![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
442 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does FVCRP stand for?
|
-FVR-Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis (Virus)
-C-Calici Virus -P-Panleukopenia (virus) |
|
|
What is added when it is FVRCPC?
|
Chlamydia (bacteria)
|
|
|
What does DHLPP stand for? Are the diseases this contains viral or bacterial?
|
Distemper (viral)
Hepititis/Adenovirus (viral) Leptospirosis (bacterial) Parainfluenza (Viral) Parvo (viral) |
|
|
What if it was DHLPPC? What has been added?
|
Corona (virus)
|
|
|
What is the normal temperature for dogs and cats?
|
101.5 +/- degrees F
|
|
|
What is the normal respiration rate for dogs?
|
15-30 breaths per minute
(should count for 15 secs and multiply by 4. Any short than 15 secs tends to be less accurate) |
|
|
What is the normal respiration rate for cats?
|
20-30 Seconds
|
|
|
What is the normal pulse rate for adult dogs? How does it differ for toy breeds?
Puppies? |
60-160 bpm
Toy breeds-up to 180 bpm Puppies-up to 220 bpm |
|
|
What is the normal pulse rate for cats?
|
110-220 bpm
|
|
|
Define palliative
|
relieving or soothing symptoms of a disease without curing
|
|
|
Define anemia
|
decrease of deficiency of RBC's and hemoglobin in the blood due to loss, destruction, or lack of production.
|
|
|
Define immunosuppression
|
reduced response by the bodies immune system
|
|
|
Define Active immunity
|
immunity that results from the bodies own response to an antigen. (best kind!)
|
|
|
Define passive immunity
|
Immunity produced by administration of PRE-FORMED antibodies.
-Artificial-through injection of plasma, serum -Maternal-ingestion of colostrum |
|
|
Define acquired immunity
|
Antigen specific immunity attributable to production of antibodies and of specific immune T-lymphs.
|
|
|
Define diagnosis
|
Complete knowledge. Art & science of distinguishing one disease from another.
|
|
|
In regards to Specific Resistance vs Non-Specific Resistance:
What type of immunity is immediate? |
Non-specific resistance
|
|
|
In regards to Specific Resistance vs Non-Specific Resistance:
What type of immunity includes antibody production? |
Specific resistance
|
|
|
In regards to Specific Resistance vs Non-Specific Resistance:
What type of immunity protects against anything? |
Non-specific resistance
|
|
|
In regards to Specific Resistance vs Non-Specific Resistance:
What type of immunity forms long term protection? |
Specific resistance
|
|
|
What is the vertebral formula for dogs & cats?
|
C7 T13 L7 S3 CY20-23
|
|
|
What is the vertebral formula for horses?
|
C7 T18 L6 S5 Cy 15-21
|
|
|
What is the deciduous dental formula for dogs?
|
2(Di3/3 Dc1/1 Dp3/3) = 28 teeth
|
|
|
What is the adult dog dental formula?
|
2(I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3) = 42 teeth
|
|
|
What is the deciduous dental formula for cats?
|
2(Di3/3 Dc1/1 Dp 3/2)=26 teeth
|
|
|
What is the dental formula for adult cats?
|
2(I3/3 C1/1 P 3/2 M 1/1) = 30
|
|
|
Give three examples of micro-organisms.
|
bacteria
fungi virus |
|
|
List the structural organization of the body in order
|
Cell
tissue organs organ systems organism |
|
|
What does stress do to the immune system?
|
Compromises it
|
|
|
What is the generic and brand name of the gas used for gas sterilization?
|
Generic: Ethylene oxide
Brand name: Anprolene |
|
|
Which objective is is used with immersion oil and what is the final magnification?
|
100x objective is the objective oil is used with
final magnification is: 1000x (Ocular 10x times Objective 1000x) |
|
|
With an ECG, where to the following leads go:
Red Black White Green Black brown |
Black -left axillary
Red- left inguinal (smoke before fire...) White-Right axillary Green-Right inguinal (snow on the grass...) Brown-chest |
|
|
What anticoagulant is in the purple top tube-LTT?
What is it used for? Sample management: |
EDTA
CBC Mix while putting blood in, make 2 blood films right away |
|
|
What anticoagulant is in the Green top?
What is it used for? Sample management? |
Heprin
Blood gas analysis mix thoroughly while putting blood in |
|
|
What anticoagulant is in Red top tube (RTT)?
What is it used for? Sample management: |
NO anticoagulant
bio-chemistries Allow to clot, spin, separate serum off top-put in separate tube |
|
|
What tube can be used for a lab test that requires serum?
|
RTT or Red and gray topped Serum separator tube
|
|
|
What is in a Grey Top tube?
What is it used for? Sample management: |
Oxylate anticoagulant
Glucose measurement Mix well while putting blood in |
|
|
What is in a Blue Top tube?
What is it used for? Sample management: |
Sodium citrate anticoagulant
Coagulation Studies Must be full to vacuum capacity, mix well, spin at 6000rpm for 6 mins, Separate off citrated plasma and put in RTT labled with Pt,s name and that it is Citrated palsma -<6hrs can be refrigerated ->6hrs-Freeze the plasma |
|
|
What kind of anticoagulant is in a Blue ring crit tube?
What is it used for? |
NONE
PCV, TP, Plasma eval in conjunction WITH a LTT |
|
|
What kind of anticoagulant is in a Red Ring Crit tube?
|
Contains HEPARIN
PCV, TP, Plasma eval. when blood is taken DIRECTLY from Pt. **no syringe involved** |
|
|
What kind of anticoagulant is in a Black Ring Crit tube?
|
HEPARIN
used for CBC and blood tests with Avian/Reptile/Pocket pets |
|
|
What is another abbreviation that means the same as HCT?
|
PCV
Hematocrit/Packed cell volume) |
|
|
What size are needles and catheters with a blue cap?
What animals are these typically used on for IM, SQ,IV injections, Cephalic blood draws? |
22g
Dogs and cats Blood draw-jugular of cat, cat size dog Cephalic of Med to large size dogs |
|
|
What size are needles with a red cap and who are these used for?
|
25g
Neonates Lateral saphenous in dogs Femoral blood draw in cats |
|
|
What size are needles with a pink cap?
Who and what are they used for? |
20g
IM & SQ-Cows, horses, very large dogs IV injections-cows and horses Blood draw-jugular large animal and jugular of med to large size dog |
|
|
What size needle is the one with a green cap? Who is it used for?
|
18g
Cows and horses for IM and SQ, jugular blood draw |
|
|
Give the formula for corrected WBC
|
WBC * 100
___________________ # of nucleated RBC +100 {(WBC*100)divided by(#nRBC+ 100)} |
|
|
When is it necessary to do a corrected WBC?
|
When there are 5 or more nucleated RBC in the WBC count.
|
|
|
What is the name used to describe reticulocytes on a blood film stained with Wrights stain or Diff Quik?
|
Polychromatophils
|
|
|
What is the name used to describe reticulocytes on a blood film stained with NMB?
|
Reticulocytes, Retics
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of Retics and how do they differ?
|
Punctate, more mature with polkadots(ribosomes)
Aggregate, less mature, clumped ribosomes -Only these are couted in cats and birds. |
|
|
What species is a retic count never done and why?
|
horses
Because they do not release polychromataphils |
|
|
What is the purpose of a retic count?
|
To determine the bone marrows response to anemia
|
|
|
How many WBCs are counted for a WBC diff?
|
100 cells on 40x
|
|
|
How many RBC's are counted for a retic count?
|
1000 RBCs are counted and Retics are tallied
|
|
|
Give the order and times of the Gram stain reagents.
|
1. CRYSTAL VIOLET-for 1 minute
2. GRAM'S IODINE- 1 minute 3. DECOLORIZER- till it runs clear 4. SAFRANIN- 1 minute *rinse gently with tap water between steps |
|
|
What color do Gram positive bacteria stain?
|
PURPLE
|
|
|
What color do Gram negative bacteria stain?
|
PINK
|
|
|
Name 2 species that are very susceptible to Tetanus and should be immunized with the Tetanus toxid?
|
Humans
Horses |
|
|
E.coli is a Gram _____ rod that commonly causes cystitis.
|
negative
|
|
|
Psittacosis is caused by __________
|
Chlamydophilia
|
|
|
The vector that transmits the plague is the __________
|
flea
|
|
|
The Coggins test is used to diagnose_______________
|
Equine Infectious Anemia (EIA)
|
|
|
Staphyloccus is a Gram positive cocci that is catalase _________
|
POSITIVE
|
|
|
STREPTOcoccus is a Gram positive cocci that is catalase __________
|
NEGATIVE
|
|
|
What is used on Gram Positive Cocci for the Catalase test?
|
H2O2 -hydrogen peroxide
|
|
|
A positive catalase test will do what indicating that it is a ____________?
|
Fizz and bubble
Gram positive cocci-Staphylococcus |
|
|
A negative catalase test will do what indicating that it is a __________?
|
Nothing
STREPTOcoccus |
|
|
A coagulase test is done on which bacteria?
|
Gram positive cocci that have tested positive on the coagulase test--indicating Staphylococcus.
|
|
|
A positive coagulase test will have what results and this will indicate what?
|
The plasma will CLOT
Indicates that it is a PATHOGENIC Staphylococcus such as: Staph. aureus Staph. intermedius Staph. hyicus |
|
|
A negative coagulase test will have what results and this will indicate what?
|
no change
Indicates nonpathogenic Staphylococcus such as: Staph. epidermis Staph coag- spp Micrococcus |
|
|
A negative catalase test indicates that it is STREPTOCOCCUS. What is the next test done to ID the bacteria?
|
Hemolysis on Blood agar.
Certain bacteria cause lysis of RBCs in Blood agar and sheep blood is often used due its sensitivity to this |
|
|
What is Beta hemolysis and what bacteria are indicated by this type of hemolysis?
|
Complete lysis of RBC's in blood agar
Indicates PATHOGENIC STREPTOcoccus such as: Strep. pyogenes Group A Strep. agalactiae Group B Strep. equi Group C Strep zooepidemicus Strep. canis |
|
|
What is Alpha hemolysis and what type of bacteria are indicated by this type of hemolysis?
|
Incomplete hemolysis of RBCs in blood agar.
Strep. pneumoniae Strep. suis Strep bovis Strep equinus |
|
|
What is gamma hemolysis and what type of bacteria are indicated by this test?
|
NO hemolysis on Blood agar
Strep. faecalis (enterococcus Strep. uberis * |
|
|
Bordetella is a GNROD that causes ______________
