![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which leads should you find a P-wave
1. Upright 2. Inverted 3. Variable |
1. 1,2,V4-6, and AVF,
2. AVR, 3. 3, AVL and other chest leads often diphasic (partly above and partly below) |
|
|
What are the main visual findings you check for when examining the P-wave?
|
A DIP N 2 I's
1. Absent P-wave, 2. Diphascity, 3. Inversion, 4. Peaking, 5. Notching, 6. Increased Amplitude, 7. Increased Width |
|
|
What pathology might you expect if you see an inverted P-wave?
|
Could indicate…
1. Ectopic atrial or A-V junctional rhythm due to unorthodox path of impulse through atria |
|
|
What pathology might you expect if you see an increased amplitude in the P-wave?
|
atrial hypertrophy or dilation found in
1. AV valve disease, 2. Hypertention, 3. cor pulmonale, 4. congenital heart disease |
|
|
What pathology might you expect if you see and increased width in the P-wave?
|
LAE (left atrial enlargement), normally doesn’t exceed .11 secs
|
|
|
What pathology might you expect if you see a diphasic P-wave?
Which lead would you see it?? |
LAE when you see second half of P-wave significantly negative in lead 3 or V1
|
|
|
What pathology might you expect if you see notching on the P-wave?
|
1. LAE- you will see differences in lead 1 (notched taller and wider) compared to 3
2. P-mitrale significant if distance exceeds .04 sec |
|
|
What pathology might you expect if you see a peaking P-wave?
|
(P-pulmonale) Atrial overload, shows tall pointed P-waves, shows higher in lead 3 than 1
|
|
|
What are the 7 features needed for inspection of the QRS complex?
|
1. Duration,
2. Amplitude or voltage, 3. Presence of Q-waves, 4. Axis, 5. Transition Zone, 6. Intrinsicoid deflection, 7. Slurring or notching |
|
|
What is the duration of a normal QRS complex and what does it usually mean if it is longer than normal?
|
usually .05-.1 sec if .12 or greater (BBB or VH) due to problem intraventricular conduction
|
|
|
What is normal amplitude or voltage of QRS complex? What might be pathology indicated if less in three standard leads?
|
5mm or less problem which may be due to many various pathologies
|
|
|
What is the minimum amplitude values for QRS complex in V1-V6?
|
V1,V6- 5 mm, V2,V5- 7 mm, V3,V4- 9mm
|
|
|
What should be observed with the ST segment? Include normal ranges…
|
1. Level relative to baseline (elevated (1mm in standard leads and 2mm in chest leads is max) or depressed (.5 or less unless black),
2. Shape |
|
|
What pathology might you expect with depression in Precordial Leads and what might you expect with ST elevation?
|
Depression- subendocardial issue, Elevation: subepicardial injury or ischemia
|
|
|
What is the normal height of T-wave standard and precordial? If you see an unusually tall T-wave what might this suggest?
|
Height- standard <5mm and precordial <10mm MI or hyperkalemia
|
|
|
Which leads should you find a T-wave 1. upright, 2. Inverted, 3. Variable
|
1. 1,2, V3-V6,
2. AVR, 3. 3, AVL,AVF, V1 and V2 |
|
|
What finding on the EKG would you find for LVH (specifically on the QRS complex)?
|
deeper S waves over RV and taller R waves over LV, but doesn’t distinguish concentric hypertrophy and dilated chamber
|
|
|
Describe the five criteria and pointage for the Ronhilt-Este's Scoring system for LVH…
|
If total is 5 or more LVH and 4pts likely LVH
1. 3 points for any one of the following... -R or S on limb 20mm or more, -S in V1, 2, or 3, 25mm or more, -R in V5,6 30mm or more 2. - Any ST shift (w/o digitalis) 3 points - Typical strain ST-T w/digitalis (1pt), 3. LAD- 30percent or more (2pt), 4. QRS interval .09 sec or more (1 pt), 5. I.D. in V5-6 .04 or more (1 pt), 6. P-terminal force in V1 more tan .04 sec in duration (3 pt)... |
|
|
What are main causes of Right ventricular hypertrophy?
|
Chronic lung disease tetralogy of fallot (congenital), mitral stenosis, tricuspid regurgitation
|
|
|
What are typical findings in RVH on ECG?
|
R:S ratio > 1 in V1,
S:R ratio > 1 in V6 ST-T strain pattern in II,III, AVF R in V1 and V6 10mm or more R-waves assume prominence in R-precordial leads and deep S waves develop in left precordial leads |
|
|
What are causes and pneumonic for Dominant R-wave causes?
