![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
170 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
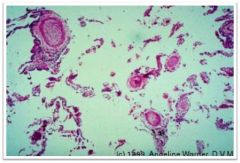
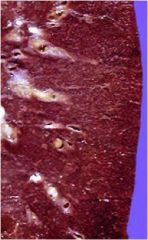
What is this?
|
Caused by:
Destruction of alveolar walls/loss of elasticity 2 Forms: Centrilobular(acinar) **Smokers** Proximal respiratory bronchioles Apex of lung most affected (b/c smoke rises) Panlobular(acinar) ***Alpha1-protease inhibitor (antitrypsin) deficiency*** Entire acinus Base of lung most affected (receives most blood) Paraseptal emphysema: Associated with bullae (air filled blebs containing no lung tissue) |
|
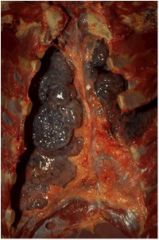
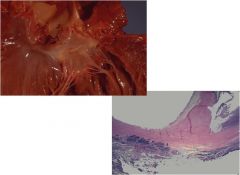
What is this and what is it associated with?
|
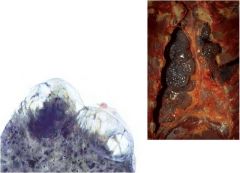
large bullae
apparent on the surface of the lungs in a patient dying with emphysema. Bullae are large dilated airspaces that bulge out from beneath the pleura. Emphysema is characterized by a loss of lung parenchyma by destruction of alveoli so that there is permanent dilation of airspaces. |
|
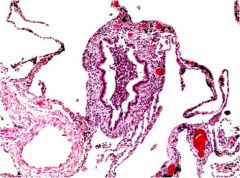
*Persistent cough w/ sputum production for >3mo in at least 2 consecutive yrs*** what is diagnosis?
|
chronic bronchitis
|
|
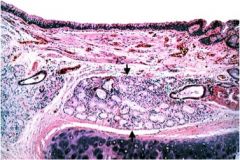
What is this?
|
Note also the goblet cell hyperplasia in the epithelium.
|
|
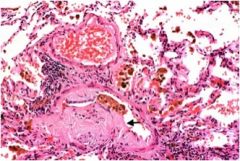
What is diagnosis after transplanted lung?
|
Bronchiolitis obliterans
Note also that there are a number of hemosiderin-filled (brown macrophages) in alveolar spaces. These are a common finding in transplanted lungs. |
|
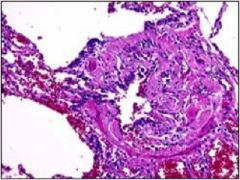
|
Bronchiolitis Obliterans
|
|
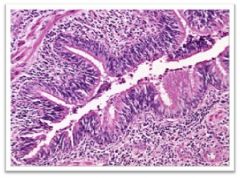
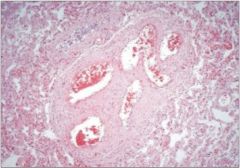
what is this?
|
Bronchiectasis
|
|
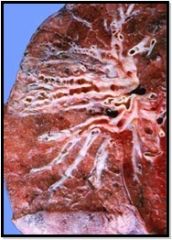
What is this diagnosis?
|
Bronchiectasis
|
|
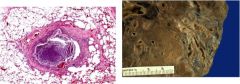
What is the diagnosis?
|
Bronchiectasis
|
|
|
What is the diagnosis?
a. Severe sleep apnea in obese patients resulting in loss of hypercarbic drive (lower O2 levels, higher CO2 levels) due to poor breathing b. Positive anti-neutrophil cytoplasm (c-ANCA) test ** Histologically: Granuloma and patchy necrosis in small and medium-sized arteries |
a. Pickwickian syndrome
b. Wegeners disease c. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis |
|
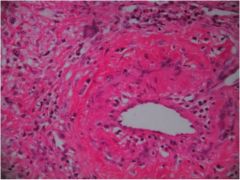
|
Wegener’s granulomatosis
|
|
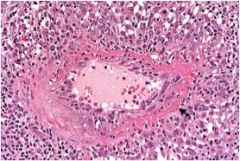
What is the diagnosis?
|
Wegener’s granulomatosis
|
|
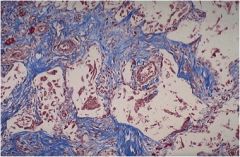
Diagnosis
|
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (Hamman Rich)
|
|
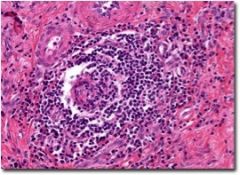
What does this show?
|
sarcoidosis
|
|
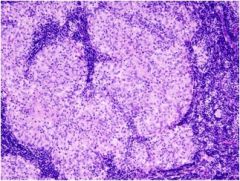
What is the diagnosis?
|
Formation of **Non-caseating Granulomas**
|
|
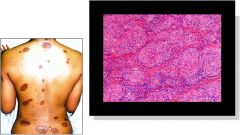
what are we looking at?
|
Sarcoidosis
Formation of **Non-caseating Granulomas** |
|
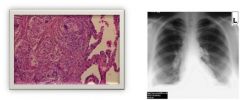
What do you see here?
|
Sarcoidosis
|
|
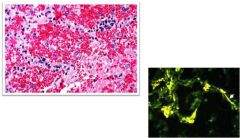
What do you see here?
|
goodpasture's disease
|
|
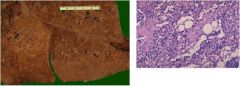
What is this known as?