|
Infectious tracheobronchitis
AKA: Kennel cough |
|
|
The gastrocnemius is found on which limbs?
|
Hind
|
|
|
Tendons connect what to what?
|
Muscle to bone
|
|
|
Ligaments connect what to what?
|
Bone to bone
|
|
|
MaConkeys agar selects for the growth of ________________ and differentiate between ___________________ and ___________________.
|
GNRODs
Lactose fermentors Non-lactose fermentors |
|
|
What quadrant is the stomach located in?
|
Left upper (LU)
|
|
|
What quadrant is the liver located in?
|
Right and left upper (RU and LU)
|
|
|
What quadrant is the spleen located in?
|
Left upper (LU)
|
|
|
At what age do puppies normally receive their first Rabies Vaccination?
|
16 weeks
|
|
|
At what age do we commonly vaccinate puppies?
|
Starting at 6-8 weeks
Boosters at 12 and 16 weeks |
|
|
Where do we give the combo vaccine in cats and dogs?
|
SQ on right front leg, distal to mid-scapula
|
|
|
Where do we give the Rabies vaccine?
|
SQ on right hind limb, distal to hip
|
|
|
Where do we give the FeLV vaccine?
|
SQ on left hind distal to hip
|
|
|
Define PO
|
by mouth
|
|
|
Define CRF
|
Chronic Renal Failure
|
|
|
Define PRN
|
As needed
|
|
|
Define PU/PD
|
Polyuric/Polydipsic
|
|
|
Define IVDD
|
Intervertebral Disk Disease
|
|
|
Define AIHA
|
Auto Immune Hemolytic Anemia
|
|
|
Define ACL
|
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
|
|
|
Define THR
|
Total hip replacement
|
|
|
Define PCV
|
Packed cell volume
|
|
|
Define CRT
|
Capillary Refill Time
|
|
|
Define hypercapnia
|
Excess CO2 in the blood
|
|
|
Define nystagmus
|
Rhythmic involuntary movement of both eyes in unison. Movements can be vertical, horizontal or rotational.
|
|
|
Define anisocoria
|
pupils of unequal size
|
|
|
Define laparotomy
|
incision through abdominal wall
|
|
|
Define orchiectomy
|
excision of one or both testes
|
|
|
Define onychecyomy
|
Declaw, excision of claw, nail, and or nailbed
|
|
|
Define Cynosis
|
bluish coloring of Mucous membranes due to lack of O2 perfusion to tissues
|
|
|
Define Ataxia
|
failure to move in a coordinated manner
|
|
|
Define gastropexy
|
surgical fixation of the stomach to the abdominal wall
|
|
|
Define pyometra
|
Infection of the uterus with purulent material build up.
Closed- not draining Open- draining through the cervix and vulva |
|
|
Define pruritis
|
Itching
|
|
|
Define encephalomyelitis
|
Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
Define NPO
|
nothing by mouth
|
|
|
Define DKA
|
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
|
|
|
Define OD
|
right eye
|
|
|
Define OS
|
left eye
|
|
|
Define AD
|
Right ear
|
|
|
Define AS
|
Left ear
|
|
|
Define CHF
|
Congestive heart failure
|
|
|
Define MCT
|
Mast cell tumor
|
|
|
Define IMHA
|
Immune Mediated Hemolytic Anemia
|
|
|
Define TPLO
|
Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy
|
|
|
Define GDV
|
Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
|
|
|
Define PVC
|
premature ventricular contraction
|
|
|
Define PU (a cat surgery....)
|
Perineal Urethrostomy
|
|
|
Give the procedure for staining a slide with Diff Quick.
|
Jar 1 Fixative-5 1 sec dips
Jar 2 Eosinophillic-5 1 sec dips Jar 3 Basophillic - 7-to 10 1 sec dips *tap slide on towel between to remove excess *rinse gently with tap water to remove excess *Sit upright to remove excess |
|
|
What is the normal WBC range for dogs?
|
6,000 to 17,000 / ul (6-17 k/ul)
|
|
|
What is the normal WBC range for cats?
|
5,500 to 19,5000/ul (5.5 to 19.5 k/ul)
|
|
|
What is the normal RBC count for dogs?
|
5-10* (10 to the 6th power)
|
|
|
What is the normal RBC count for CATS?
|
5-11*(10 to the 6th power)
|
|
|
What is the normal PCV for dogs?
|
37- 55%
Average is 45% |
|
|
What is the normal PCV for cats?
|
30-45%
Average is 35% |
|
|
What is the normal MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume) for dogs?
|
60 to 70fl
Above 70flMacrocytic less than 60fl Microcytic |
|
|
What is the normal MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume) for cats?
|
39-55 fl
Above 55fl -Macrocytic below 35fl -Microcytic |
|
|
What is the normal MCHC (Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration) for both dogs and cats?
|
30-36 g/dl
Above 36 g/dl is Hyperchromic below 30 g/dl is hypochromic |
|
|
What is the normal range for TP in dogs?
|
5.0 to 7.0 g/dl
|
|
|
What is the normal range for TP in cats?
|
5.0 to 8.0 g/dl
|
|
|
What is the normal range for Platelets/ul in dogs and cats?
|
200,000 to 500,000 platelets/ul
|
|
|
What is the normal blood volume in dogs?
|
88 mls/kg
|
|
|
What is the normal blood volume in cats?
|
66 ml/kg
|
|
|
What is the formula for figuring normal blood volume?
|
Animals weight in Kgs times species norm
|
|
|
What is the fluid replacement formula?
|
(Weight in #s)*(%dehydrated)*454= mls of fluid needed
OR you can use kgs- Kgs* % dehydrated*1000=mls needed |
|
|
How do you arrive at the Observed Retic %?
|
Move the decimal over to left by one.
For ex- 35 retics becomes 3.5% 6 retics becomes 0.6 % |
|
|
What is the formula for figuring the Corrected Retic %?
|
PCV of Pt
______________ * Observed Retic PCV Avg of Species ---> PCV of Pt divided by PCV average of species TIMES Observed Retic Percentage |
|
|
What is the formula for figuring Absolute Retics?
|
# of retics
____________ * RBC(w/o exponent) 1000 =Retics/ul If RBC is 3.1 *(10 to 6th) you would use 3,100,000 in above formula |
|
|
What is the formula for MCV?
|
Mean corpuscular volume is figured by:
PCV * 10 ________ = fl (femtoliters) RBC |
|
|
What is the formula for MCHC?
|
Mean Cell Hemoglobin content is figured by:
Hgb*100 ------------- = g/dl PCV |
|
|
What is the formula for MCH?
|
Mean Cell Hemoglobin is figured by:
Hgb * 10 -------------- = pg (picograms) RBC |
|
|
What is the formula for figuring Fibrinogen?
|
TP less the hp (heat precipitate)
=g/dl *1000 equals ___mg/dl |
|
|
What is the formula for figuring TP:F ratio?
|
Total protein
------------------ Fibrinogen (g/dl answer) *no units >15 dehydrated or normal 10-15 gray area <10 absolute increase in Fibrinogen due to inflammation |
|
|
What is the medical term for abnormally shaped RBC?
|
Poikilocytosis
|
|
|
Term for small RBC's with no central pallor?
|
Spherocytes
|
|
|
Term for nucleated RBC (nRBC)?
|
Polychromatophil in Diff Quik/ Wrights
Retic in NMB stain |
|
|
Term for RBC with long, irregular projections:
|
Acanthocytes
|
|
|
Term for RBC fragments?
|
Schistocytes
|
|
|
Term for RBC that is spiculated with EVEN small projections over the entire cell surface appearing at times as darker red staining areas.
|
Echinocytes
|
|
|
Term for RBC that have one or two long spikes coming off of cell that result from a blister or vacuole on surface on cell. Look similar to elmer Fudd hat or half moon...
|
Keratocytes
|
|
|
Term for an RBC with more surface area than contents. Similar to a half full zip-lock bag. Cell membrane folds and will be lighter in color.
|
Leptocyte
|
|
|
Term for RBC that has a pale colored mouth area in the center of the cell and is only seen in dogs with chondrodystrophy.
|
Stomatocyte
|
|
|
Term for a punched out cell. It appears there is a hole in the cell due to very little central pallor with a thickened rim. (red life saver...)
|
Torocyte
|
|
|
Term for a blister cell that is commonly seen in conjunction with Heinz bodies. Rarely seen
|
Eccentrocyte
|
|
|
Term for tear drop shaped RBC and is usually artifact, espcially if tear points all point in the same direction.
|
Dacrocyte
|
|
|
Term for empty RBC membrane and usually indicates IVH.
|
Ghost cell
|
|
|
Term for residual RNA appearing as very small multiple round spots that stain bluish on routinely stained blood films.
|
Basophilic Stippling
|
|
|
Term for a Single, sometimes double, inclusion on a RBC seen on a routinely stained film blood film. These dots are basophilic nuclear remnants.
|
Howell-Jolly bodies
|
|
|
Term for a clear nipple like protrusion from cell wall with routine stain. With NMB stain it will appear as a blue-green protrusion. Can be single or double.
|
Heinz bodies
|
|
|
What are Heinz bodies caused by and what they result from?
|
Caused by oxidized and denatured hemoglobin that can result from:
-Oxidant drugs or chemicals like acetominophin, maple leaves and zinc. -Associated with IV hemolysis Seen frequently in sick stressed cats |
|
|
What is the common name of the infection caused by dermatophyte molds?
|
Ringworm
|
|
|
Dermatophyte test media turns what color______ if positive for Ringworm? What color will the actual growth ON the media be?
|
Red
White/light colored |
|
|
What does MRSA stand for?
|
Methicillian Restistant Staph Aureus
|
|
|
Which is larger in diameter-a 16g or an 18g needle?
|
16g
-smaller the #, bigger the needle diameter |
|
|
Which is larger in diameter- a 12fr red rubber cath or a 10fr?
|
12 french is larger
With Caths-the larger the #, the larger the cath diameter |
|
|
Is 3-0 suture bigger or smaller than 2-0?
Is size 1 suture bigger or smaller than 4? |
3-0 is smaller than 2-0
smaller smallest ----------------------------largest <-------------------0--------------------------> (3-0)(2-0)(1-0) 0 1 2 3 4 5 |
|
|
Autoclaved packs are good for how long?
|
30 days
|
|
|
Gas sterilized packs are good for how long?
|
90 days
|
|
|
What size clipper blade should be used for shave a small animal Pt prior to surgical procedure?
|
#40
|
|
|
A scalpel blade should be passed in what manner?
|
Overhand with handle to surgeon
|
|
|
Name 5 types of absorbable suture
|
Vicryl
PDS Dexon Maxon **note these have <6 letters** Surgical Gut |
|
|
Name 5 types of NONabsorbable suture
|
Ethilon (Dermalon)
Prolene Surgilene/Surgipro Vetcassette Novafil Silk Steel |
|
|
Name the tasks the Circulator is responsible for?
|
Wears only a cap, mask & shoe covers
Drape the back up table Scrub the Pt Tie in the surgeon Plug in cautery Run anesthesia Anticipates needs of surgical team Opens only outer later of packs Counts USED sponges |
|