|
NPH does not like WoRMs…
1. Normal variant, 2. Posterior or lateral MI, 3. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, 4. WPW (wolf-parkinson-white syndrome), 5. RVH, 6. Muscular dystrophy |
|
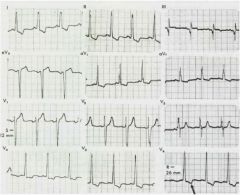
What is wrong with this ECG and what pathology might you expect?
|
LVH
Notice: S wave of V1, 2, 3, >25mm R of V4-6 >30mm See ST-T strain V6 |
|
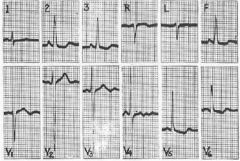
What can you possibly diagnose from this ECG and why?
|
LVH and strain
R V4-6 > 30mm S V1-3 > 25 ST-T changes in 2,3 AVF and V5-6 |
|
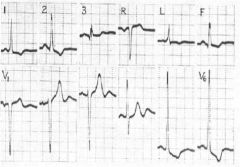
What do you see from this ecg and what might it indicate?
|
LVH
Elevated R in V5-6 Elevated S in V1-3 see Axis is about 40 degree (typical for LAD) |
|
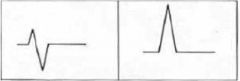
QRS complex left is Lead I and right is V1 what might you think?
|
RVE
V1 shows R:S > 1 |
|
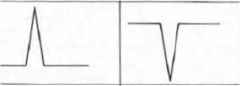
QRS complex left is Lead I and right is V1 what might you think?
|
LVE-
V1 shows very prominent S wave Lead 1 shows very prominent R wave |
|
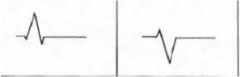
QRS complex left is Lead I and right is V1 what might you think?
|
Normal see q,r,s in I
VI se |
|
What pathology would you expect from this ekg?
|
LVH due to S very prominent in V1-3, ST shift seen, R wave in lead 1 very high
|
|
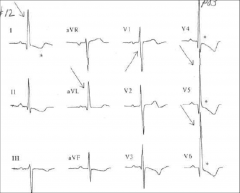
What pathology is this and why?
|
RVH from R-waves but could be RAH
See from looking at Lead I and AVF the 145(+) deviation V1 shows R-wave > 10mm P- wave high on V1 |
|
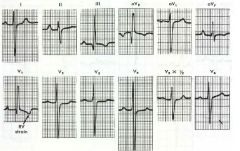
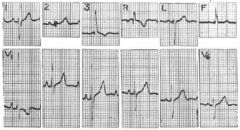
What pathology or normalities do you see in the EKG?
|
1. V1 r-wave > 10mm, R:S >1
2. V6 S:R > 1, S-wave > 10mm II,III,AVF- ST-T strain |
|
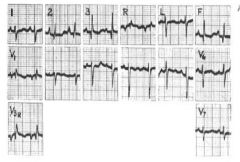
What pathology or normalities do you see in the EKG?
|
note RAD= +130
V1- R:S >1 V6- S:R >1 |
|
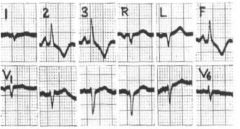
What might we assume this one is?
|
RAD for sure
ST-T patter of Right ventricular strain seen in 2,3,aVF P-wave in 2,3, and aVF suggest p-pumonale |
|

Both show p-waves left is lead II and right is VI... What is pathology?
|
normal
|
|

Both show p-waves left is lead II and right is VI... What is pathology?
|
RAE
|
|
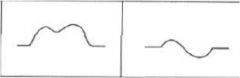
Both show p-waves left is lead II and right is VI... What is pathology?
|
LAE
|
|
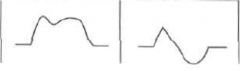
Both show p-waves left is lead II and right is VI... What is pathology?
|
both RAE and LAE
|
|
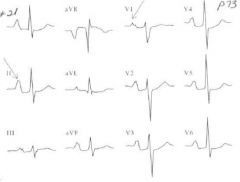
What might you expect...
|
Something wrong with the tricuspid valve, see II and M from VI
|
|
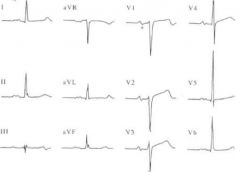
What does this show and how do you know?
|
LAE
Lead II- p-wave is M and VI shows two rounded humps |
|
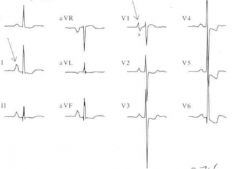
What do you think we are looking at here?
|
RAE due to II Pwave amplitude
or LVH due to VR deep S waves V1,2,3 show huge S V5,6, show huge R |
|
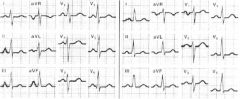
What are the two here?
|
Left is RAE
Right is LAE |