|
Lipid Pneumonia (“Golden lung”)
|
|
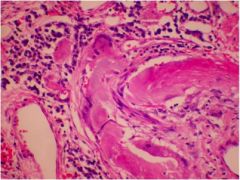
What is this?
|
Diffuse Pulmonary Amyloidosis
|
|
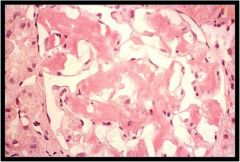
What is this?
|
Diffuse Pulmonary Amyloidosis
|
|
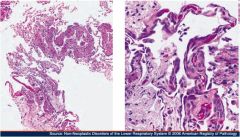
What is this?
|
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
|
|
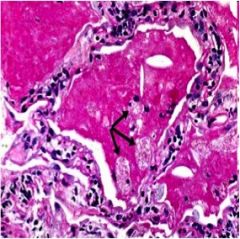
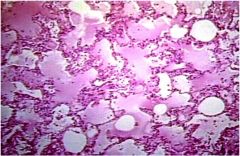
What is diagnosis
|
alveolar proteinosis
Accumulation of surfactant in the alveoli, interfering with gas exchange |
|
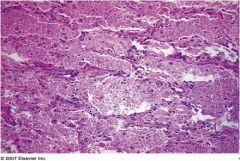
What is this?
|
alveolar proteinosis
Accumulation of surfactant in the alveoli, interfering with gas exchange |
|
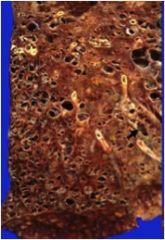
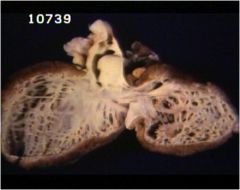
What do we have here?
|
honeycom lung
|
|

What is the diagnosis?
|
honeycomb lung
|
|
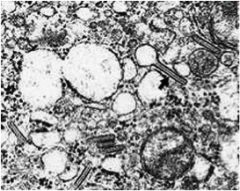
What is the diagnosis?
|
Eosinophilic granuloma (Histiocytosis X)
Giant cells abnormally infiltrate the lungs **Birbeck granules** (looks like tennis racket) Histiocytes show "coffee bean nuclei” |
|
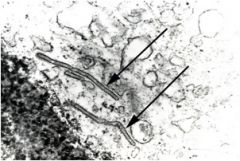
What is diagnosis?
|
Eosinophilic granuloma (Histiocytosis X)
|
|
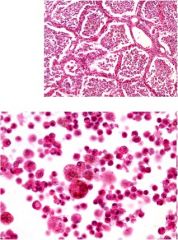
Diagnosis?
|
Lobar pneumonia
Note: Neutrophilic exudate Some fibrin |
|
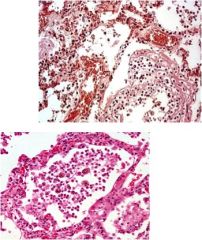
Diagnosis?
|
Lobar pneumonia
Note: Neutrophilic exudate Some fibrin |
|
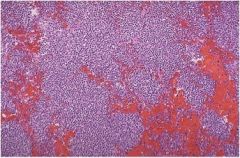
What is diagnosis?
|
bronchopneumonia
Inflammation of bronchioles into adjacent alveoli Can contain multiple lobes |
|
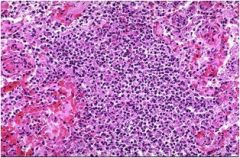
What is going on here?
|
bronchopneumonia
Inflammation of bronchioles into adjacent alveoli Can contain multiple lobes |
|
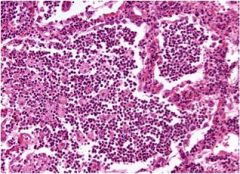
What is this?
|
bronchopneumonia
Inflammation of bronchioles into adjacent alveoli Can contain multiple lobes |
|
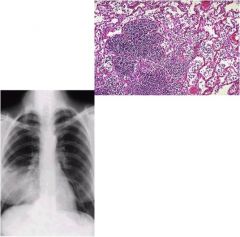
Diagnosis?
|
lobar pneumonia
|
|
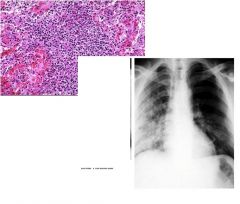
diagnosis this bitch?
|
broncho pneumonia
|
|
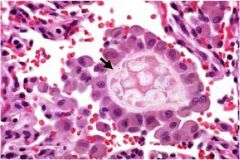
diagnosis?
|
aspiration pneumonia
Ingestion of foreign body into lungs Histology: Note the giant cells of foreign body aspirate |
|
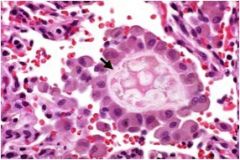
What is the diagnosis?
|
aspiration pneumonia
Ingestion of foreign body into lungs Histology: Note the giant cells of foreign body aspirate |
|
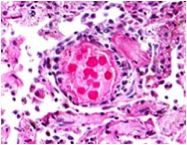
What is diagnosis?
|
Aspiration pneumonia
Ingestion of foreign body into lungs Histology: Note the giant cells of foreign body aspirate |
|
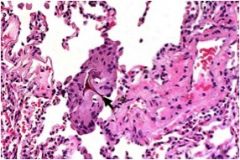
Diagnosis?