Identify this yeast.
Peanut men, bowling pins....) |
Malassezia is commonly found in the ear canal, interdigital area (between the toes), anal sacs, vagina, and rectum of healthy dogs. Disease-causing infections with this yeast can occur in dogs of all ages and breeds. There are however, several dog breeds that appear to have an increased susceptibility to developing Malassezia infections including:
* Basset Hounds * Cocker Spaniels * English Setters * Shih Tzus * Maltese * West Highland White Terriers * German Shepherd Dogs ---an opportunistic organism |
|
|
Name the tasks the Scrub nurse is responsible for
|
Wears cap, mask, shoe covers, sterile gown and gloves
Gown and glove the surgeon Load the needle drivers Drapes the mayo stand Drapes the Pt Arranges instruments on Mayo stand Counts UNused sponges uses a closed gloving technique |
|
|
With a refractometer, what is read on the right hand side scale?
Left hand scale is for? Middle scale? |
Urine Specific gravity (USG), no units
1.018 would be siad out load as ten-eighteen. Total Protein (TP), g/dl Nothing we care about |
|
|
What is the lab procedure for preparing PCV tube?
|
-Obtain EDTA blood or several heparinized HCT tubes. Mix well
-Fill at least 2 plain(non-hepranized) HCT tubes 2/3 to 3/4 full -Plug ends with crit clay -Spin for 5 minutes at 6000RPM |
|
|
What is the anatomy of a spun crit tube?
|
Plasma, buffy coat, RBC's
|
|
|
What does PCV measure?
|
The percent quantity of blood which is made up of RBCs
|
|
|
How do you measure the PCV?
|
Using a PCV/Hematocrit card, -bottom of the Red Cell Column is placed at 0%
-top of the plasma is placed where it hits 100%. -Read PCV where the Red Cell column top is at. |
|
|
What is the procedure for figuring TP?
|
Take the previously used PCV tube after reading PCV % and break it just above the buffy coat.
-Put the plasma on the glass pane of the refractometer, close and look through eyepiece -Read left hand scale to the nearest 0.2 g/dl |
|
|
What can be seen in the buffy coat if it is examined under a microscope on 10x?
|
Circulating microfilaria
|
|

