![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Once they are convicted, offenders are sentenced and moved to the final stage of the criminal process, called _____. |
Corrections |
A. Corrections B. Jail C. Prison D. Sentencing |
|
|
Most convicted offenders are serving their sentences in |
Community |
A. Jail B. Prison C. Community D. None of the above |
|
|
_____ is a substitute for confinement in prison or jail. |
Probation |
A. Probation B. Parole C. None of the above D. All of the above |
|
|
_____ follows confinement in prison. |
Parole |
A. Probation B. Parole C. None of the above D. All of the above |
|
|
Local judges decide whether and under what conditions to put offenders on _____. |
Probation |
A. Probation B. Parole C. None of the above D. All of the above |
|
|
State boards decide whether and under what conditions to release prisoners on _____. |
Parole |
A. Probation B. Parole C. None of the above D. All of the above |
|
|
The penologist Zebulon Brockway introduced _____ to the United States when he became superintendent of the famous Elmira Reformatory in New York. |
Parole |
A. Probation B. Parole C. None of the above D. All of the above |
|
|
Employment is a primary risk factor in that low levels of vocational achievement highly correlated with _____. |
Recidivism |
A. Recidivism B. Drugs use C. Prison time D. None of the above |
|
|
_____ sentences more people to prison and keeps them longer than any other other major country in the world. |
United States |
A. Russia B. Germany C. United States D. England E. None of the above |
|
|
This is a county or municipal facility for either keeping adults while they said for trial or for punishing them for less than a year after they have been convicted. |
Jail |
A. Prison B. Jail C. Penitentiary D. Correctional institution |
|
|
Your textbook defines this as a place of confinement to remove offenders from a corrupting environment and make them work, isolating them in cells. |
Penitentiary |
A. Prison B. Jail C. Penitentiary D. Correctional institution |
|
|
Your textbook defines this a place of confinement to reform offenders into law-abiding people who worked to support themselves through a coherent, scientifically sound program. |
Correctional institution |
A. Prison B. Jail C. Penitentiary D. Correctional institution |
|
|
This is "repeat offending" |
Recidivism |
A. Recidivism B. Drug use C. Prison time D. None of the above |
|
|
In 1785, _____ became the first state to use prisons to punish convicted offenders. |
Massachusetts |
A. New Jersey B. Pennsylvania C. New York D. Massachusetts E. None of the above |
|
|
The _____ reformers attacked penitentiary as cruel, barbaric, just as the creators of the penitentiary had attacked capital, corporal, and mutilation punishments as cruel and barbaric. |
Progressive |
A. Child saving B. Progressive C. Rehabilitation D. None of the above |
|
|
The _____ reforms became known as the medical model of corrections. |
Progressive |
A. Child saving B. Progressive C. Rehabilitation D. None of the above |
|
|
_____ is the first mission of all prisons. |
Security |
A. Reduce recidivism B. Punishment C. Reform D. Security E. None of the above |
|
|
Alcantraz introduced the _____ model of managing prisoners who most threatened prison security and safety. |
Concentration |
A. Institutional B. Security C. Confinement D. Concentration E. None of the above |
|
|
Under this model of imprisonment, offenders are sent to prison for punishment. |
Punishment |
A. Punishment B. Confinement C. Indigenous D. Importation |
|
|
Under this model of imprisonment, offenders are sent to prison as punishment. |
Confinement |
A. Punishment B. Confinement C. Indigenous D. Importation E. None of the above |
|
|
Under this theory of imprisonment, prison society is created inside prison walls independent of the outside world. |
Indigenous |
A. Punishment B. Confinement C. Indigenous D. Importation E. None of the above |
|
|
Under this theory of imprisonment, the roots of prison lie outside prison. |
Importation |
A. Punishment B. Confinement C. Indigenous D. Importation E. None of the above |
|
|
The highest "age at risk" population is said to be males in this age range |
18-29 |
A. 13-17 B. 18-29 C. 30-45 D. 45-55 E. Over 55 |
|
|
The first prison built exclusively for women in The united States was in this state and on this year |
