![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the normal values for the following blood gas measurements?
PaO2 PaCO2 pH BE Bicarb |
PaO2. 95-100mmHg
PaCO2. 40mmHg pH. 7.4 BE. 0 Bicarb. 26Meq/L |
|
|
How much oxygen is dissolved in the plasma per 100mL of blood compared to that bound to haemoglobin?
|
0.3mL oxygen per 100mL plasma
20mL oxygen per 100mL red blood cells |
|
|
Describe the mechanism by which different types of chemoreceptors detect oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Include their location and the nature of their response.
|
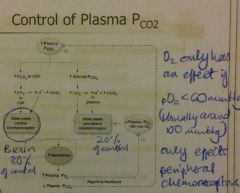
Central chemoreceptors in the medulla
Detect CO2 (highly soluble, crosses blood-brain barrier into CSF) Produce a linear response Peripheral chemoreceptors in the carotid body and aortic arch Detect O2 and CO2 Produce a linear response |
|
|
What are the 2 patterns of respiratory failure and how do they differ?
|
Hypoxic respiratory failure
Low arterial O2 with normal/low CO2. Type A ("pink puffer") Hypercapnic respiratory failure Low arterial O2 and high CO2. Type B ("blue bloater"). Worse with sleep: plays key role in disease progression "Won't" breathe - pump or control problem "Can't" breathe - lung (gas exchange) problem |