ID this dermatophyte mold. What does it cause?
|
Microsporum canis
Ringworm |
|

ID general type of bacteria
|
GNROD
|
|

ID general type of bacteria
|
GNROD
|
|
|
What crit tube is used for WBC count blood film?
|
Blue ring with no anticogulant in it in conjuction with LTT
|
|
|
What is the technique for making a blood film?
|
-Use fresh whole EDTA well mixed blood
-Using blue ring crit tube, place small drop on end of clean glass slide -Using coverslip or spreader slide, draw the slide backwards through drop so blood collects along the edge. -With Coverslip or spreader slide at a 30 degree angle, move it along the slide in an even stroke along the slide -wave in air to dry -Make sure there is a good feather, monolayer and body -Stain with Diff Quik, or Wrights |
|
|
What is ID'd on 10x in the feather?
|
-WBC distrubution
-Platelet clumping (too much may invalidate platelet count-REDO film)* -Abnormal cells* -Microfilaria* *items to be quantified |
|
|
What is ID'd on 10x in the Monolayer of the blood film?
|
Is it of Adequate size?
WBC distribution |
|
|
What is ID'd and checked in the body of the blood film?
|
-RBC associations
-Rouleaux-stacked pancakes, chains* -Agglutination-clusters and blank spots of RBC's **Never normal |
|
|
What test is used to differentiate if an RBC association is Rouleaux or agglutination?
|
Saline Wash-
Rouleuaux will wash out, agglutination sticks together like glue |
|
|
What species is Rouleaux a normal finding?
|
horses
|
|
|
Where do we examine the blood film for WBC?
|
Monolyer on 40x
Begin dif and morphology assessment |
|
|
Where and at what objective do we use for RBC & WBC morphology, platelet assessment?
|
Monolayer
100x oil objective |
|
|
What RBC morphology is assessed on 100x?
|
Size,
shapes, color +/- inclusions ALL are quantified as mild, moderate, marked |
|
|
What type of WBC morphology is assessed on 100x?
|
nuclear assessment
cytoplasmic condition ALL are quantified as mild, moderate, marked |
|
|
What is assessed for Platelets on 100x?
|
-Macro or mega size
-Shape -Membrane reactivity (hairy=reactive) -Estimate 10 fields -8-30 pltlts appear adequate -< 8 appear decreased >30 appear increased |
|
|
What is the flow of blood through the heart and body?
|
1. Vena cava-
2. Right atrium 3. Tricuspid valve 4. Right ventricle 5. Pulmonary valve 6. Pulmonary artery 7. Lungs 8. Back to heart via the pulmonary vein 9. Left atrium 10. Bicuspid valve 11. Left ventricle 12. Aortic valve 13. Aorta 14. Organs in the body |
|