|
Aspiration pneumonia
Ingestion of foreign body into lungs Histology: Note the giant cells of foreign body aspirate |
|
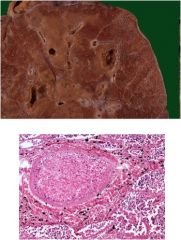
What is diagnosis?
|
lung absess
Cavity filled with pus, usually resulting from bronchial obstruction (i.e. cancer) aspiration (i.e. alcoholics, epileptics, loss of consciousness) Often caused by **S aureus** Note: : Cavity filled with pus surrounded by inflammatory cells |
|
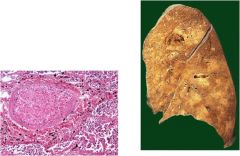
Diagnosis?
|
lung absess
Cavity filled with pus, usually resulting from bronchial obstruction (i.e. cancer) aspiration (i.e. alcoholics, epileptics, loss of consciousness) Often caused by **S aureus** Note: : Cavity filled with pus surrounded by inflammatory cells |
|
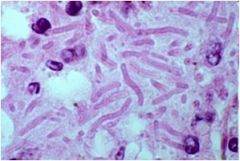
Patients cough up “red-currant jelly” sputum what is this?
|
Klebsiella pneumonia
|
|
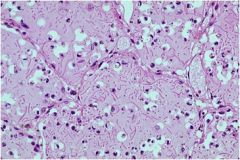
Patients cough up “red-currant jelly” sputum what is this?
|
Klebsiella pneumonia
|
|
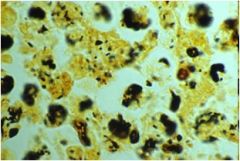
what is this?
|
legionella
Causes Legionnaire’s disease (Or Legionellosis) |
|
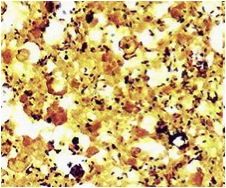
what is this?
|
legionella
|
|
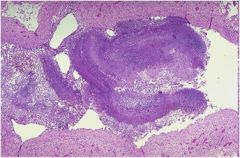
Diagnosis?
|
Characteristics:
Fungus formed in lesions of lungs Makes fungus ball in TB |
|
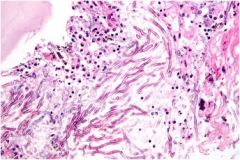
Diagnosis?
|
Characteristics:
Fungus makes a fungal ball when it inhabits lesion on lung from TB |
|
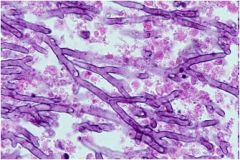
What do we have here?
|
aspergillus
Characteristics: Fungus Bottom pic is: A fungus ball composed of blue-staining hyphal elements of Aspergillus is seen here in a bronchus (forms fungus ball in Aspergillosis). Fungus balls may also form when fungi colonize cavitary lesions of tuberculosis. |
|
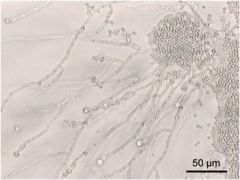
diagnosis?
|
Candida albacans
Characteristics: Fungus **Looks like balloon animals** Commonly affects immunocompromised |
|
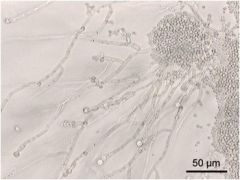
diagnosis?
|
Candida albacans
Characteristics: Fungus **Looks like balloon animals** Commonly affects immunocompromised |
|
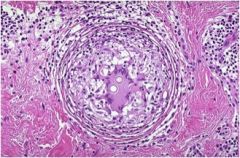
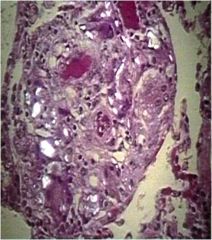
Diagnosis
|
Coccidioides
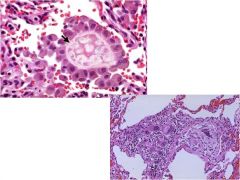
Characteristics: Fungus **Found within a giant cell** Found in SW USA Notes about pics: This well-formed granuloma has a large Langhans giant cell in the center. Two small spherules of Coccidioides immitis are seen in the giant cell. Bottom: At higher magnification, the thick wall of the C. immitis spherule is seen in a giant cell in the center of the photomicrograph. |
|
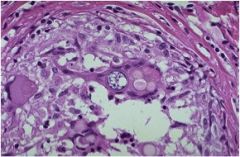
What is diagnosis
|
Coccidioides
Characteristics: Fungus **Found within a giant cell** Found in SW USA Notes about pics: This well-formed granuloma has a large Langhans giant cell in the center. Two small spherules of Coccidioides immitis are seen in the giant cell. Bottom: At higher magnification, the thick wall of the C. immitis spherule is seen in a giant cell in the center of the photomicrograph. |
|
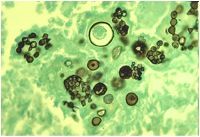
What is diagnosis?
|
Coccidioides
Characteristics: Fungus **Found within a giant cell** Found in SW USA Notes about pics: This well-formed granuloma has a large Langhans giant cell in the center. Two small spherules of Coccidioides immitis are seen in the giant cell. Bottom: At higher magnification, the thick wall of the C. immitis spherule is seen in a giant cell in the center of the photomicrograph. |
|
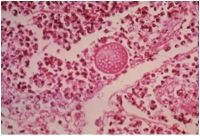
What is diagnosis?