Indiana 1873 |
A. Illinois 1873 B. Indiana 1873 C. Illinois 1893 D. Indiana 1893 E. None of the above |
|
|
This percentage of incarcerated females have dependent children at home |
80% |
A. 30% B. 40% C. 60% D. 80% E. None of the above |
|
|
_____ is a sentence entailing the conditional release of a convicted offender into the community under the supervision of the court, subject to certain conditions for a specified time. |
Probation |
A. Probation B. Parole C. Incarceration D. Boot camp |
|
|
The first state to legislate probation and appoint paid probation officers in the United States was |
Massachusetts |
A. Pennsylvania B. Missouri C. Massachusetts D. New York |
|
|
About how many people are currently on probation in the United States |
4,000,000 |
A. 40,000 B. 400,000 C. 4,000,000 D. 40,000,000 |
|
|
An adminstrative act performed by a parole authority that removes a person from parole due to a violation on the part of the parolee |
Revocation |
A. Recognizance B. Revocation C. Retraction D. Reprieve |
|
|
The process in which a probation officer settles cases at the initial appearance before the onset of formal criminal proceedings |
Presentence diversion |
A. Presentence diversion B. Intake C. Classification D. Declassification |
|
|
The accumulation of important information on the background and activities of an offender being considered for probation is called |
Presentence investigation |
A. probation narrative B. Presentence investigation C. Presentence examination D. Probationary review |
|
|
An assessment of the threat level probationers pose to the community and themselves |
Risk classification |
A. Risk classification B. Recognizance C. Probationary taxonomy D. Intermediate sanctions |
|
|
National data indicates that about _____ percent of probationers successfully complete their probationary sentence. |
65 |
A. 30 B. 53 C. 65 D. 75 |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT one of the primary probation initiatives used throughout the United States? |
Comparative probation |
A. Hotspots probation B. Area needs probation C. Making probationers pay D. Comparative probation |
|
|
The group of punishments falling between probation and prison which are primarily community based and usually administered by probation departments |
Intermediate sanctions |
A. Intermediate sanctions B. Community probation resource programs C. Hotspot probation D. Transitional sentencing |
|
|
The seizure of personal property by the state as a civil or criminal penalty |
Forfeiture |
A. Forfeiture B. Repossession C. Reclamation seizure D. Restitution |
|
|
A condition of probation in which the offender repays society or the victim of their crime for trouble the offended caused |
Restitution |
A. Family circle sentencing B. Restitution C. Restoration D. Forfeiture |
|
|
A practice that requires convicted criminals to spend a portion of their sentence behind bars and the remainder in the community |
Split sentence |
A. Community probation B. Split sentencing C. Surprise sentencing D. Electronic monitoring |
|
|
A sentence in which offenders serve a short prison term before they begin probation in an attempt to show the probationer pains of imprisonment |
Shock probation |
A. Community probation B. Shock probation C. Electronic probation D. Intensive probation |
|
|
The main goal of restitution is to |
Pay back the victim |
A. Pay back the victim B. Specifically deter the criminal C. To create smaller caseloads D. Shock the inmate |
|
|
A view of the criminal justice system that focuses on crime as an act against the community rather than the state |
Restorative justice |
A. Restitution B. Probation C. Parole D. Restorative justice |
|
|
The intended process of restorative justice is to |
Repair injuries suffered by the victim and community, and ensure reintegration of the offender into the community |
A. Repair injuries suffered by the victim and community B. Ensure reintegration of the offender into the community C. Repair injuries suffered by the victim and community, and ensure reintegration of the offender into the community D. Reduce prison crowding and administrative costs of probation |
|
|
A type of sentencing in which all parties, victims, offenders, communities, and family members participate in an effort to devise fair and reasonable sanctions aimed at reintegration of the offender into the community |