ID and what does it cuase?
|
Coccidia are small protozoans (one-celled organisms) that live in the intestinal tracts of dogs and cats. They cause disease most commonly in puppies and kittens less than six months of age, in adult animals whose immune system is suppressed, or in animals who are stressed in other ways (e.g.; change in ownership, other disease present).
In dogs and cats, most coccidia are of the genus called Isospora. Isospora canis and I. ohioensis are the species most often encountered in dogs. Regardless of which species is present, we generally refer to the disease as coccidiosis. As a puppy ages, he tends to develop a natural immunity to the effects of coccidia. |
|
|
What is FIV and what causes it?
|
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
--family Retroviridae, Genus Lentevirus Because biting is the most efficient means of viral transmission, free-roaming, aggressive male cats are the most frequently infected. -Infected cats may appear normal for years. However, infection eventually leads to a state of immune deficiency that hinders the cat's ability to protect itself against other infections. The same bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi that may be found in the everyday environment--where they usually do not affect healthy animals--can cause severe illness in those with weakened immune systems. These secondary infections are responsible for many of the diseases associated with FIV. |
|

ID and what does this cause?
|
Otodectes ear mite
ear mites move about and feed along the cat or dog's ear canal they create substantial irritation and subsequent inflammation. The mites feed on tissue debris and secretions from the ear canal lining. With repeated irritation, the ear canal thickens and debris builds up within the ear canal. This debris, caused by mite waste products, dead tissue and fluid resembles coffee grounds. In chronic (long term) cases of ear mites in cats and dogs, there often is secondary bacterial and yeast infections present that complicate the treatment and create even more stress on the animal. |
|
|
What is the normal gestation of dogs and cats?
|
63 days
|
|
|
What type of sling is used to immobilize a HIND limb AFTER coxofemoral dislocation?
|
Ehmer sling/aka Figure 8 sling
-rotates hip inwards so head of femur will sit in acetabulum |
|
|
What type of splint is used for non-displaced fracture typically to help stabilize it?
|
Schroeder Thomas Splint
-frame made of aluminum, sits on hip, limb suspended after wrapping within frame. |
|
|
What type of sling is used to prevent weight bearing on front limbs such as for shoulder dislocations and injuries?
|
Velpeau sling-holds flexed limb against chest
|
|
|
What is the bandage application procedure?
|
-clean wound
-Apply Telfa pad/non-adherent dressing -Apply tape stirrups if needed- -Apply cotton padding/cast padding -wrap with gauze -Fold stirrups up if used -wrap with vet wrap, elasticon, tape -date bandage with a permanent marker |
|
|
When wrapping a bandage, what direction is it done?
|
Distal to proximal
-helps blood flow back to the heart and prevents swelling |
|
|
If you are wrapping a long bone fracture, what is one important thing that should be done to immobilize it?
|
Wrap above and below the joints proximal and distal to fracture
|
|
|
Why are at least 2 toes left exposed when wrapping a limb?
|
To check for swelling, temp, swelling, bandage tightness
|
|
|
When is a Modified Robert Jones bandage used?
|
-Most common lower limb bandage
-Used for light support to reduce swelling due to Sx and to cover wounds that require protection. |
|
|
What is a Robert Jones bandage?
|
-A short term bandage
-Provides temporary support/stabilization of Fx/dislocations distal to elbow or stifle -Generally used Pre-op --VERY bulky _Animal typically stays in hospital due to size of bandage |
|

ID instrument and its use
|
Periodontal Probe- hand instrument w/indentations spaced in millimeters for measuring the depth of the gingival sulcus around the tooth
Norms: Dogs 1-3 mm, cats 0-1mm |
|

ID this instrument and it use
|
Hand scaler-instrument with a triangular blade that curves and tapers to a point on end.
-Used to remove tartar/calculus SUPRAgingavally |
|

Id this instrument and its use
|
Dental Curette-has 2 sharp sides and a rounded tip
-Used to remove SUBgingival calculus |
|
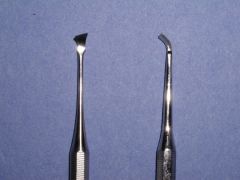
Id this instrument and its use
|
Dental hoe-
Used for removal of large deposits of calculus on the supragingival surface of the tooth |
|

ID this intrument and its uses
|
Dental elevator-spoon like tip with sharp edges on a large handle
-Used to break the periodontal ligaments BEFORE extraction of a tooth. |
|

ID this instrument and its uses
|
Extraction forceps
-used to grip the tooth to lift it out for extraction after periodontal ligaments have been broken down -Can be used to remove very large chunks of tartar |
|
|
Name the 5 lymph nodes sites in a dog
|
Axillary
inguinal, prescapular popliteal submandibular |
|

Lymph node locations
|
image
|
|
|
Define CVT
|
Certified Veterinary Technician
A Certified Veterinary Technician's duties include taking medical histories, treating routine problems, and counseling pet owners. Technical duties involve: * taking blood, urine, skin and other samples * performing lab procedures * administering anaesthesia and other medications * taking x-rays, ultrasounds, and sonographs * Assisting veterinarians in surgery * maintaining and servicing veterinary equipment * keeping treatment records and supply inventories |
|
|
Define enucleation
|
Sx removal of the eyeball
|
|
|
Define idiopathic
|
Disease or condition of unknown origin
|
|
|
Define mydriasis
|
Dilation of the pupils
|
|
|
Define miosis
|
constriction of the pupil
|
|
|
What is the medical term for incision into the bladder?
|
Cystotomy
|
|
|
What is the medical term for heartworm and what is responsible for transmitting?
|
Dirofilaria immitus
mosquito |
|

ID this cath
|
Foley cath- a longer term indwelling cath
|
|

ID this cath
|
Red Rubber cath that can be indwelling.
Also used as O2 NG tube and a feeding tube |
|