|
Coccidioides
Characteristics: Fungus **Found within a giant cell** Found in SW USA Notes about pics: This well-formed granuloma has a large Langhans giant cell in the center. Two small spherules of Coccidioides immitis are seen in the giant cell. Bottom: At higher magnification, the thick wall of the C. immitis spherule is seen in a giant cell in the center of the photomicrograph. |
|
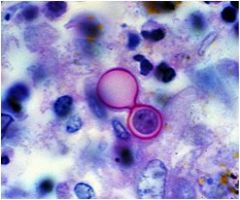
diagnosis?
|
blastomyces
Characteristics: Fungus **Spheres found in pairs** |
|
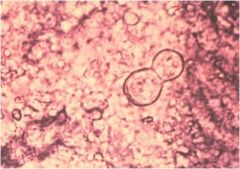
Diagnosis?
|
blastomyces
Characteristics: Fungus **Spheres found in pairs** |
|
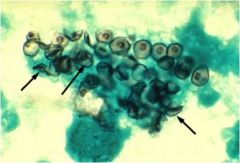
diagnosis?
|
Pneumocystis jeravicci
Characteristics: Fungus **Look like crushed ping pong balls** |
|
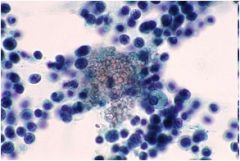
diagnosis?
|
Pneumocystis jeravicci
Characteristics: Fungus **Look like crushed ping pong balls** |
|
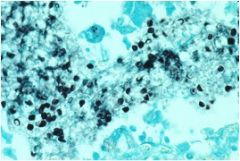
Diagnosis?
|
Pneumocystis jeravicci
Characteristics: Fungus **Look like crushed ping pong balls** |
|
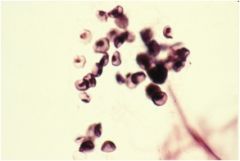
Diagnosis?
|
Pneumocystis jeravicci
Characteristics: Fungus **Look like crushed ping pong balls** |
|
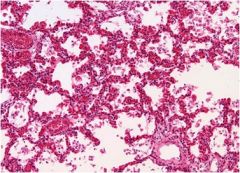
Diagnosis?
|
viral pneumonia
Characteristics: **Inflammatory cells are found interstitially (within the tissues), rather than exudative (above surfaces or in spaces) like acute inflammation.** |
|
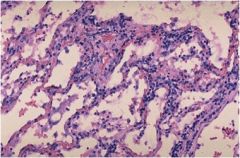
Condidtion?
|
viral pneumonia
Characteristics: **Inflammatory cells are found interstitially (within the tissues), rather than exudative (above surfaces or in spaces) like acute inflammation.** |
|
|
|
Cytomegalovirus
Charateristics: Herpesvirus **Looks like owl eyes** Immunocompromised |
|
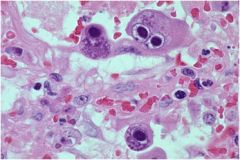
Diagnosi?
|
Cytomegalovirus
Charateristics: Herpesvirus **Looks like owl eyes** Immunocompromised |
|
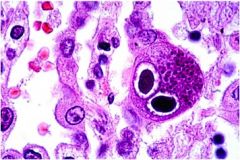
Diagnosis?
|
Cytomegalovirus
Charateristics: Herpesvirus **Looks like owl eyes** Immunocompromised |
|
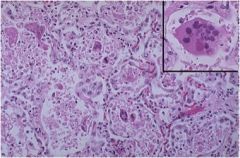
diagnosis?
|
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
**One of the major viral causes of respiratory infections in kids** Characteristics: **Pink, rounded intracytoplasmic inclusions found within giant cells** |
|
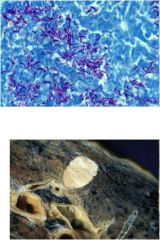
diah?
|
TB
Infection of the lungs, contracted from the air Characteristics: **Red snappers** Ghon complex Requires acid fast stain Causes caseous necrosis (Caseating granulomas) Looks like cheese |
|
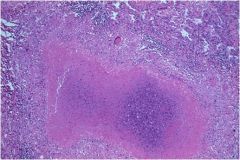
diag?
|
TB
Infection of the lungs, contracted from the air Characteristics: **Red snappers** Ghon complex Requires acid fast stain Causes caseous necrosis (Caseating granulomas) Looks like cheese |
|
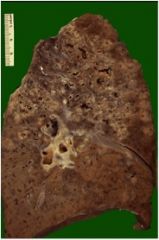
disg?
|
TB
Infection of the lungs, contracted from the air Characteristics: **Red snappers** Ghon complex Requires acid fast stain Causes caseous necrosis (Caseating granulomas) Looks like cheese |
|
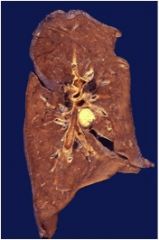
diag?
|
TB
Infection of the lungs, contracted from the air Characteristics: **Red snappers** Ghon complex Requires acid fast stain Causes caseous necrosis (Caseating granulomas) Looks like cheese |
|
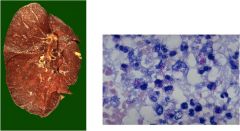
diagnos?
|
TB
Infection of the lungs, contracted from the air Characteristics: **Red snappers** Ghon complex Requires acid fast stain Causes caseous necrosis (Caseating granulomas) Looks like cheese |
|
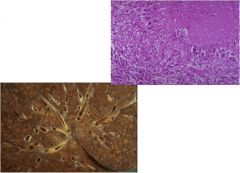
diagnosis?
