![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Before WC can be sold and placed on the recommended list it must undergo test: |
DUS test - distinct, uniform and stable VCU testing - value for cultivation and use. Yield, persistence (ground cover following close mowing) + presence of any disease Added value traits - protein levels, abiotic stress tolerance, nutrient use efficiency, water use efficiency before |
|
|
Before RC can be sold and placed on the recommended list it must undergo test: |
Yield + persistent (2 year), protein + pest and disease resistance Added value traits - persistence beyond 2 years, PPO content, phytoestrogens levels |
|
|
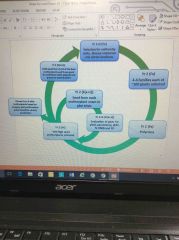
Breeding cycle - progeny testing |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Recurrent selection with progeny selection |
Based on ryegrass breeding at IBERS Cyclic scheme, breeding populations not individual lines Predicts optimum crosses using progeny testing Allows previous improvement to be built on |
|
|
Spaced plants nursery Yr1 + 2 - selection for uniformity traits, disease resistance and winter hardiness |
Plants are grown in fields to identify best individuals for crossing Plants are selected on basis of : potential yield, synchronicity of flowering, uniformity of morphology (leaf size, stem and stolen length and girth) Individual plants are then collected for crossing |
|
|
Spaced plants nursery Yr1 + 2 - selection for uniformity traits, disease resistance and winter hardiness |
Plants are grown in fields to identify best individuals for crossing Plants are selected on basis of : potential yield, synchronicity of flowering, uniformity of morphology (leaf size, stem and stolen length and girth) Individual plants are then collected for crossing |
|
|
Polycross of selected plants (yr 2 polycross) |
Plants selected from the Spaced plant nursery (field) + crossed: plants are crossed in insect proof isolation glasshouses. Watered automatically. Bumble bee are used to pollinate. Seeds are then collected from individual plants |
|
|
Field trails of progeny (yr2, 3 + 4 100 high seed mother plants selected, seeds where put to plot trails, evaluation of plots for yield, persistence, WSC, N, DMD, and FD |
Small trial plots sown to determine best mother plants Seeds sown in quadruplicate from each mother plant PRG companion Harvested + weighed using huldrup harvester NIRS estimation of clover content Best performing mother plants taken forward |
|
|
Variety production (yr2) clones from 4 elite mother plants based on progeny plot performance polycrossed for variety production |
The best performing mother plants are crossed again Seed produced for large scale trails Plot trialled for 3-4 years Large scale multiplication to produce seed for national list trails carried out in third year Final decision on NL entry made following 4th harvest year |
|
|
Polycross to produce seed for spaced plant nursery (yr4) |
Larger numbers of best performing mother plants are used for poly cross Cycle is repeated, with progressive improvements to population in each turn of the cycle |
|
|
Plant breeding takes a long time, it can be sped up in 2 ways though technology : |
Phenomics: for automated characterisation of plant population Genomics, particularly marker assisted selection and genomic selection |
|
|
Simplified model of plant genome: |
- 5 chromosomes, made of DNA and a list of instructions of how to build and operate a plant - orange squares show position of some genes (individual instructions) |
|
|
What are alleles? |
Alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the some place on a chromosome. - slightly different versions of the same gene - gives almost the same instruction but sometimes can have a marked effect on how a plant function |
|
|
Crossing allows: |
Us to combine desirable alleles in a single plant If combined alleles affect same trait, the progeny can be superior to either parent |
|
|
What are Molecular markers: |
- small, identifiable sections of DNA that identify specific regions of a chromosome - identified using various marker technology (AFLPs, SSR, SNP) |
|
|
Definition of molecular markers |
A MM is indirect selection of genetic determinations of traits of interest (e.g. Disease resistance, productivity, yield, stress tolerance and quality) to plant breeders or animal breeders |
|
|
Polymorphic markers (SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism) |
Genetic marker is a gene or DNA with a known location on the chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. Polymorphic markers that are located close to the genes that influence traits of interest can be used to identify plants that contain desirable alleles. This can speed up breeding by reducing need for long trails |
|
|
Markers are useful for: |
Identifying: - alleles that are expressed under certain conditions (disease stress) - recessive traits - traits that take time to be expressed Markers need to be close the gene or linkage can be disrupted by genetic recombination |
|
|
Conclusion |
Forage legumes are increasingly being used in pasture based agriculture. New varieties of legumes will continue to be required to increase productivity in a sustainable way. Conventional breeding techniques are still the primary tool that breeders rely on for selection. Technological advances, particularly marker assisted selection, will help speed up the process of trait selection |
|
|
Papers not to relevant
|
Previous studies on pollination of rapeseed confirm that insect pollination increases fruit set (4 studies; 1986-2012), the number of seeds per pod and yield. (2005) found insect pollination can increase yield by 46% however another study found a yield increase of 18% |