Id this cath
|
Steel bitch cath used only on female dogs
|
|
|
What are polypropylene caths used for?
|
A rigid plastic cath for very short term use such as obtaining a urinary sample
|
|
|
Who do cows typically get rabies from?
|
Bats and sometimes skunks
|
|
|
What are the 2 general types of test for parasites?
|
i. Qualitative “find the parasite” more common
1. Simply-does the animal have the parasite at that time ii. Quantitative- “how many does the animal have?” 1. Approximate degree of infestation 2. Never do unless there is a positive qualitative test 3. Seen more often in research |
|
|
What are the 3 sample types for parasite quantitative tests?
|
Fecal
Urine blood |
|
|
What are the 3 QUALITATIVE tests done most often on fecal samples?
|
Gross visual Exam
Direct Smear Concentration or float technique |
|
|
If you are doing a fecal and you see no ova or parasites, what do you write in the record and lab log?
|
NSATT-nothing significant seen at this time
OR- NoPSATT-no parasites seen at this time |
|
|
What is the fecal 3?
|
Direct exam
Float Cytology |
|
|
What are the 3 main purposes in veterinary parasitology?
|
Locate
ID Treat |
|
|
What is the rule about objectives in parasitology?
|
LOCATE on 10x, ID on 40x
Can see tapeworm segments, fleas, ticks, mites on 4x Giardia cysts & trophazoites are located and ID'd on 40x |
|
|
What is looked for on a Gross Visual exam?
|
a. Tapeworms often diagnosed this way
b. Sometimes adult worms are passed this way c. Odor can give hints to –foul smelling may = Giardia or Parvo puppy d. Consistency-may hint towards Giardia or viral bacterial disease e. Mucus may be indicative of colitis i. Whipworms are known to cause excessive mucus in sample |
|
|
A DIRECT SMEAR is always done.
Give the basic procedure of how this is done. |
i. Tiny fleck of well mixed sample
ii. 2-3gtts of PSS iii. Place fleck on slide, add PSS. Take cover slip and with even pressure, skim sample across, Drop slip on sample. iv. Place slide on stage-condenser down, locate on 10x, ID 40x v. ONLY TEST YOU CAN SEE LARVAE ON |
|
|
When doing a a microscopic evaluation in parasitology, where should you condenser be positioned ?and why?
|
DOWN
Too much light will make it difficult or impossible to see the ova, larvae---washes out the sample making diagnosis difficult. |
|
|
What is the specific gravity of flotation solution?
|
1.180-1.200
This leads to heavier material sinking and OVA floating on top & sticking to coverslip. LARVAE will SINK--so will NOT be seen |
|
|
How long do fecal float cover slips typically sit on the meniscus of float?
|
10 minutes, it is then placed on slide for examination.
*Giardia trophozoites usually rupture in these solutions, so will not be seen. |
|
|
IHow much feces is typically used with a fecal float? Why is this an advantage?
|
About the size of a pea, so larger than a direct smear, giving a better chance of seeing something.
|
|
|
What are 3 types of Floatation media?
|
Sodium nitrate/NaNO3-Fecasol, Flomed, Ovassay
Zinc Sulfate/ZnSO4-best type but more expensive Sheather's suger-specific gravity and will float ANY ova |
|
|
Once your fecal float cover slip is placed on a slide, what objectives are used?
|
LOCATE on 10x, ID on 40 x
|
|
|
What can be ID'd on a Fecal float slide?
|
Parasite ova, Coccidia and possibly Giardia with Zinc Sulfate
|
|
|
What are the advantages of using the Centrifugation for floatation/concentration exam?
|
i. More efficiently recovers eggs and cysts
ii. Requires less time iii. Less egg/cyst distortion, less rupture potential iv. Even less fecal debris than all other techniques |
|
|
What type of centrifuge is used for fecals?
|
A swinging head centrifuge
*must be balanced with even number of Test tubes |
|
|
How long are samples for parasitolgy fecals spun for?
|
1200-1500 for 3 minutes
|
|
|
What is the procedure for doing a FECAL CYTOLOGY/FECAL SMEAR?
|
1. Obtain a FLECK of feces
2. Roll sample onto slide-THIN layer, allow to dry or heat fix 3. Stain with Dif-Quik 4. Examine on 100x oil immersion |
|
|
What is the purpose of a fecal cytology?
|
Only method that can be used to ID CLOSTRIDIUM-looks like spores, safety pins, tennis rackets
and CAMPYLOBACTER- looks like seagulls, spirochetes |
|
|
What is is the Dif Quik staining procedure?
|
1. Jar 1-Fixative (bluish-green) Do 5 1 second dips
2. Jar 2-Eosinophilic (Red) Do 5 1 second dips 3. Jar 3-Basophilic (Purplish) 7-10 1 second dips 4. Rinse with sink water and allow to dry |
|
|
What is the procedure for reporting out findings on a fecal cytology/
|
i. Normal to see <5/hpf
ii. Always report out # per hpf iii. Check a minimum of 10 fields and average |
|

ID
|
Giardia cysts and trophozoites
|
|
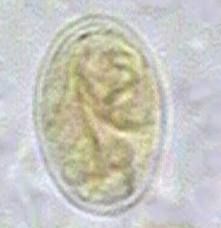
ID
|
Giardia cyst
|
|

ID
|
Giardia trophozoites
|
|

ID
|
Campylobacter bacteria
|
|

ID
|
Campylobacter bacteria
|
|

ID
|
Clostridium perfringes
|
|

What are the major categories of neurotransmitters?
|
Amino acids (NH2) (glutamate, GABA, glycine, aspartate)
Acetylcholine (a mModified amino acid) Monoamines (indoleamines, eg serotonin; catecholamines, eg dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine) Peptides (endorphins, substance P, neuropeptide Y) Purines (ATP, adenosine) Gases (Nitric oxide) |
|

ID
|
Coccidia unsporulated
*can't tell which one it will be till it sporulates |
|

ID
|
Coccidia isospora
|
|

ID
|
Coccidia isospora
|
|

What are the 2 major activities for daily living (ADL) assessment guidelines for the Young Adult
|
(Healthy Lifestyle)
1. Exercise 2. Diet |
|

ID
|
Coccidia eimeria (large animals only)
|
|
|
What is DIC?
|
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
-Secondary to some other disease -Is an excessive activation of clotting factors -Clots flow throughout the microcirculation-->hypoxia--> ischemia-->organ dysfunction-->Clotting factors leads to body reversing and no longer clotting---->Fibrinolysis is activated and excessive FDP's break down clots and keep others from forming---->animal bleeds out......... Rapid process that is VERY difficult to reverse. May give heprin to reverse process early on but low chance of success. |
|
|
Define gingiva
|
periodontal MM covering bone of maxilla and mandible
|
|
|
define gingival sulcus
|
groove formed between neck of tooth and free edge of gingiva.
|
|
|
Where is the neck of the tooth?
|
found at hte gingival margin where crown and root meet
|
|
|
Where is enamel?
|
covers the crown of each tooth, hardest substance in the body.
|
|
|
Where is cementum?
|
substance covering the root of a tooth.
|
|
|
Where is dentin located?
|
a porous bony substance located beneath enamel and cementum of tooth
|
|
|
Where is the pulp cavity located?
|
A canal located in the center of dentin that is filled with soft tissue, blood vessels and nerves.
|
|