Sentencing circles |
A. Family group counseling B. Sentencing circles C. Victim-offender mediation D. Restorative counseling |
|
|
One of the William Penn's most noteworthy additions to the correction system was |
Removal of torture and public punishments |
A. Increased sanitary conditions B. Removal of torture and public punishments C. The creation of watch towers in American jails D. Hiring female correctional officers in an attempt to create normalcy in the prison environment |
|
|
The birthplace of the modern prison system and the Pennsylvania system of confinement was at |
Walnut Street Jail |
A. Pittsburg City Jail B. Quaker Village Penitentiary C. Walnut Street Jail D. Philadelphia House |
|
|
A prison system developed during the 19th century that was bases on total isolation and individual penitence |
Pennsylvania Style |
A. Pennsylvania Style B. Auburn Style C. New York Style D. Philadelphia Style |
|
|
A type of prison in which cells are located along corridors in multiple layers or levels |
Tier system |
A. Panopticon B. Tier system C. Congregate system D. Quaker system |
|
|
A prison system, developed in the 19th century based on congregate group work during the day and separation at night |
Auburn style |
A. Pennsylvania style B. Auburn style C. New York style D. Philadelphia style |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a style of the Pennsylvania System of corrections? |
Congregate model |
A. Single cells in a semi circle B. Bible study C. Congregate model D. Silence |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a style of the Auburn System of corrections? |
Single cells in a semi circle |
A. Tiered cells B. Group work C. Silence and harsh punishments D. Single cells in a semi circle |
|
|
Zebulon Brockway is most known for being the warden of the _____, which advocated indeterminate sentencing and treatment. |
Elmira Reformatory |
A. Primanti Rehabilitation Prison B. Elmira Reformatory C. Walnut Street Jail D. Madison Prison Medical Facility |
|
|
Which state created the first parole agency in 1884? |
Ohio |
A. Ohio B. West Virginia C. Illinois D. Virginia |
|
|
In discussion of new generation jails, the type of jail which contains a cluster of cells surrounding a living area or pod with an officer's station located within the pod |
Direct-supervision jails |
A. Direct-supervision jails B. Explicit-supervision jails C. Ancillary-supervision jails D. Indirect-supervision jails |
|
|
A correctional institution that houses dangerous felons and maintains strict security measures, high walls, and limited contact with the outside world |
Maximum-security prisons |
A. Enhanced super-maximum-security prisons B. Maximum-security prisons C. Minimum-security prisons D. Medium-security prisons |
|
|
The private prison was opened in 1986 in which state? |
Kentucky |
A. Tennessee B. New Mexico C. Ohio D. Kentucky |
|
|
The inmate was housed in a correctional environment that mandated Bible study and incell work. He is most likely housed in the: |
Pennsylvania System |
A. Pennsylvania System B. Auburn System C. New York System D. Alabama System |
|
|
If the man were housed in a penitentiary in which silence and harsh punishments were the norm, he would most likely be housed in: |
Either the Pennsylvania System |
A. Pennsylvania System B. Auburn System C. Either the Pennsylvania System D. Neither the Pennsylvania or Auburn System as they did not condone harsh treatments |
|
|
If the man was arrested 60 years later, which system of punishment would most likely he incarcerated in? |
Auburn System |
A. Pennsylvania System B. Auburn System C. New York System D. Egalitarian System |
|
|
Jason would most likely serve his time in a: |
Medium-security prison |
A. Minimum-security prison B. Medium-security prison C. Maximum-security prison D. Super-maximum-security prison |
|
|
John would most likely serve his time in a: |
Minimum-security prison |
A. Minimum-security prison B. Medium-security prison C. Maximum-security prison D. Super-maximum-security prison |
|
|
James would most likely serve his time in a: |
Maximum-security prison |
A. Minimum-security prison B. Medium-security prison C. Maximum-security prison D. Super-maximum-security prison |
|
|
