![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Building
Deliverables |
Problem Solving
Design and Build Deliverables Coaching/Motivating/Leading Team Politics/Managing Expectations |
|
|
Building Phase Competencies
|
Producing Deliverables
Team Performance Politics/Managing Expectations |
|
|
Producing Deliverables
|
Ensures orderly progress is made on data gathering, analysis, assembly, and the development of deliverables.
Effective decision-making in the face of ambiguity and time constraints Ensure accountability of individual consultants for agreed upon goals Seek constructive feedback about the deliverables as they are being developed |
|
|
Team Performance
|
Set challenging but realistic goals
Build people’s confidence in themselves and their work Encourage team-based decision-making when solving problems Ask team members for self-assessment of progress towards goals |
|
|
Politics/Managing Expectations
|
Understand how stakeholders in client's organization use their power and influence
Balance advocacy and diplomacy with clients to win support Draw upon ability to influence (and personal networks) to get things done Avoids taking credit for successful initiatives begun by others |
|
|
Problem Solving Framework
|
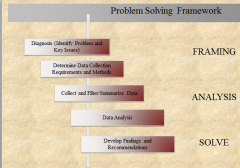
Issues/Questions That Need Answers “MECE”
Information Needed to Answer Questions Identification of the Information Sources Data Collection Techniques |
|
|
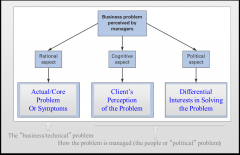
Framing a Business Problem
|
|
|
|
Manufacturing Engineering
|
RP – High operating costs relative to competitors (and deeper – poorly maintained equipment, obsolete facilities and inefficient processes)
PP – unionized operators/employees have negative attitudes, supervisors are inexperienced, ME’s are constantly busy with crisis after crisis – unable to address new development |
|
|
Corporate Planning
|
RP – Strategic Plans need constant revision, operational plans and objectives at functional levels not coordinated
PP – managers view long range planning as just an exercise, no real personal commitment to planning at the senior executive levels (and deeper -- strained relationships and distrust between the field and corporate office operations). |
|
|
Understanding All Aspects of the Problem
|
What is the (technical or business) problem that you are facing?
What are other individuals or groups in the organization doing to either cause or maintain this problem at its current level of severity (in the SPIN framework these are implication questions)? What is there in your approach or way of managing the situation |
|
|
MECE
|
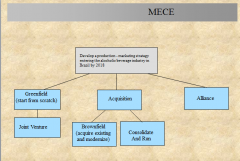
(Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhausted)
Is each a separate and distinct issue (no overlaps) Does every aspect of the problem come under one of the issues (no gaps) |
|
|
Data Gathering Must Be…
|
Systematic (clear goals, scope and strategy, and disciplined)
Fact-Based Focused on the Right Issues Directed Towards Validating the Teams’ Hypotheses |
|
|
Data Collection Techniques
|
Interviews and Focus Groups
Surveys or Questionnaires Direct Observation Review Existing Records and Databases (Document Analysis) *The soundness of deliverables, solutions, and recommendations are directly related to the efficacy of the data gathered and the value of the Insights found in the information |
|
|
Interviews
|
Unstructured
Structured Focus Groups Customers |
|
|
Executive Interviews
|
Interview Schedule
talk to senior people early use multiple interview teams if necessary to compress the schedule don’t overwhelm the interviewee (typically limit a team to 1 consultant/ 1 client/1 note taker) never schedule more than 3/day per team Interview Protocols (interview questions/topics) distribute before interview layout areas of inquiry – typically a top down approach. Don’t be afraid to ask tough questions Interview Write-ups prepare immediately after interview use standard formats distribute back for comment Follow-up act quickly as possible on points or suggestions made |
|
|
Interviewing – Best Practices
|
Clarify the purpose before starting
Create and maintain a relaxed atmosphere (and try to have the meeting in a quiet space where you are unlikely to be interrupted) Consider the interview to be a joint learning event (and a networking opportunity) Refer to the Interview Protocol but stay flexible Ask open ended questions. Probe. Ask why. Drive to dig down to get to underlying cause. Ask follow-up questions to clarify details Observe behaviors as well as listen. Note where is the interviewee uneasy or defensive Don’t interrupt unless to maintain focus. Let the interviewee talk Provide support but don’t appear biased or political Take notes (or have a note keeper) |
|
|
Standard Format
|
Introduce yourself and establish a human connection
Explain the purpose and length of the interview (and acknowledge the Interview Protocol). Establish expectations. Ask Interviewee a few questions about themselves to confirm their demographics (title, overall responsibilities, etc.) and their relationship to the project (but no questions where the answers are obvious or make you appear to be uninformed) Execute the Protocol. Generally questions will go from more general to more specific on a topic by topic basis. Its important to realize that you can deviate from the Protocol to let the conversation flow but periodically check back to ensure that you are covering the key points. Ask a final open ended questions that gives the interviewee the opportunity to bring up any issue overlooked Thanks the Interviewee and if relevant arrange for a follow-up |
|
|
The Customer Interview
|
Select a cross-section of customers. Look to management for guidance here.