Review
|
diagram review
|
|
|
Define Apical delta
|
where blood vessels and nerves enter and exit the tooth
|
|
|
What is the purpose of periodontal ligaments?
|
connective tissue that holds tissue to bone
|
|
|
What is the buccal surface of a tooth?
|
comes in contact with CHEEKS
|
|
|
What is the labial surface of a tooth?
|
Comes in contact with lips (incisors)
|
|
|
What is the lingual surface of a tooth?
|
comes in contact with the tongue (mandibular teeth only)
|
|
|
What is the palatal surface of a tooth?
|
Comes in contact with palate (maxillary teeth only)
|
|
|
What is the mesial surface of a tooth?
|
Side of tooth that comes in contact with mid-line, closest to front of mouth, incisors
|
|
|
What is the distal surface of a tooth?
|
Side of tooth farthest away from mid-line, incisiors
|
|
|
What is the occlusal surface of a tooth?
|
surface of the tooth that comes in contact with opposite tooth on opposite jaw. the BITE surface
|
|
|
In the dog, which tooth is the upper carnassial tooth?
How many roots does it have? |
4th premolar, #108 and 208
3 roots |
|
|
By what age are most permanent teeth in?
|
5-6 months
|
|
|
By what age do most puppies and kittens eyes open?
|
7-14 days
|
|
|
What is the common name for the Trichuris vulpis?
|
Whipworm
|
|
|
What is the common name for the Ancylostoma caninum?
|
Canine hookworm
|
|
|
What is the common name for Toxocara canis?
|
Canine roundworm
|
|
|
What is the common name for Dirofilaria immitus?
|
Heartworm
|
|
|
What is the common name for Dipylidium caninum?
|
Double Poured tapeworm
|
|
|
What is the common name for Paragonimus kellicoti?
|
Lung fluke
|
|
|
What is the family name for the Isospera/Eimeria?
|
Coccidia
|
|
|
What is the common name for the Strongylus vulgaris?
|
Blood worm, Large strongyle
|
|
|
What is the common name for the Oxyuris equi?
|
Pinworm
|
|
|
What is the common name for Fasicola hepatica?
|
Common liver fluke
|
|
|
What is the common name for Rhipicephalus sanguineus?
|
Brown Dog tick
|
|
|
What is the common name for Cutebra?
|
Rabbit bot
|
|
|
Pregnant women should stay away from cleaning litterboxes due to possible transmission of which parasite?
|
Toxoplasmosis gondi
|
|
|
VLM in people is caused by which parasite?
|
Roundworms
|
|
|
CLM in people is caused which parasite?
|
Hookworms
|
|
|
What is the genus and species of the most common cause of ringworm in dogs and cats?
|
Microsporum canis, a mold
|
|
|
What lab animals require supplementary vitamin C?
|
Guinea pigs and NH primates
|
|
|
What are the common names for the 3 most distal joints in the equine front leg from distal to proximal?
|
Coffin joint
Pastern joint Fetlock joint |
|
|
Give the common name for the distal phalynx in a horse.
|
Coffin bones
|
|
|
In a dog and cat, what bones are immediately distal to the carpus?
|
Metacarpals
|
|
|
For a small animal bandage, list the order of bandaging material for a basic bandage.
|
Primary layer dressing-Telfa pad
Cotton and or Cast padding Kling or conforming gauze Vet wrap/Elastikon |
|
|
What type of fractures is a Robert jones bandage used for?
|
To stabilize fractures distal to elbow or stifle
|
|
|
What is an Ehmer sling used for?
|
To immobilize the hindlimb following a reduction of a luxated hip
|
|
|
What is responsible for causing walking dandruff?
|
Cheyletiellosis, a surface mite
|
|
|
What is the common name for the yeast that causes otitis in dogs?
|
Malassezia
|
|
|
What is the name of the tick that is a vector for Lyme disease?
|
Ixodes tick
|
|
|
Demodex is a burrowing mite that is diagnosed with what type of procedure?
|
Deep skin scraping
|
|
|
ELISA heartworm tests detect what types of antigens?
|
Adult female heartworm
|
|
|
What is the genus name of the common ear mite?
|
Otodectes
|
|
|
FelV and FIV are in what virus family?
|
Retroviradae
|
|
|
What family is FIP virus in?
|
Cornaviridae
|
|
|
What family is the Panleukopenia virus in?
|
Parvoviridae
|
|
|
Define tachycardia
|
abnormally rapid heartbeat
|
|
|
Define dyspnea
|
labored or difficulty with breathing
|
|
|
define hyperkalemia
|
Abnormally high potassium concentration in the blood
|
|
|
Define hyponatremia
|
deficiency of sodium in the blood
|
|
|
Define sublingual
|
beneath the tongue
|
|
|
Define anastamosis
|
surgical procedure to connect 2 previously unconnected tubular organs or parts of the same organ
|
|
|
Define intussusception
|
Prolapse of one part of the intestine into the lumen of the immediately adjacent part, causing intestinal obstruction
|
|
|
Define entropion
|
inversion, turning inward, of margin of the eyelid
|
|
|
What is Strangles caused by?
|
Streptococcus equi
|
|
|
What causes Circling Disease?
|
Listeria monocytogenes
|
|
|
What causes Lyme disease?
|
a spirochete-Borrelia burgdorferi
Transmitted by Ixodes tick |
|
|
What causes Tropical Canine Pancytopenia?
|
Erlichia canis,
Transmitted by Brown dog tick |
|
|
What causes tuberculosis?
|
Mycobacterium spp
|
|
|
What causes Cat Scratch Disease?
|
Bartonella henselae
|
|
|
What causes Rocky Mountain Spotted /Tick fever?
|
Rickettsia ricketsii
|
|
|
What are 3 Flatworm Flukes we studied?
|
Fascicola hepatica
Paragonimus kellicotti Nanophtes salmincola |
|
|
What are the Genus of tapeworms we studied?
|
Dipylidium caninum
Taenia spp. Echinococcus spp (causes Hydatid cysts!) Ancoplocephala spp (horses) Monezia spp (cows) |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Tapeworms?
|
All L1 infective except Taenia pisiformis
-Indirect life cycle -Monecious -Have hexacanth embryos within ova -Segment is a proglottid -A strobila is a chain of reproductive units |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Roundworms/Ascarids?
|
-Direct life cycle
-Dioecious -Migration needed to complete life cycle -Tracheal, Somatic, Muccosal |
|
|
What are the roundworms/Ascarids with a Ropey OUTER shell with a large dark nucleus?
|
Toxocara spp
|
|
|
Which are the roundworms with SMOOTH Ropey INNER shell and a lighter smaller nucleus?
|
Toxascaris leonina
|
|
|
What are some basic facts about Hookworms?
|
-BLOOD FEEDERS!
-Reported as hookworms in small animals, TASE in large animals |
|
|
What are the basic groups of hookworms discussed in parasitology?
|
Ancylostoma spp
Uncinaria stephala Bonostomun spp. |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Lungworms and what are some groups?
|
-Type of roundworm
-Aleurostrongylus abstrusus (cat) -Dictyocaulus spp (cattle) Metastrongylus apri (swine) Eucolus (Capillaria) aerophila |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Ruminant TASE?
|
-Reproductively aggressive
-Premunition is the buildup of resistance -L4 is the hypobiotic stage-arrested development until time (season) is right to continue |
|
|
What are the parasites that make up the HOCT complex of Ruminent TASE?
|
Haemonchus contortus
Ostertagia spp(imp parasite in young cattle) Cooperia spp ( Cattel Bankrupt worm) Trichostrongylus spp and Nemotodirus spp, which is not a TASE |
|
|
Which is more pathogenic, large or small strongyles?
|
LARGE
|
|
|
What is a facultative parasite?
|
When only the female is pathogenic
|
|
|
What are 2 types of equine TASE?
|
Strongyloide westeri -small
Strongyloide vulgaris - large |
|
|
What is the Genus & species of the Esophageal worm?
|
Spirocerca lupi
|
|
|
What is the Genus and species of the Giant kidney worm?
|
Dioctophyma renale
|
|
|
What is the genus and species of the Bladderworm?
|
Pearsonema (capillaria) plica and cati
|
|
|
What is the genus of the whipworm?
|
Trichuris spp.
-double operculated ova |
|
|
What is the genus and species for the parasite that causes Heartworm and what is it's IH?
|
Dirofilaria immitis
Mosquito |
|
|
What are the Burrowing mites?
|
-Recovered w/a deep skin scraping for diagnostics
-Demodex spp Demodectic mange Follicular Mange -Sarcoptes Scabei (Mange) -Notoentendres cati (Feline scabies) -Knemokoptes spp. (mange) |
|
|
What are 2 types of Surface mites?
|
-Recovered with a light skin scraping and a scotch tape prep is used
-Otodectes cynotis (Ear mite) -Cheyletiella spp -walking dandruff, have palpebral claws |
|
|
What are the 2 types of Gram positive cocci?
|
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus -Catalase test used to differentiate Bubbles-positive test, indicates Staph |
|
|
What test is used to differentiate between Pathogenic and non-pathogenic Staph?
|
Coagulase test-clot is positive result which means it is Pathogenic
|
|
|
Name some SMALL Gram positive rods
|
Remember CLEAR!!
-Corneybacterium -Listeria -Erysipelothrix -Arcanobacterium -Rhodococcus -More important in large animals |
|
|
Name some Large Gram positive rods
|
Bacillus
-aerobic, endospores, produce exotoxins -Clostridium -ANAEROBIC, endospores, exotoxins |
|
|
What are some branching Gram positive Rods?
|
* these are a higher evolutionary form of bacteria that are fungi like and show filamentation and branching
-Actinomyces -Nocardia -Streptpmyces -Dermatophilus |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Corneybacterium?
|
-Club shaped rods
Cause: C. pseudotuberculosis -CLA Caseous lymphadenitis (sheep & goats) -Ulcerative lymphangitis (horses and mules) AKA-Pigeon fever C. renale -has pili -causes bovine peyelonephritis, cystitis -Sheep-causes "pizzle rot" (balanothitis, vulvulitis) - |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Listeria monocytogenes?
|
-Motile bacteria
-Ubiquitous-found everywhere ( water, feces, soil, silage, milk) -Common cause of food poisoning due to the fact that it replicates at fridge temps. 2 forms- Visceral-monogastric causes abscesses on internal organs NEURAL-Causes CIRCLING DISEASE in ruminants, esp cattle and sheep. -affects CNS, meningitis, Unilateral ataxia |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae?
|
-Pathogenic for pigs, birds (turkeys), fish, marine mammals, people
-NF in mouth and throat of swine, fish slime -Swine form Causes: -Diamond Skin disease -Arthritic Form in older pigs, -Acute-causes septicemia, -Cardiac Form -Causes Fish Handlers disease in people who handle fish |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Arcanobacterium pyogenes?
|
-Affects ruminants via a wound
-Causes pyogenic infections of wounds, Sx incisions as well as mastitis, Pneumonia, Umbilical infections |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Rhodococcus equi?
|
-Causes a suppurative Bronchopneumonia in foals btwn 1-6 months, will have dyspnea, crackles
|
|
|
What does a positive result on a H2S production test look like?
|
Agar will have black pigment
|
|
|
What does a positive motility test look like?
|
Agar will be cloudy throughout media
|
|
|
What are some basic facts about Bacillus?
|
-Aerobic, form chains and endospores, excrete exotoxins
|
|
|
What are some basic facts about Bacillus anthrasis?
|
-Large GPROD
-Causes ANTHRAX -Obiligate pathogen of people and animals-Usually fatal if inhaled -Can be inhaled or penetrate skin 3 forms: Cutaneous-spores enter a wound (Woolsorters disease in people) Pulmonary-inhalation of spores, most deadly-fatal w/in 24 hours GI-ingestion of spores. Most common form in dogs and cats -Reportable to the state |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Clostridium?
|
-ANAEROBIC, endospores, excrete exotoxins
Species: -botulinum -tetani -perfringes -septicum -chauvoei -novyi -haemolyticum |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Clostridium botulinum?
|
-Causes botulism
-Acquired via ingestion of pre-formed exotoxin in a food source -Exotoxin is a neurotoxin-one of the most potent biological toxins -this endotoxin acts on the neuromuscular junction to prevent the release of acetylcholine which results in weakness and paralysis -Causes weakness in hind legs at first and progresses crainally, eventually paralyzing diaphragm leading to respiratory arrest |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Clostridium tetani?
|
Large GPROD, anerobic, exotoxin, endospore that resides in the soil
-Causes Tetanus/Lockjaw --Humans and horses most susceptible -Carnivores least susceptible -Acquired by spore from enviro entering a deep puncture wound, it grows in the anerobic enviro and releases exotoxin -Exotoxin is a neurotoxin that acts on CNS and blocks the function of inhibitory neurons, which results in inhibitory neurons not being able to tell muscles to release contraction |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Clostridium perfringes?
|
-Causes Clostridial enterotoxemia in people, dogs, cats & large animals
-common cause of food poisoning in people -Can cause would infection, gas gangrene -Acquired by ingesting spores -Causes: -Hemorrhagic enteritis-diarrhea w/blood and mucus -Systemic toxemia in large animals -Diagnosed via fecal cytology- will see bacteria that look like SAFETY PINS |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Clostridium septicum?
|
-Histotoxic
-Causes Malignant edema (anaerobic myocytis) that causes muscle inflammation -affects large animals -Exotoxin causes tissue necrosis, edema, gas gangrene, systemic toxemia **HIGHLY FATAL |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Clostridium chauvoei?
|
-Causes Black Leg Disease in large animals via spores being ingested or entering a wound
-Causes swelling, edema, gas gangrene, DISCOLORED skin, systemic toxemia |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Clostridium novyi?
|
-Causes Black Disease/Infectious Necrotic hepatitis
-Acquired via ingestion of spores and worse w/pre-existing liver damage -Exotoxin causes liver necrosis |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Clostridium haemolyticum?
|
-Causes Red Water Disease or bacilliary hemoglobinuria in large animals
-Acquired via ingestion of spores which grow in damaged liver |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Branching GPRODS?
|
-Less common cause of disease
-Four genuses: Actinomyces Nocardia Dermatophilus Streptomyces |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Actinomyces?
|
-Anaerobic to microaerophilic depending on species
-NF in GI tract & oral cavity of many animals including humans -Invade previously damaged tissue or penetrate a body cavity -Highly diagnostic-clumps or masses of branching bacteria -Will have Sulfur granules that will need to be squashed & stained--then you will see the branching filamentous G+ rods |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Actinomyces bovis?
|
-NF in oral cavity of cows
-Causes Lumpy Jaw in cattle |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Actinomyces viscosus?
|
*Important cause of periodontal disease in people
-Causes Actinomycosis -Acquired via spores entering wounds in oral cavity, penetration of body cavity |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Nocardia asteroides?
|
AEROBIC branching GPROD, less common
-Causes Nocordiosis -Will seen in wounds such as fistulas and draining tracts -Causes pyothorax -Can cause Mastitis -Desseminated form spreads to internal organs |
|
|