Given what we know about their crimes, which of the brothers will be most likely to have educational opportunities in his facilities? |
All three brothers have educational opportunities as part of the prison experience |
A. James only B. John only C. Jason and John only D. All three brothers have educational opportunities as part of the prison experience |
|
|
Although most prisons are classified as medium-security prisons, more than half of all inmates are held in _____ institutions. |
Maximum-security prison |
A. Minimum-security prison B. Maximum-security prison C. Super-maximum-security prison D. Drug Rehabilitation |
|
|
A regimented, dehumanizing institution, in which like-situated people are kept in social isolation, cut off from the world at large |
Total institution |
A. Total institution B. Complete prison C. Extensive incapacitation D. Inclusive institute |
|
|
A correctional policy that stipulates that prisons are meant to punish, not coddle, inmates |
No frills policy |
A. No frills policy B. Hard-hitting corrections C. Robust rehabilitation D. Stringent sentencing |
|
|
Before inmates are sent to prison, they must first go through a battery of psychological and personality tests in a process known as |
Classification |
A. Cataloging B. Divisional placement C. Correctional clutching D. Classification |
|
|
The loosely defined culture that pervades prisons and has its own norms, rules, and language |
Inmate subculture |
A. Inmate social code B. Inmate subculture C. Prisonization code D. Inmate cipher |
|
|
An unwritten code of behavior, passed from older inmates to younger ones, that serves as a guideline for appropriate inmate behavior |
Inmate social code |
A. Inmate social code B. Inmate subculture C. Prisonization D. Inmate cipher |
|
|
Assimilation into the separate culture of prison is known as |
Prizonation |
A. Inmate social code B. Prisonization C. Inmate code D. Inmate induction |
|
|
The theory which explains that riots and other forms of violence occur when prison officials make an abrupt effort to take control of the prison and limit freedoms |
Inmate-balance theory |
A. Administrative-control theory B. Social bond theory C. Inmate-balance theory D. Anomie |
|
|
The theory which states that collective violence is caused by prison mismanagement and inadequate control by prison officials is |
Administrative-control theory |
A. Administrative-control theory B. Inmate-behavior theory C. Inmate-balance theory D. Social control theory |
|
|
The theory which states that as a prison population continues to climb, unmatched by expanded capacity, prison violence may increase |
Prison overcrowding theory |
A. Administrative-control theory B. Inmate-behavior theory C. Inmate-balance theory D. Prison overcrowding theory |
|
|
The first prison treatment programs open were educational programs in 1784 at |
Walnut Street Jail |
A. Pittsburgh Penitentiary B. Walnut Street Jail C. Moundsville Penitentiary D. Pelican Bay |
|
|
A prison treatment program that allows inmates to be released during the day for employment and return to prison at night |
Work release |
A. Furlough B. Work release C. Therapeutic communities D. House arrest |
|
|
Civil rights that include the right of inmates to receive mail and medical benefits and to practice their religion are called |
Substantive rights |
A. Jailhouse rights B. Practical rights C. Fundamental rights D. Substantive rights |
|
|
This term for a juvenile that has committed an act that, if they were an adult, would be a crime |
Delinquent act |
A. Delinquent act B. Status offense C. Crime D. None of the above E. All of the above |
|
|
This is the term for an act committed by a juvenile that would not he considered a crime if committed by an adult such as running away, truancy, and disregarding parental authority |
Status offense |
A. Delinquent act B. Status offense C. Crime D. None of the above E. All of the above |
|
|
This is probably the single most important piece of legislation in juvenile justice. It did a great deal to separate delinquent from non delinquent juveniles and to emphasize working with juveniles outside of institutions |
Juvenile Justice & Delinquency Prevention Act (1974) |
A. Roper v. Simmons (2005) B. Juvenile Justice & Delinquency Prevention Act (1974) C. Juvenile Substance Abuse Act (2000) D. Juvenile Super Predator Act (2010) E. None of the above |