|
TB
Infection of the lungs, contracted from the air Characteristics: **Red snappers** Ghon complex Requires acid fast stain Causes caseous necrosis (Caseating granulomas) Looks like cheese |
|
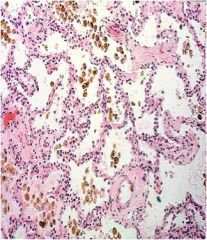
diag?
|
pulmonary congestion
Increased pulmonary venous hydrostatic pressure resulting from: Left-sided heart failure Mitral valve disease **Will see Hemosiderin-laden macrophages (heart failure cells)** Hemosiderin –Iron containing pigment Indicates bleeding |
|
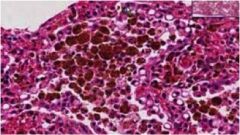
diag?
|
pulmonary congestion
Increased pulmonary venous hydrostatic pressure resulting from: Left-sided heart failure Mitral valve disease **Will see Hemosiderin-laden macrophages (heart failure cells)** Hemosiderin –Iron containing pigment Indicates bleeding |
|
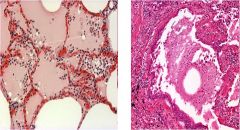
Diag?
|
Pulmonary Edema
Fluid accumulation within the lungs Causes: Left-sided heart failure Mitral valve stenosis Fluid overload Nephrotic syndrome Liver dz Infections, drugs, shock, and radiation |
|
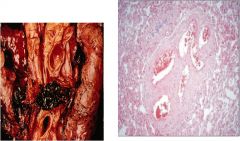
diga?
|
Pulmonary embolism
Arise from: **Deep vein thrombosis** (calf-most common) Saddle embolus When embolus straddles the division of the pulmonary arteries |
|
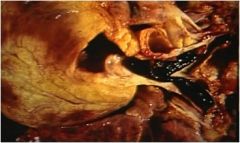
diag?
|
pulmonary embolism
Arise from: **Deep vein thrombosis** (calf-most common) Saddle embolus When embolus straddles the division of the pulmonary arteries |
|

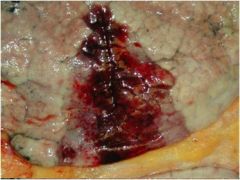
diag?
|
pulmonary infarct
Area of tissue death due to ischemia Red infarct Due to dual blood supply |
|
diag?
|
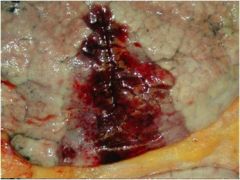
pulmonary infarct
Area of tissue death due to ischemia Red infarct Due to dual blood supply |
|
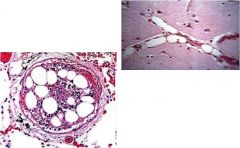
diag?
|
fat embolism
Complication of bone fracture |
|
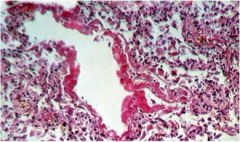
diag?
|
ARDS (Acute respiratory distress syndrome)
Life-threatening lung condition that prevents enough oxygen from getting into the blood. Causes: Trauma Sepsis (most common) Shock Gastric aspiration Uremia Acute pancreatitis Amniotic fluid embolism Diffuse alveolar damage -> Increased alveolar capillary permeability -> Protein-rich leakage into alveoli -> Results in formation of intra-alveolar hyaline membrane |
|
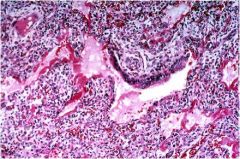
diag?
|
ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome)
Diffuse alveolar damage -> Increased alveolar capillary permeability -> Protein-rich leakage into alveoli -> Results in formation of intra-alveolar hyaline membrane |
|
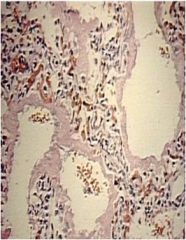
diag?
|
ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome)
Diffuse alveolar damage -> Increased alveolar capillary permeability -> Protein-rich leakage into alveoli -> Results in formation of intra-alveolar hyaline membrane |
|
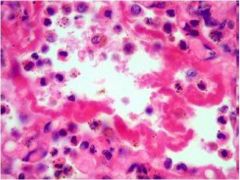
|
NRDS- neonatal rspiratory distress
Surfactant deficiency leading to increased surface tension, causing alveolar collapse Type II pneumocytes –Make surfactant Surfactant most abundantly made after 35th wk Lecithin-Sphingomyelin ratio in amniotic fluid (measure of lung maturity) should be >1.5 In NRDS, the ratio is < 1.5 Risk factors: Prematurity Maternal diabetes C-section delivery Histology looks exactly like ARDS |
|
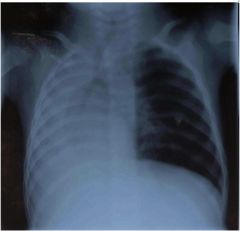
diag?
|
atelactasis
Lack of gas exchange within alveoli due to alveolar collapse or fluid accumulation |
|
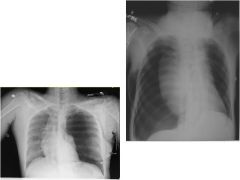
diag
|
Pneumothorax
Types: Primary spontaneous pneumothorax –Spontaneously occur in young people without lung dz Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax –Occurs with underlying lung condition Traumatic pneumothorax –As a result of a hole to the chest (stab, gunshot) Tension pneumothorax –Medical emergency, results in severe hypoxia secondary to blunt or penetrating injury of the lung Can differentiate because it causes a shift in the mediastinum (heart should be left of midline!) |
|
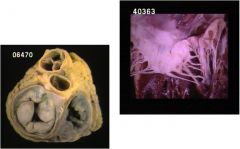
What is the diagnosis
|
Mitral valve prolapse... Barlow's
Mitral leaflets project back into the Left atrium during systole 7 % of US population Most commonly in women Marfan syndrome |
|
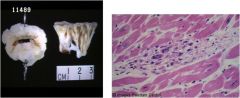
What the diagnosis?
