![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the Bones of the Skull |
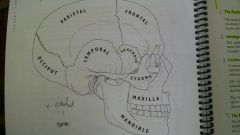
Parietal, Frontal, Occiput, Temporal, Sphenoid, Zygoma, Maxilla, Mandible. |
|
|
Main Objective of a Cranial Sacral Therapist |
To find and Release tensions (Called Restrictions and Compressions) |
|
|
Who discovered that in the 1800's that by inhibiting movement of Individual bones, specific dysfunctions were created? |
William Sutherland |
|
|
Recent studies of Cranial Sacral Therapy |
John Upledger 1970's |
|
|
According to Upledger's theroy of Cranial Sacral Therapy, which fluid creates the movement of the cranial rhythms intact? |
Cereberal Spinal Fluid |
|
|
Which Theory states that we crawled out of the ocean with out ancient rhythms intact |
Energetic |
|
|
Which Theory is based on the rise and fall of CSF |
Upledger |
|
|
How does a therapist identify restrictions and compression? |
Palpation Stations |
|
|
Which characteristics describe how far flexion moves away from the midline |
Amplitude |
|
|
Which characteristic describes how many times the rhythm occurs in one minute? |
Rate 6-14 |
|
|
Which Characteristic describes the comparison from left and right? |
Symmetry |
|
|
What are the two basic movements of the cranial sacral rhythm |
Flexion and extension |
|
|
Which characteristic of the cranial rhythm describes how strong or weak the rhythm feels |
quality |
|
|
why is it that we can feel the cranial rhythm at the palpation stations? |
Fascia |
|
|
What are the three layers of Meninges covering the brain and spinal cord |
Dura, Arachnoid, Pia |
|
|
Which Diaphragm area is located directly under the clavicles |
Thoracic |
|
|
Which direction do the majority of fascial fibers run in the body |
Vertical |
|
|
What are the areas of dense transverse or horizontal fascial fibers called? |
Diaphragm |
|
|
What is an example of restrictions being released |
Swallowing, Twitching, REM |
|
|
How do you perform Hyoid release |
Anterior and Inferior |
|
|
While performing a Diaphragm release what do you do if you notice it's moving in a repetitive pattern |
Go the opposite direction |
|
|
What are the three master bones |
Sacrum, Occipitals, Sphenoid |
|
|
If you have Trauma to the occiput, where might it refer pain to? |
Sacrum |
|
|
When performing a compression technique we maintain contact until when? |
Tissue Softens |
|
|
Which Technique introduces a gentle rocking motion? |
Sacral Occipital hold |
|
|
Crown Chakra |
White |
|
|
Eye Chakra |
Indigo |
|
|
Throat Chakra |
Blue |
|
|
Heart Chakra |
Green |
|
|
Solar Plexus Chakra |
Yellow |
|
|
Hara Chakra |
Orange |
|
|
Root Chakra |
Red |
|
|
Frontal Characteristic |
Intelligence |
|
|
Occiput Characteristic |
Flexibility in life |
|
|
Sphenoid Characteristic |
Objective Perception |
|
|
Sacrum Characteristic |
Stability |
|
|
Parietal Characteristic |
Aspirations |
|
|
Temporal Characteristic |
Balance |
|
|
Mandible Characteristic |
Expression of emotion |
|
|
Zygoma Characteristic |
Pride in appearance |
|
|
Frontal Lift |
D- Anterior Pinky to the end of Eyebrow |
|
|
Parietal Compression And Decompression |
C- Medial D- Superior Apex of the ear and move one and a half inches superior |
|
|
Sphenoid Compression and Decompression |
C- Posterior D- Anterior May feel bending or twisting |
|
|
Zygomae Decompression |
D- Lateral, Anterior |
|
|
Ethmoid Decompression |
Energetic |
|
|
Temporal Ear Pull |
D- Lateral, Posterior Under age of 9 only use Lateral decompression not posterior |
|
|
Mandible Compression and Decompression |
C- Superior D- Inferior |
|
|
Osteopathic Theory |
Sutherland suggested the brain has contractile capacity. Thus, the force of creating the movement in the brain expanding and contracting in rhythmic cycles |
|
|
Upledger Theory |
The Cranial movement is based on the rise and fall of cerebrospinal fluid As the ventricles of the brain pump CSF into the membrane system of the brain, the pressure from the fluid produced creates an expansion in the head. A nerve located in the sagittal suture monitors the expansion |
|
|
Energetic Theory |
Following evolutionary thought, some believe we crawled out of the sea with this rhythm intact |
|
|
Palpation stations |
Feet Thighs Pelvis Shoulder Head |
|
|
CV4 |
Hold no longer than 5 minutes Produces a calming effect |
|
|
Falx Cerebri |
Separates the right and left hemispheres of the brain |
|
|
Tentorium Cerebelli |
Supports the weight of the brain |
|
|
Falx Cerebelli |
Blends the meninges of the dural tube |
|
|
Dural Tube |
Creates a physical and energetic relationship between the occiput and the sacrum |
|
|
Contraindications Compressive strokes |
Under the age of 9 |
|
|
Cranial nerve IX, Glossopharyngeal |
"Tongue curled up in ear" Sensation, Taste |
|
|
Cranial Nevre X, Vagus |
"Vegas buffets are a 10" Swallowing, Digestion and bowel function |
|
|
Cranial Nerve XI, Accesory |
"Choker is a good accesory" Motor coordination for the trapezius and the Sternocleidomastoid. |
|
|
The Cranial Sacral system is made up of what four structures? |
-Brain and Spinal cord -Meningeal Membranes -Cerebrospinal Fluid -The Bones |

