![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Song for COPD |
1) State diagnosis of COPD: Patient has got hyperinflated chest with reduced chest expansion bilaterally at 2cm. The percussion note is resonant with loss ofliver and cardiac dullness. There is prolonged expiratory phase with expiratory ronchi. Vocal resonance is normal. Trachea iscentral and apex beat is not displaced. 2) State complications: a. Pulmonary hypertension: Loud/Palpable P2, and left parasternal heave b. Cor pulmonale: Raised JVP, B/L pedal oedema c. Polycythemia: Palmar erythema, plethoric facies, conjunctival suffusion d. Chronic systemic steroid cx: Oral thrush, hoarse voice 3. Functional status of patient: a. Respiratory distress - tachypnea, tachycardia, accessory muscles b. Respiratory failure - oxygen dependent? presence of central cyanosis? c. CO2 retention - flapping tremor, bounding pulse 4. Aetiology: a. Smoking - nicotine staining b. Malignancy - enlarged cervical lymph nodes, cachexia c. Suppurative lung diseases - clubbing |
|
|
How do you grade the severity of dyspnea? |
Medical Research Council (MRC) scale: 1 – SOB on strenuous exercise 2 – on hurrying or up hill 3 – walks slower than contemporaries and stops for breaths 4 – stops for breath after walking 100m 5 – SOB on ADLs |
|
|
What is another way to grade COPD? |
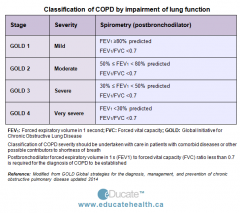
GOLD classification |
|
|
How do you dx COPD? |
Clinical (>35 years, smoking, wheeze, SOB, cough with sputum, winter bronchitis) Airflow obstruction – FEV1/FVC<70 and FEV1<80 o Mild – 50-80% o Mod – 30-50% o Severe - <30% Exclude differential diagnoses o Asthma (>400mls to dilators or PO pred 30mg OM 2 weeks or variation in PEFR >20%) o Cancer o Bronchiectasis o ILD |
|
|
How would you investigate admitted with an acute exacerbation? |
FBC (anaemia, polycythemia), biochemical, theophylline levels, ABG Blood C/S if febrile CXR Spirometry ECG, 2D echo (looking for AMI and heart strain) |
|
|
What is the conservative management for COPD? |
o Stop smoking o Regular follow up (if >500 mls decline over 5 years implies accelerated decline) o Pneumococcal and influenza vaccination o Pulmonary rehabilitation for MRC 3 or above(PT/OT) o MSW, Nurse o Assessment of inhaler technique (should not clean space more than once a month due to increased static) |
|
|
What is the pharmacological management for COPD? |
o Bronchodilators: Beta agonist and anticholinergics ( Short acting and long acting Improves symptoms and exercise capacity) o Theophylline (competitively inhibits type III and type IV phosphodiesterase (PDE), resulting in bronchodilation) o Steroids + Prophylaxis against osteoporosis if >65y/o : Reduce exacerbations and decline in health status Used if FEV1<50% (moderate/severe) 2 or more exacerbations a year requiring antibiotics or steroids o Mucolytics (not anti-tussive) |
|
|
What is the management of exacerbation? |
1. Bronchodilator - Nebs or via spacer 2. Systemic steroids 3. IV aminophylline 4. Antibiotics such as macrolide (increase volume or purulence) 5. Oxygen therapy Intranasal if hypoxic NIPPV if hypercapneic and pH 7.25-7.35 Intubation |
|
|
Management of COPD complications |
1. Hypoxemia (assess for long term O2 therapy) - PaO2 < 55 or PaO2 <60 + presence of complications (polycythemia, pulmonary HTN, Cor Pulmonale, Nocturnal hypoxaemia) - For at least 15 hours/day 2. Cor Pulmonale - Diuretics 3. Polycythemia - Venesection if >55% |
|
|
Surgical interventions for COPD |
1. Bullectomy if: - single large bulla - FEV1<50% 2. Lung Volume Reduction Surgery if: - Upper lobe bullous involvement - FEV1>20% - TLCO >20% (carbon monoxide transfer factor ) - PO2 <45 3. Transplant |