|
Rheumatic fever
Inflammatory dz following a Group A Strep infection affecting the heart, brain, joints, and skin Characteristics: **Aschoff bodies** (inflammation of connective tissue in heart) Thickened chordae tendineae Aortic and mitral valve (most commonly affected valve |
|
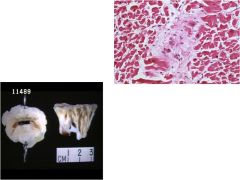
Diagnosis?
|
Rheumatic fever
Inflammatory dz following a Group A Strep infection affecting the heart, brain, joints, and skin Characteristics: **Aschoff bodies** (inflammation of connective tissue in heart) Thickened chordae tendineae Aortic and mitral valve (most commonly affected valve |
|
|
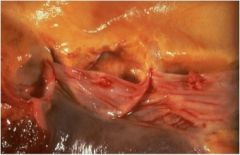
What the cardinal signs of Bacterial endocarditis?
|
FROM JANE
1. Fever 2. Roth’s spots (cotton wool spot surrounded by hemorrhage –white centered hemorrhage) 3. Osler’s nodes (painful, red lesions of hands/feet) 4.Murmur 5. Janeway lesions (Flat, painless, bluish-red spots on palms/soles) 6. Anemia 7. Nail-bed (splinter) hemorrhage 8. Emboli |
|
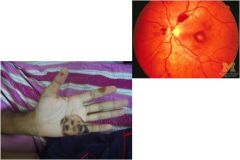
What are these called and shown in what pathology?
|
Osler node and Janeway lesions
endocarditis |
|
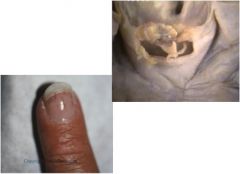
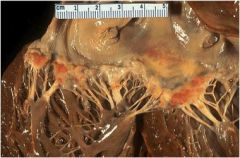
What are these two things?
What pathology are they usually related to? |
Splinter hemorrages and vegetation
Endocarditis |
|
What do we see here?
|
Marantic Endocarditis
Non-bacterial accumulation of fibrin and platelets on valves Seen in… **Cancer patients (pancreatic cancer)** Patients with hypercoaguability |
|
|
Libman sacks- lupus endocarditis (non-infections)
**Most common heart manifestation of SLE** Can be associated with… Mitral regurgitation Mitral stenosis |
|
|
Endomyocardial fibroelastosis
Rare disorder affecting kids <2 yrs old Characteristics: Thickening of endocardium (due to increased amount of connective tissue and elastic fibers) |
|
|
For Carcinoid disorder..
1. Hormone associated? 2. Effect on heart? |
1. Serotonin
2. The serotonin released into the big veins will promote endocardial fibrosis usually limited to the right side leading to tricuspid regurgitation |
|
|
What is common effect of opiate use?
|
Results in pulmonary edema
and constipation Users foam at the mouth |
|
|
What are the five main ways stimulants such as cocaine can kill you?
|
Ways it can kill you
1. Blocks Na+ channels in the heart slows HR 2. Stroke 3. Excited delirium 4. MI/ischemia/cardiomyopathy 5. Tachyarrhythmia (most common) |
|
|
What is a common problem seen in cocaine abuse?
|
Excited Delirium
Hyperthermia Delirium Respiratory arrest Death |
|
|
Explain the process of metabolizing cocaine
|
Serum ½ life is 1 hr metabolized to benzoylecgonine and ecgonine methyl ester both of those degrade into ecgonine
|
|
What do you see and what is diagnosis?
|
The shiny (birefringent) white stuff in there is talc, which is commonly used to cut drugs (especially cocaine) and stays in the lung
|
|
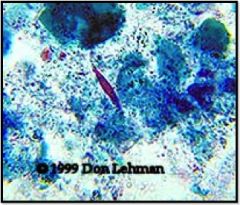
What is seen here?
|
Charcot-Leyden crystals (found in asthma)
|
|
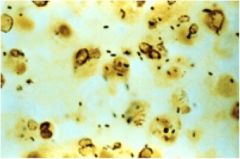
|
Legionella pneumophilia
|
|
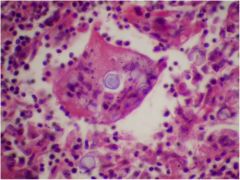
What is this? Patient has respiratory problems and find this
|
Coccidoides
|
|
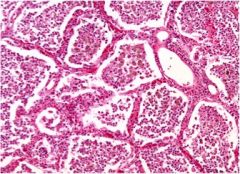
|
Pneumonia
|
|
|
Pulmonary embolism (recanalized)
|
|
|
pulmonary edema
|
|
|
bacterial endocarditis
|
|
|
Asthma (mucus plugs)
|
|
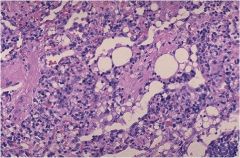
|
lipid pneumonia
|
|
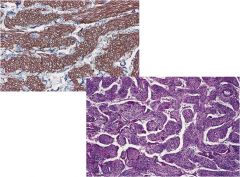
|
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
|
|
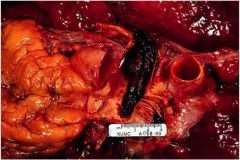
What is this?