Lead customer Large customer Marginal customer Non-customer If at all possible go to the customer site rather than rely on phone interviews Avoid the management temptation to use the customer interview to stroke the customer. Use the interview to understand the customer’s perspective of the business relationship and business value. Try to understand the customers criteria or motives in “using” your client. Interview multiple customers to develop consensus. DON’T create expectations (promises) unless specifically authorized by your client management. |
|
|
Interviewing – Advantages
|
Advantages
Flexible In-depth Can observe “body language” Provides “networking” opportunities |
|
|
Interviewing – Disadvantages
|
Disadvantages
Labor Intensive - Expensive Interviewer Bias may creep in Can get repetitive quickly |
|
|
Best Practices – Focus Groups
|
Select Focus Group Participants Carefully Considering
Diversity of experience and background Organizational level (diversity of authority) Typically limit to 8 to 12 participants or so Moderate with open ended questions Avoid moderator bias or leading to conclusions Observe interactions between participants. Look for “group think” |
|
|
Surveys and Questionnaires
|
Easy to get data on large numbers of people
Easy to quantify responses – compare and contrast Very cost effective Can be administered in many ways – internet, email, physical distribution, attended, etc |
|
|
Weaknesses of survey and questionnaires
|
Typically relies on multiple choice format (or a Likert scale) – difficult to ask open ended questions so can dig down or get at underlying causes in ways interviews can. No good way to follow-up
Question design is critical and easy for biases to creep in (that directs the respondent towards an answer) Response rates typically an issue and actual sample must be representative |
|
|
Direct Observation
|
People’s actual behavior whether interacting with a product, doing a business process, managing a co-worker, etc. occurs in its natural environment.
What people say they do is often different from what they actually do – and in some cases the individual are not aware of the discrepancies (very important in understanding how work actually flows in an organization) Make sure to observe at different times and under different conditions (routine, under stress, etc.) Be unobtrusive but remember the Heisenberg Effect (People Will Behave Differently if they Know they are Being Observed/The act of data gathering affects the gathered) Also remember to keep observer bias minimized Similar to interviewing observation is labor intensive and expensive. |
|
|
Secondary Sources – Records/Databases
|
Organization Internal Records – financial, operational, HR. Clients can provide a lot of support here.
Public Records – very helpful in competitive research. SEC, Census Bureau, various government agency websites; plus industry websites Subscription databases: Lexus/Nexus Hoovers S&P Gartner Group IBIS World Many, many others Clipping and email services Can be overwhelming and expensive |
|
|
Data Collection
|
“Funnel”, and Summarize The Data
Avoid Collecting Data Not Relevant to the Analysis Balance Cost of Data Collection to Likely Benefit Understand when to stop Analyze Data Determine analytical frameworks before collecting the data Involve the client even if he/she does not have the expertise Think graphically and ultimately how the analysis will be presented |
|
|
What Motivates Professional Consultants?
|
Praise and Time Off
Money and Perks Challenging, Interesting, Rewarding Work |
|
|
What are 3 main motivational factors?
|
Meaningful Autonomy Feedback
Doing work that is challenging and interesting Working with people they enjoy being with and can learn from Being listened to when they give opinions on something important Seeing their views and ideas put into action Completing a project that makes a difference to the firm Learning new things |
|
|
Hertzberg’s 2 Factor Theory
|
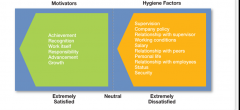
|
|
|
Job Characteristics Model
|
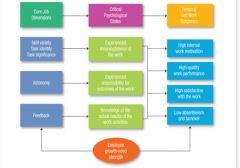
|
|
|
Goals (Think SMART)
|
S specific
M measurable A achievable R relevant T time-bound Examples. Finish the “as is” workflows for the Personal Property adjudications process by March 8. Complete and document all executive level interviews by February 19. |
|
|
Goals that are project workplan related should focus
on .... |
roles, tasks, specific deliverables and due dates.
|
|
|
Coaching
|
“Positive” coaching can be used to enhance, improve, develop, and increase anyone’s (subordinates, peers, clients, and management) abilities.
“Corrective” coaching is necessary when mistakes have been made (not producing a deliverable on time, inappropriate behavior with a peer or client, introducing a bias into a research method, etc.) |
|
|
“Positive” coaching can be used to enhance, improve, develop, and increase anyone’s (subordinates, peers, clients, and management) abilities.
“Corrective” coaching is necessary when mistakes have been made (not producing a deliverable on time, inappropriate behavior with a peer or client, introducing a bias into a research method, etc.) |
Purpose (to create an open atmosphere)
Observation (state the issue or problem, provide examples and facts) Impact (discuss the impact of the problem) Solution (define optimal solutions, choose a new course of action, or new behavior) Expectations and Encouragement (provide empathy, create a safe place, and offer help/encouragement) |

