracker with more plain-/cipher-text pairs
|
Parallelism
|
|
|
Key length = P length and is never reused, you have an unbreakable ____
|
one time pad
|
|
|
The Algorithm/cipher must be public (T/F)
|
True
|
|
|
Security strength depends on
|
- Strength/security of algorithm/cipher
(max confusion, max diffusion) - Key Length |
|
|
Cryptographic techniques include:
|
-substitution
-transposition |
|
|
What is Kerckhoff's Principle?
|
- A crypto-system should be secure even if everything about the system, except the key, is public knowledge.
- A crypto algorithm must be implemented by hardware or software which is widely distributed among its users - secrecy problem is reduced to that of secure key management. |
|
|
The goal of confusion is to obscure relationship between the ___ and the ____.
|
Key and the Cyper Text
|
|
|
The goal of diffusion is to obscure the relationship between the ____ and the _____.
|
Plain Text and the Cipher Text
|
|
|
since most modern public ciphers are in the public domain, their security relies primarily on size of the ____ and ... indirectly to the time taken to ______.
|
Key Space, and Test one Key.
|
|
|
2^keylength
|
Keyspace
|
|
|
- ASIC can check one key in one clock cycle.
- The ASIC is driven by a 1GHz clock. - how many keys per second can the ASIC check? |
1 billion
|
|
|
If a cracker employs n such ASICS and divides the key space by n. How many keys/second could be checked?
|
n*1billion
|
|
|
What is the hindrance to fast key testing?
|
Each iteration i cannot proceed until iteration i-1 is complete
|
|
|
What is the minimum theoretical time to run one iteration
|
1 clock cycle
|
|
|
What is the min theoretical time to test one key?
|
n*clockcycles
|
|
|
One block of DES undergoes 16 sequential processes (T/F)
|
Ture
|
|
|
Moore's Law states:
|
CPU processing power doubles about every 1.5 years
|
|
|
What is the general equation for Moore's Law?
|
Power x 2^yrs/1.5
|
|
|
If today's fastest general purpose computer can brute force a given key space in T time.
- Use Moore's Law to guesstimate how long (expressed with T) it will take to brute it in Y years from now with the then fastest general purpose computer. |
T/2^Y/1.5
|
|
|
Hashing is a one way function
|
True
|
|
|
The purpose of a hash function is to provide a kind of ___ of the original data
|
finger print
|
|
|
Compare to SHA-1 and its _____ bit fingerprint
|
160
|
|
|
What is the theoretical chance of a collision between two different messages hashed with SHA-1
|
1/2^160
|
|
|
Compare to SHA-1 and its _____ bit fingerprint
|
160
|
|
|
What does MOD mean?
|
put the one number into the other and then throw away the extra left over values ( in a hash we throw data away)
|
|
|
What is the theoretical chance of a collision between two different messages hashed with SHA-1
|
1/2^160
|
|
|
Compare to SHA-1 and its _____ bit fingerprint
|
160
|
|
|
What does MOD mean?
|
put the one number into the other and then throw away the extra left over values ( in a hash we throw data away)
|
|
|
RSA is an example of ____ key crypto.
|
Symmetric/Secret
|
|
|
What is the theoretical chance of a collision between two different messages hashed with SHA-1
|
1/2^160
|
|
|
RSA is an example of ____ key crypto.
|
Symmetric/Secret
|
|
|
AES is and example of ____ key crypto
|
Asymmetric/Public
|
|
|
What does MOD mean?
|
put the one number into the other and then throw away the extra left over values ( in a hash we throw data away)
|
|
|
AES is and example of ____ key crypto
|
Asymmetric/Public
|
|
|
RSA is an example of ____ key crypto.
|
Symmetric/Secret
|
|
|
AES is and example of ____ key crypto
|
Asymmetric/Public
|
|
|
Moore's Law states:
|
CPU processing power doubles about every 1.5 years
|
|
|
What is the general equation for Moore's Law?
|
Power x 2^yrs/1.5
|
|
|
If today's fastest general purpose computer can brute force a given key space in T time.
- Use Moore's Law to guesstimate how long (expressed with T) it will take to brute it in Y years from now with the then fastest general purpose computer. |
T/2^Y/1.5
|
|
|
Compare to SHA-1 and its _____ bit fingerprint
|
160
|
|
|
Hashing is a one way function
|
True
|
|
|
The purpose of a hash function is to provide a kind of ___ of the original data
|
finger print
|
|
|
What is the theoretical chance of a collision between two different messages hashed with SHA-1
|
1/2^160
|
|
|
What does MOD mean?
|
put the one number into the other and then throw away the extra left over values ( in a hash we throw data away)
|
|
|
RSA is an example of ____ key crypto.
|
Symmetric/Secret
|
|
|
AES is and example of ____ key crypto
|
Asymmetric/Public
|
|
|
Moore's Law states:
|
CPU processing power doubles about every 1.5 years
|
|
|
What is the general equation for Moore's Law?
|
Power x 2^yrs/1.5
|
|
|
If today's fastest general purpose computer can brute force a given key space in T time.
- Use Moore's Law to guesstimate how long (expressed with T) it will take to brute it in Y years from now with the then fastest general purpose computer. |
T/2^Y/1.5
|
|
|
Hashing is a one way function
|
True
|
|
|
The purpose of a hash function is to provide a kind of ___ of the original data
|
finger print
|
|
|
What is Symmetric/Secret Key Crypto?
|
- Same key to encrypt and decrypt
- faster than asymmetric - distribution of the key is the problem |
|
|
What is Asymmetric/Public Key Crypto?
|
- one key encrypts another key decrypts.