|
saddle embolism
|
|
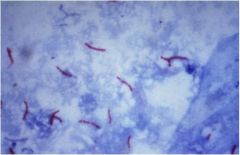
|
TB
|
|
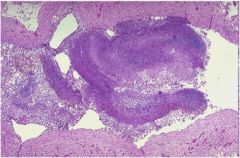
|
aspergillus fungus ball
|
|
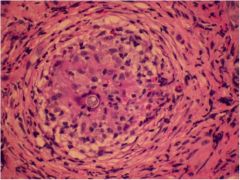
|
Coccidioides
|
|
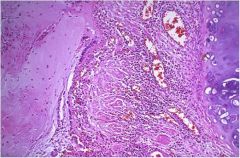
|
Asthma
|
|
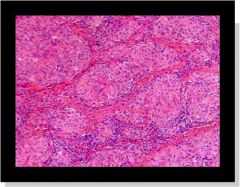
What is this?
|
sarcoidosis
|
|
|
Blue blebs in emphysema
|
|
|
Aspiration pneumonia (note giant cells of foreign body aspirate)
|
|
|
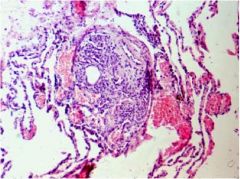
Plexiform lesion (pulmonary hypertension)
|
|
|
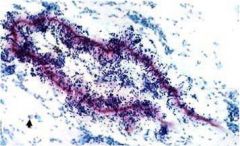
Curschmann’s spirals
|
|
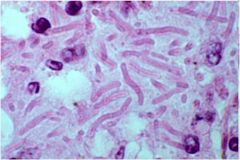
|
Klebsiella
|
|
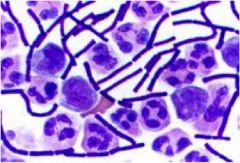
What is this?
|
Anthrax
|
|
|
|
Chronic bronchitis (mucus gland hyperplasia)
|
|
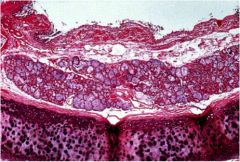
|
Chronic bronchitis (mucus gland hyperplasia)
|
|
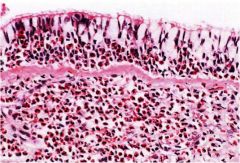
|
Asthma (lots of eosinophils)
|
|
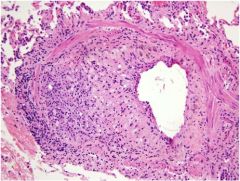
|
Obliterative bronchiolitis (constrictive bronchiolitis)
|
|
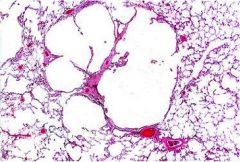
|
Centrilobular emphysema
|
|
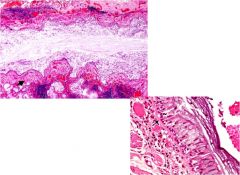
|
Asthma
|
|
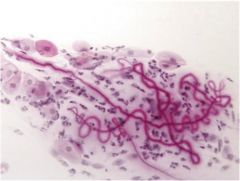
|
Curschmann’s spirals
|
|
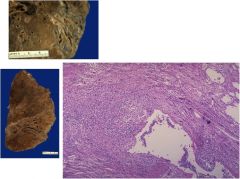
|
Bronchiectasis
|
|
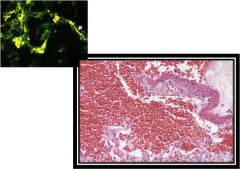
|
Goodpasture’s syndrome
|
|
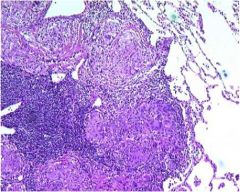
|
Sarcoidosis
|
|
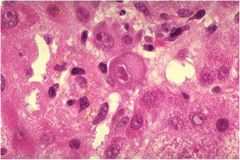
What is thsi virus?