What color do Gram negative bacteria stain and what kind of toxins are they associated with?
|
Pink
ENDOtoxins |
|
|
What are the 2 types of Gram Negative Rods?
What test is done to differentiate between the 2? |
Enteric and Non-enteric
Oxidase test- A purple/dark spot on filter paper means it is a NONenteric |
|
|
Name the Enteric Gram negative Rods
|
-Escherichia coli
-Klebsiella (slimy, snotty colonies) -Proteus -Serratia -Shigella -Yesenia (pestis causes PLAGUE!) -Enterobacter -Citrobacter |
|
|
Name the NON-enteric Gram Negative Rods
|
(the -ellas, -monas and a -bacter)
-Brucella -Pasturella -Francisella -Pseudomonas -Bordetella -Moraxella -Campylobacter |
|
|
What are 2 spirochetes we discussed in microbiology?
|
Leptospira
Borrelia burgdorferi-causes Lyme disease via vector-Ixodes tick (reservoir is White footed mouse) |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Escherichia coli?
|
-aka---E. Coli
-Most encountered bacteria in microlab -NF in small intestine and Colon -MANY different strains and serotypes -2 Catagories Opportunistic-NF but will cause infections if the get into an area that is supposed to be sterile (bladder, uterus, wounds) Enteropathogenic-have pili, cause Gastroenteritis in newborns. |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Enteropathogenic E. Coli?
|
Pathogenic in 2 ways:
-Invasive-invade tissues Penetrate intestinal mucosa, causing lesions, enteritis leading to septicemia, endotoxemia Enterotoxin-releases exotoxin into intestines which binds with and disrupts cell membranes of intestines resulting in those cells losing water, electrolytes, bicarb. -death due to dehydration and metabolic acidosis |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Klebsiella pneumoniae?
|
-Encapsulated bacteria, with a characteristic colony morphology that involves mucoid, slimey, stringy colonies--will "string off of plate"
Causes: Cervicitis and metritis in mares Pneumonia in foals Mastitis in cattle |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris?
|
-highly motile, swarms on blood agar
-Swarming colony morphology -Smells like ammonia -Causes a variety of infections UTI, Otitis,Wounds infec., Mastitis |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Salmonella?
|
-Many species and serotypes
-Fecal-oral route of transmission -Causes Salmonellosis from contaminated food or water. 2 forms: Gastroenteritis-most common, bacteria invade intestinal mucosa and cause diarrhea, fever Septicemia-enters bloodstream of immunocompromised animals |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Yersinia pestis?
|
-Causes plague, which occurs in western 1/3 of US.
-Reservoir host-Rodents, Prairie dogs are sentinels -Humans and Cats are most susceptible -Vector is the flea 3 forms: -Bubonic -most common, enlarged LN's, fever, lethargy -Septicemic -Pneumonic |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Shigella?
|
-Similar to Salmonella
-Causes Shigellosis-hemorrhagic watery diarrhea Pathogenic for primates, rare in dogs & cats |
|
|
What are some basic facts about ID'ing Enteric GNRODs?
|
Gram stain -PINK
Oxidase negative-no color on filter paper Grow on MacConkey's Agar -Lactose fermentors will have PINK growth -NON-lactose fermentors will have Colorless growth |
|
|
What do Fusobacterium and Bacteriodes cause?
|
-Foot rot in large animals
-Fuso-causes thrush in horses 9stinky necrotic tissue) |
|
|
Broad spectrum antibiotics are effective against?
|
Gram positive and some Gram negative bacteria
|
|
|
Narrow spectrum antibiotics are effective against?
|
Either Gram negative or Gram positive bacteria, depending on the type. Will only work on one type
|
|
|
Define bacteriocidal
|
Antibiotic that KILLS bacteria
|
|
|
Define Bacteriostatic
|
Antibiotic that inhibits replication of bacteria and then relies on host's immune system to clear up remaining bacteria
|
|
|
What are antibiotics 5 Mechanisms of action (MOA)?
|
-Inhibit cell wall synthesis (cidal)
-penicillin -Alter cell membrane permeability (cidal) -polymixins -Inhibit protein synthesis (static) -tetracyclins -Inhibit nucleic acids metronidazole/Flagyl -Interfere with a metabolic pathway (static or cidal) -sulfonimides |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Brucella?
|
-Small non-enteric GNROD
-Aerobic to microaerophilic -Some species can remain viaible in urine, milk, damp soil, aborted fetus for as long as 4 months --Intracellular bacteria that survives and multiplies within phagocytes -Invades tissues of Reproductive tract |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Brucella canis?
|
-infects dogs, reportable to state
Causes: -Abortion at about 45-55 days -epididymitis/orchitis/protatitis -testicular atrophy, scrotal dermatitis -infertility and conception failures Diagnosed w/serology Breeding dogs should be tested yearly -Very difficult to Tx and euthanasia is recommended |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Brucella abortus?
|
-Infects cattle and related animals
-Called BANGS disease -Causes -undulant fever in humans -Abortion storms in last trimester -mastitis -testicular abnormalities/orchitis -Infertility, conception failures -Transmission via : ingestion of aborted fetus/placenta, urine on grass, milk -breeding and AI |
|
|
How is Brucellosis controlled in cattle?
|
-Immunization of female calves at 4-12 months-ID'd by tattoo in right ear and an orange ear tag
-Serology tests-prior to breeding, shipping, sales. Dairy cows tested annually |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Brucella suis?
|
-infects swine via ingestion or breeding
|
|
|
What are some basic facts about Brucella ovis?
|
-infects sheep, rams more than ewes
-Causes orchitis, epididymitis, infertility -Males are tested and immunized |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Brucella melintensis?
|
-infects cattle, sheep, goats, camels, llamas
|
|
|
What are some basic facts about Bordetella bronchseptica?
|
-Causes KENNEL COUGH/Infectious tracheobronchitis in dogs
and atrophic rhinitis in piglets -Have pili that make them resistant to MCTS -Infection via inhalation -Destroys ciliated epithelium -Classic symptom is a DRY hacking non-productive cough |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Pasteurella?
|
Non-enteric GNROD
-Antibiotic resistant _NF in oral cavity & respiratory tract in many species, esp cats |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Pasteurella haemolytica?
|
-Now known as Mannheimia haemolytica
-Reservoir is NF of nasopharynx in Cattle Called: Shipping Fever causing bronchopneumonia Can affect all cows but calves more susceptible -3 predisposing factors -Presence of Pasteurella/Mannhemia bacteria -Presence of additional virus such as IBR, BVD, -Stress ( such as shipping) Tx-antibiotics Can vaccinate for respiratory viruses |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Pasteurella multocida?
|
-NF in oropharynx of many species
-Causes: Snuffles in Rabbits Avian cholera in birds BITE WOUND ABSCESSES URI, Otitis Septicemia, meningitis in humans from bite wounds (found in 75% of bite wounds...) |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Moraxella bovis?
|
Non-enteric Gram negative coccobaccilus (tiny!)
-NF on conjunctiva & nasopharynx of cattle Disease is called IBK-Infectious Bovine Keratoconjuctivitis (cattle Pink Eye) Solar radiation predisposes white faced cattle to higher rate of infection -flies are a mechanical vector dry dusty conditions can cause outbreaks causes conjuntivitis,corneal edema, mucopurulent ocular discharge -Zoonotic |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Francisella tularensis?
|
-Non-enteric GNROD
Reservoir-rabbits, rodents Disease is called Tularemia/Rabbit fever and can affect humans, dogs, cats -Transmitted via tick vectors, ingestion of rabbit meat and inhalation of aerosolized blood -Pathology similar to bubonic plague-enlarged lymph nodes, high fever, fatigue, anorexia |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
|
-Ubiquitous in unsanitary, moist enviro.'s
-Large cause of nosocomial infections -colony morphology-flat, greenish/grayish irregular shape with a characteristic sweet fruity or corn tortilla smell -Pus from this will have blue-green/yellow-green color in it -Opportunistic Causes: HORSES-Abortions, repro problems CATTLE-mastitis, abortions DOGS & CATS-Dermatitis, cystitis, otitis ALL-wound infections, Sx incision infection, burn infections |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Campylobacter?
|
-GN slightly curved rods-look like flying gulls
- May stay stained together and look like spirochetes -Very motile -Microaerophilic to aerophilic |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Campylobacter fetus?
|
-Affects cattle and sheep
-Called Vibrosis -Pathology-abortions, infertility -Acquired via breeding & AI -Diagnosis: Screen males via preputial wash sent off to lab. Positives are culled |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Campylobacter jejuni/coli?
|
-Called Wet Tail in hamsters
-Causes Winter Dysentery in cattle and sheep -Can cause enteritis, diarrhea in amny animals and humans -Acquired via ingestion |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Leptospira?
|
-Causes Leptospirosis in animals and people
-ZOONOTIC -Many strain and serovars -spirochete bacteria |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Leptospira interrogans?
|
-Most common cause of lepto in animals
-increased incidence during years of flooding and animals exposed to wildlife -4 of the 8 most common servars can be immunized for -L. canicola -L. icterohaemorrhagiae -L. pomona -L. grippotyphosa -survives in reservoir hosts(rodents, raccoons, skunks) -shed in urine -Causes renal and hepatic damage Causes Moon blindness in horses and abortions and infertility in cattle |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Borrelia burgdorferi?
|
Causes Lyme disease
-Endemic on East coast, mid west and Western seaboard -Reservoir host is the white footed mouse -vector is the Ixodes deer tick -Progressive disease that causes: Intermittent shifting lameness, ADR, mild fever, depression, lameness, reduced appetite, stiffenss, reluctant to move. Progresses to arthrisitis, neuro signs such as head tilt, confusion, seizures, cardiac issues |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Mycobacterium?
|
-Rod shaped bacteria
-causes Tuberculosis -Don't gram stain well -survive phagocytosis -resistant to disinfectants, heat, pH changes, humoral defnese mechanisms (B-lmph mediated...) -Cell mediated hypersensitivity reaction causes body to attempt to wall off bacteria and form Granulomas/ tuberculosis lesions in lungs -Antibiotic resistant 2 types: -Inhalation=Pulomonary TB -Ingestion=alimentary TB -Can cross species lines -inversely zoonotic |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Mycobacterium paratuberculosis?
|
-Called Johne's Disease (Yo-knees)
-Affects Cattle, sheep, goats -Contagious, chronic and usually fatal intestinal infection of ruminents -Causes chronic enteritis, severe diarrhea, weight loss, wasting away -Most animals infected in 1st year of life -Can survive in enviro for close to a year, long incubation period |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Chlamydophila?
|
-Obligate intracellular organism that requires a living host cell to survive (like a virus)
-Infects cats, birds, humans and a few other species |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Ricketsial organisms?
|
-Obligate intracellular organisms
-Vector important for Transmission -Cause RMSF/Tick fever in dogs -causes severe vascular damage due to damaging endothilial cells lining blood vessels, fever, hemorrhage due to thrombocytopenia |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Erlichia canis?
|
Canine ehlichiosis/Tropical canine pancytopenia
-tick is vector -Lives in canine WBC -Fever, depression, anorexia, weight loss, ocular and nasal discharge, Bone marrow suppression |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Erlichia risticii?
|
-New name Neorickettsia risticii
Causes POTOMAC horse fever -Flies are most common vector -Causes mild colic, fever, depression, anorexia, diarrhea |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Anaplasma marginale?
|
Causes Anaplasmosis in ruminents
-Vector is ticks and other blood sucking insects -lives on RBC's and causes them to lyse |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Bartonella henselae?
|
-Causes CAT SCRATCH DISEASE in people-a self limiting mild disease
-Many cats, esp kittens, carry but show no signs -Vector is fleas from cat to cat |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Mycoplasmas?
|
-Smallest free living cells known to exist
-lack cell wall -Stain gram negative fragile -resistant to cell wall inhibiting antibiotics like penicillin -Commonly causes pneumonia as well as mastitis, arthritis -Diagnosed with Candle jar |
|
|
What are 4 common bacteria known to cause mastitis?
|
Staph. aureus
Staph agalactia E. coli Mycoplasma bovis |
|
|
How is Malassezia diagnosed?
|
A yeast that is a leading cause of otitis
-Swab ear, roll on slide, heat fix, stain with Wrights stain -Look for peanut men |
|
|
What are some basic facts about yeasts?
|
-Unicellular
-Spherical to oval -larger than bacteria -form colonies like bacteria -reproduce by budding -Gram stain + -Facultative anerobes Diagnosis: Ear cytology swab, scotch tape prep on skin, India ink prep for Cryptococcus |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Candida albicans?
|
-Causes Sour crop in birds, an infection of mouth, esophagus and crop
Causes oral thrush in people, vaginitis |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Crytococcus neoformans?
|
-Produces a large gelatinous capsule making diagnosis easier
-Pigeons are carriers -opportunistic infection acquired via inhalation. -Cats- URI -Dogs cryptococcal meningitis-CNS signs, seizures, ataxia, blindness -Diagnosed w/India ink prep-capsule will look like a halo around yeast |
|
|
What are some basic facts about Dimorphic fungi?
|
-Are molds in soil/room temp and become yeasts once they enter tissue/body temp
-cause respiratory infections when mold spores are inhaled-may become systemic depending on immune status of host 4 Types: Blastomyces-spread systemically from resp. system to lymph nodes, skin, eyes, testicles Histoplasma-spreads systemically within macrophages and monocytes to lymph nodes, spleen, liver and GI tract in dogs(diarrhea common) Cocciodioides-spreads to bones, joint and CNS (seizures common) Spriothix-Rose pickers disease, infection establishes in skin causing SQ lesions -Diagnosed with Rads, cytology, biopsies, serology |
|
|
What is the Kirby-Bauer Susceptibility test?
|
Test used to test certain bacteria's resistance to certain types of antibiotics
-area around disk is measured in mm. -Resistant: no clearing -Intermediate-May or may not work - Susceptible-clearing around disk-drug should work |