- private key is singularity property - public key must be signed/trusted - relationship facilitates digital signatures. - solves the problems with key distribution - slower than symmetric by a factor of 1000 |
|
|
For any 2 of n users to communicate securely using symmetric keys they need ____ unique keys.
|
n(n-1)/2
a copy of each must be distributed securly |
|
|
For any 2 of n users to communicate securely using asymmetric keys they need ___ unique keys?
|
n unique private and public keys must be generated, n(n-1) keys (Public) must be distributed.
|
|
|
Do public keys need to be distributed with integrity?
|
Yes because you need to know who gave you the key
|
|
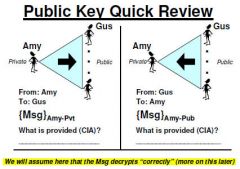
|
Integrity and Confidentiality
|
|
|
Is a digital signature trying to accomplish confidentiality?
|
No you are not
|
|
|
What are the minimum requirements for a digital certificate?
|
name and public key
|
|
|
What is FIPS 140-2
|
Federal Information Processing Standard, published by the NIST
- Security Requirements for Crypto Modules (2001) |
|
|
What are the two potential problems with crypto employment?
|
1) Non-human reader
2) Non-human text |
|
|
What assumptions do humans make with regard to crypto employment?
|
1) Doesn't look like something it didn't decrypt properly
2) doesn't look like something it didn't work properly. |
|
|
How does the decryptor know that what is decrypted is the same as what was encrypted?
|
the hash verifies
|
|
|
What is a nonce?
|
random number provided to detect replay.
|
|
|
Correct decryption is knowable with out any preconditions.
|
Hash
|
|
|
Will know if modified/changed accidental or malicious
|
encrypted hash
|
|
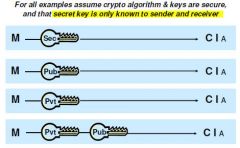
|
Confidentiality
Confidentiality |
|
|
What is entropy?
|
The measure of the uncertainty of a random variable.
|
|
|
Which has more entrophy, cipher x's 10 bit key or a cipher y's 12 bit key?
|
y has 4 times that of x being 2^12 vs 2^10
|
|
|
Entropy only works when:
|
- The key bits are completly random
- we careful measure the keys entropy by their bit length rather than their resulting key spaces. |
|
|
What is the entropy (measured in bits) of a completely random 8 bit key?
|
8 bits of entropy
|
|
|
(T/F) it is possible to have an n-bit key that does not have n-bit entropy
|
True
|
|
|
The entropy of the random bit 8 bit key was 8 bits, but what is the entropy of the BCD encoded 8 bit key?
|
How many BCD 8 bit keys are there? 10^2=100
of x Log(keyspace)/log2=# bits entropy |
|
|
When left unmolested by the security nazis, users will generally
|
choose the easiest password that they can remember
|
|
|
What is the bit entropy of an 8 character password randomly chosen from all lower-case English letters?
|
- 26 possible states
- possible places - 26^8 password space - 8 log 26/log 2= 8log26x3.33=37 |
|
|
Port 47 GRE, 50 ESP, and 51 AH are used to create
|
VPN's
|
|
|
What is source routing?
|
mechanism for sender to specify the route that a datagram should travel
|
|
|
What are the types of source routing?
|
Strict source routing, and loose source routing.
|
|
|
What is strict source routing?
|
Sender specifies exact path, router that cannot conform returns an ICMP "source route fail" msg
|
|
|
What is loose source routing?
|
Sender specifies list of IP addresses that must be traversed along the way, but en-route routers may hit additional IPs between
|
|
|
ICMP is a layer 3 protocol (T/F)
|
True
|
|
|
Services do not have to be activated or listening for ICMP to talk to a host, as do TCP and UDP (T/F)
|
True
|
|
|
Just about all hosts listen and respond to ICMP (T/F)
|
True
|
|
|
tcpdump does not display all fields of a packet, unless you opt for ___ output
|
hex
|
|
|
If you can interpret a hex-dump of entire packet...
|
you should have no trouble using any packet analysis tool
|
|
|
What is active FTP?
|
Client syns with server on port 21, client issues port command telling server which port to est. data connection to, server syns to designated port from ftp-data port.
|
|
|
What is passive FTP?
|
Client initiates both 21 and 20 commands, server sends the prot command to the client.
|
|
|
what are the protections from an FTP bounce attack?
|
- port command may not specify an IP different from that of the command's origin
- all service ports reject connections originating from port 20 - don't permit anonymous FTP writes, and if it is necessary properly isolate the writable directory - proper use of network isolation and boundaries |
|
|
What is labrea tar pit used for?
|
anti scan tool developed by Tom Liston
|
|
|
entity has no memory, thus is incapable of maintaining any context among its attributes as they change over time.
|
stateless
|
|
|
entity can remember previous information, and can thus assess current information in context of what has previously occurred
|
stateful
|
|
|
Can the attack signature be split over several datagrams
|
Yes
|
|
|
If the attack signature is spread over several datagrams will the IDS or the packet filtering routers/firewalls correctly identify and block?
|
no
|
|
|
What are the two ways to authenticate (excluding biometrics)?
|
shared key, and proof of possession of the private key.
|

