![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Palpable purpura, arthritis, abdominal pain, renal failure
|
Henoch–Schönlein Purpura-Small vessel vasculitis.
|
|
|
Henoch–Schönlein Purpura criteria
|
Age under 21
Palpable purpura without thrombocytopenia Bowel angina or ischemia or bloody diarrhea (worsen by eating) Biopsy with granulocytes in walls of arteries/venules Any 2 of 4 = sensitivity of 87%, specificity of 88% |
|
|
It has livedo reticulari. Testicular bilateral pain. It causes secondary HTN. 1/3 of the pts had hepatitis infection so antigen may be causative. Characteristic arteriography
(ANCA negative) |
Polyarteritis Nodosa. Medium sized artery vasculitis
|
|
|
Churg–Strauss Syndrome
BLANES: |
Biopsy with extravascular eosinophils in lung or sinuses
Migratory lung infliltrates on CxR History of asthma or wheezing on exam Mononeuritis multiplex or polyneuropathy Eosinophilia > 10% Paranasal sinusitis Any 4 |
|
|
Granulomas of the upper respiratory tract
Granulomas of the lower respiratory tract Focal segmental glomerulonephritis |
(Wegener’s) Granulomatosis w/ Polyangiitis
|
|
|
(Wegener’s) Granulomatosis w/ Polyangiitis LUNG
|
Abnormal Chest X-ray (Lung)
Nodules, infiltrates or cavities (not migratory) Urinary Sediment Abnormal (Urine) > 5 RBCs or RBC casts Pauciimmune (no immunofluorescence) Nasal or oral inflammation (Nasal) Ulcers or purulent/bloody discharge Granulomas on biopsy (Granulomas) Granulomas in arterial wall or perivascular Any 4 |
|
|
Age < 45
Current or recent tobacco use Distal extremity ischemia No evidence of autoimmune disease No evidence of hypercoagulable state Arteriography without atherosclerotic disease |
Thromboangiitis Obliterans
|
|
|
-Symmetric proximal muscle weakness with pain
-Elevated plasma muscle enzymes -Myopathic changes on electromyography -Characteristic muscle biopsy abnormalities and the absence of histopathologic signs of other myopathies |
Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis
|
|
|
Dermatomyositis
|
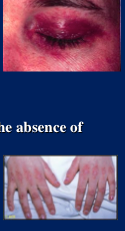
Gottron’s papules and heliotrope eyelids
Humorally mediated vasculitis Adult form associated with malignancy |
|
|
Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis tx
|
Steroids, cytotoxics, plasmapheresis, IVIG
|
|
|
Insidious onset, mean 6 years prior to Dx
Proximal weakness, may be asymmetric and effect cricopharyngeals Mild CK elevations, ESR and Hb normal, ANA negative MRI with anterior muscle groups, occasional distal and asymmetrical |
Inclusion Body Myositis
|
|
|
Inclusion Body Myositis pathophysiology
|
Immune–mediated CD8+ attack
HLA associations and familial cases |
|
|
Inclusion Body Myositis dx
|
Biopsy: rimmed vacuoles, atrophic muscle, perivascular and endomysial inflammatory cells
Theres no therapy |
|
|
Common Myopathies
|

|