|
|
This is a Latin phrase which serves as the basis for authority of the juvenile court in the United States. It means "state as parent." |
Parens patriae |
A. Parens patriae B. Parens precipitate C. State precipitate D. None of the above |
|
|
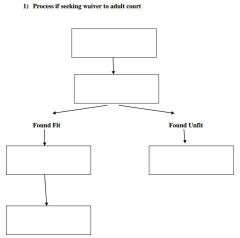
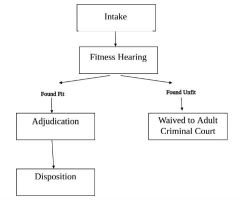
This is the sending of a juvenile case to an adult criminal court |
Waiver |
A. Waiver B. Transfer C. Recharge D. Superpredator E. None of the above |
|
|
The _____ movement relied on two institutions, the house of refuge and the reform school |
Child saving |
A. Child saving B. Punishment C. Rehabilitation D. None of the above |
|
|
In 1870, this state was one of the first to pass legislation requiring separate hearings for juveniles |
Massachusetts |
A. Massachusetts B. Illinois C. Indiana D. Florida E. None of the above |
|
|
This state created what is considered to be the first juvenile court in the US |
Illinois |
A. Massachusetts B. Illinois C. Indiana D. Florida E. None of the above |
|
|
This is when the first juvenile court was created |
1899 |
A. 1890 B. 1899 C. 1910 D. 1950 E. None of the above |
|
|
By this year, every state had legislation focusing on juveniles |
None of the above |
A. 1890 B. 1899 C. 1910 D. 1950 E. None of the above |
|
|
The Society for Prevention of Pauperism established the first house of refuge in 1824 in this state |
None of the above |
A. Massachusetts B. Illinois C. Indiana D. Florida E. None of the above |
|
|
Idealizing country living, emphasizing traditional values and hard work, this focused on pre-delinquent youth who showed propensity for more serious crimes |
Reform school |
A. House of refuge B. Reform school C. Detention center D. All of the above E. None of the above |
|
|
This was designed to save children from lives of poverty and crime; here you would find thieves, vagrants, and runaways |
House of refuge |
A. House of refuge B. Reform school C. Detention center D. All of the above E. None of the above |
|
|
Most states exclude children under age _____ from juvenile justice jurisdiction |
8 |
A. 6 B. 8 C. 10 D. 12 E. None of the above |
|
|
Rather than being found "guilty," a juvenile is found _____ |
Responsible |
A. Responsible B. Not responsible C. Not delinquent D. Delinquent E. None of the above |
|
|
Rather than being found "not guilty," a juvenile is found _____ |
Not responsible |
A. Responsible B. Not responsible C. Not delinquent D. Delinquent E. None of the above |
|
|
In juvenile justice, this is the term for what would be called parole in adult court |
Aftercare |
A. Institutionalization B. Commitment C. Rehabilitation D. Release E. Aftercare |
|
|
In juvenile justice, this term refers to the prosecutor |
Petitioner |
A. Respondent B. Petitioner C. Judge D. None of the above |
|
|
In juvenile justice, this term refers to the defense |
Respondent |
A. Respondent B. Petitioner C. Judge D. None of the above |
|
|
In juvenile justice, this term refers to the trial |
Adjudication |
A. Intake B. Adjudication C. Disposition D. Commitment E. Aftercare |
|
|
In juvenile justice, this term refers to the sentence |
Disposition |
A. Intake B. Adjudication C. Disposition D. Commitment E. Aftercare |
|
|
In juvenile justice, we seek to do what is in the _____ _____ of the _____ |
Best interest of the child |
A. Best interest of the public B. Best interest of the family C. Best interest of the child D. All of the above E. None of the above |
|
|
The ultimate goal, when possible in juvenile justice, is _____ |
Rehabilitation |
A. Rehabilitation B. Reunification C. Commitment D. All of the above E. None of the above |
|
|
In juvenile justice, institutionalization is called |
Commitment |
A. Intake B. Adjudication C. Disposition D. Commitment E. Aftercare |
|
|
Rather than being sent to a correction facility, juveniles are sent to |
Detention center |
A. House of refuge B. Reform school C. Detention center D. All of the above E. None of the above |
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is a correctional ideology? |
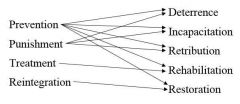
An underlying thought or idea about how corrections should be operating or what the purpose of corrections should be |
|
|
|
What is a correctional goal? |
How ideologies are put into practice |
|
|
|
Four ideologies |
|
|