|
Cytomegalovirus
|
|
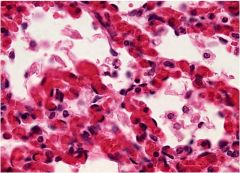
|
viral pneumonia
|
|
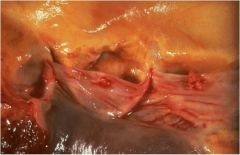
|
Marantic endocarditis (Non-bacterial endocarditis)
|
|
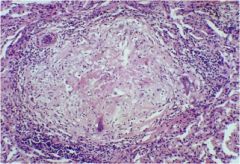
|
Caseating granuloma (TB)
|
|
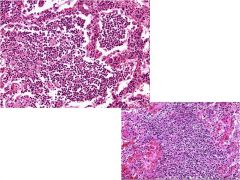
|
bronchopneumonia
|
|
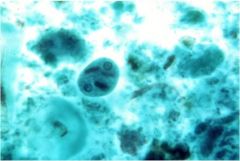
|
Amoeba
|
|
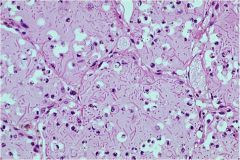
|
Molluscum contagiosum
|
|
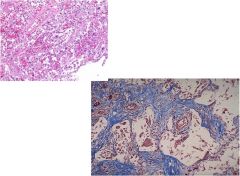
|
Hamman-Rich syndrome
|
|
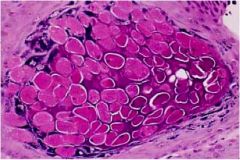
|
klebsiella
|
|
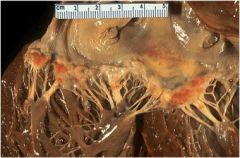
|
Libman-Sacks endocarditis
|
|
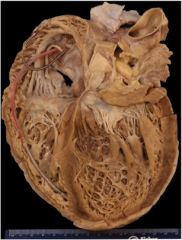
|
Dilated cardiomyopathy
|
|
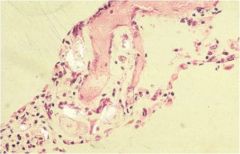
|
talc back in the lung
|
|
|
|
talc in the lung
|
|
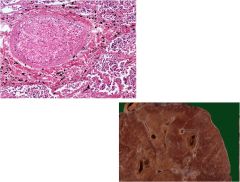
|
talc in the lung
|
|
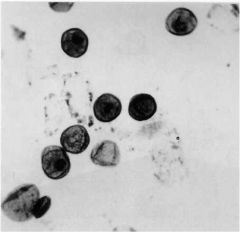
|
Pneumocystis
|
|
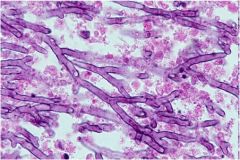
|
asperigillus
|
|
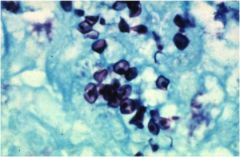
|
Pneumocystis carinii
|
|

|
Emphysema
|
|

|
Honeycomb lung (from fibrosis seen in restrictive lung disease)
|
|
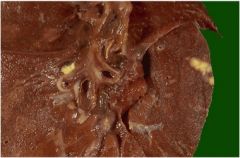
|
TB (Ghon complex yellow spot on far right)
|
|
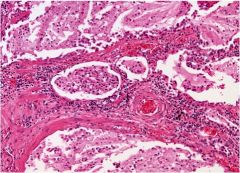
|
Pulmonary edema
|
|
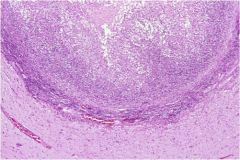
|
Caseating granuloma (TB)
|
|
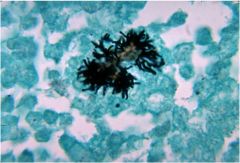
|
Actinomyces
|
|
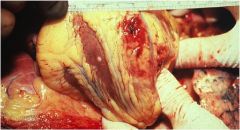
|
Ruptured MI
|
|
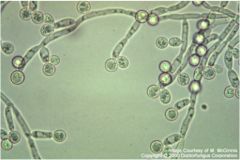
|
Candida
|
|
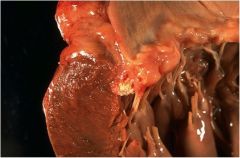
|
Calcified mitral valve
|
|
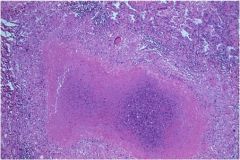
|
Caseating necrosis (TB)
|
|
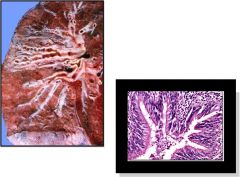
|
Bronchiectasis
|
|
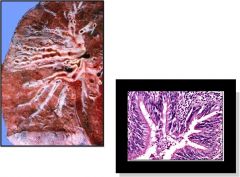
|
Bronchiectasis
|
|
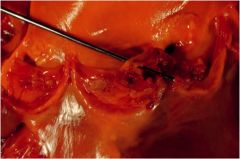
|
Bacterial endocarditis
|
|
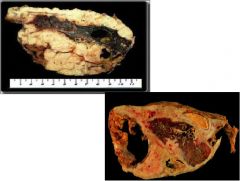
|
Mesothelioma
|
|
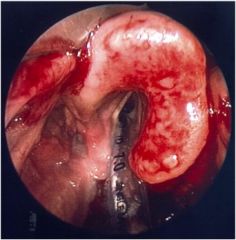
|
Epiglottitis -->Croup
|
|
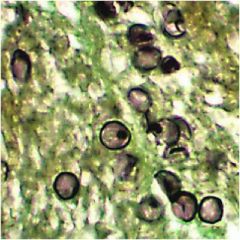
|
Pneumocystis carinii
|
|
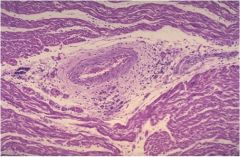
|
Aschoff nodule of Chronic Rheumatic Fever
|
|
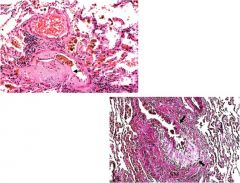
|
Obliterative bronchiolitis (constrictive bronchiolitis)
|
|
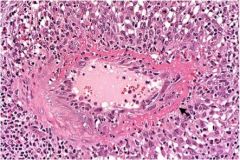
Kidney and lungs
|
Wegener’s Granulomatosis
|
|
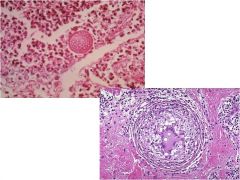
|
Coccidioides
|

