![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Articles of Confederation |
A plan for national government ratified in 1781 |

|
|
|
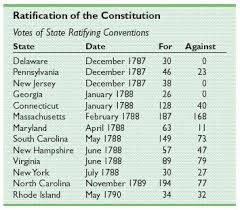
ratification
|
Act of offcial confirmation |
|
|
|
levy
|
impose or raise a tax
|

|
|
|
Founders (or Framers)
|
People that helped creat the U.S. Constitution
|

|
|
|
Virginia Plan
|
Plan that gurantees a two-house legislature, where the number of members would be determined by the states population. Powers were divided into three branches. |

|
|
|
New Jersey Plan
|
Plan that guranteeded a legislature, that each state had an equal vote. |

|
|
|
Great Compromise
|
Agreement that allowed all states to have equal representation, and each state had representation based on population. This established the House of Reprsentatives. |

|
|
|
Three-Fifths Compromise
|
Agreement that called for three-fifths of state's slave population would be counted for taxation and representation |

|
|
|
Executive Branch
|
The part of the government that enforces laws
|

|
|
|
Judicial Branch
|
Government department that interprets laws
|

|
|
|
Legislative Branch
|
Governmant part that creates the laws |

|
|
|
Checks & Balances
|
limits imposed on all branches of a government by vesting in each branch the right to amend or void those acts of another. |

|
|
|
Antifederalists
|
People that thought the Constitution took away to much power from the states and did not gurantee the rights of citizens. |

|
|
|
Federalists
|
People that supported the Constitution |

|
|
|
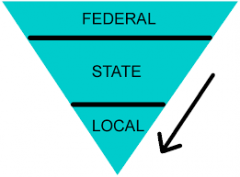
Federalism
|
Type of government where power is shared between the states and federal government
|
|
|
|
majority rule
|
a decision rule that selects alternatives that is more than half the votes. |

|
|
|
amendment
|
addition to a motion, bill, constitution, etc.
|

|
|
|
Bill of Rights
|
a formal statement of the fundamental rights of the people of the United States, incorporated in the Constitution as Amendments 1–10, and in all state constitutions. |

|
|
|
House of Representatives
|
The lower house of the United States Congress.
|

|
|
|
Senate
|
council of citizens having the highest deliberative functions in a government, especially a legislative assembly |

|
|
|
Congress
|
the national legislative body of the U.S., consisting of the Senate, or upper house, and the House of Representatives |

|
|
|
Popular Sovereignty
|
the principle that the authority of the government is created and sustained by the consent of its people, through their elected representatives or rule by people |

|
|
|
Republicanism
|
the ideology of governing a society or state as a republic where the head of state is a representative of the people who hold popular sovereignty |

|
|
|
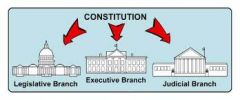
separation of powers
|
an act of puttting the legislative, executive, and judicial powers of government in separate bodies. |
|
|
|
limited government |
A political system in which legalized force is restricted through delegated and enumerated powers. |

|
|
|
bicameralism |
A feature of mixed government. Bicameral legislatures usually require a concurrent majority to pass legislation. |

|
|
|
judicial review
|
Review by the US Supreme Court of the constitutional validity of a legislative act.
|

|
|
|
impeachment
|
a formal process in which an official is accused of unlawful activity, the outcome of which, depending on the country, may include the removal of that official from office as well as criminal or civil punishment |

|
|
|
quorum
|
the minimum number of members of an assembly or society that must be present at any of its meetings, in order for that meeting to be valid |

|
|
|
revenue |
a state's annual income from which public expenses are met.
|

|
|
|
veto
|
a constitutional right to reject a decision or proposal made by a law-making body. |

|
|
|
naturalization
|
the legal act or process by which a non-citizen in a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. |

|
|
|
elastic clause
|
a statement in the U.S. Constitution, granting Congress the power to pass all laws necessary and proper for carrying out list of powers. |

|
|
|
natural born citizen |
the United States is one of the eligibility requirements established in the United States Constitution for election to the office of President or Vice President. This requirement was intended to protect the nation from foreign influence. |
|
|
|
electoral college
|
a body of people representing the states of the US, who formally cast votes for the election of the president and vice president. |
|
|
|
Supreme Court
|
the highest judicial court in a country or state.
|

|
|
|
suffrage
|
the right to vote in political elections. |

|
|
|
due process of law
|
The government may not deprive citizens of “life, liberty, or property” without due process of law. This means that the government has to follow rules and established procedures in everything it does. |

|
|
|
bail
|
some form of property deposited or pledged to a court to persuade it to release a suspect from jail, on the understanding that the suspect will return for trial or forfeit the bail |

|
|
|
Constitution |
a body of fundamental principles or established precedents according to which a state or other organization is acknowledged to be governed. |

|

