![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Articles of Confederation |
plan for national government ratified in 1781
|

|
|
|
ratification
|
act of official confirmation |

|
|
|
levy
|
impose or raise a tax
|

|
|
|
Founders (or Framers)
|
people who helped create the U.S. Constitution
|

|
|
|
Virginia Plan
|
proposal for a two-house legislature with representation according to each state's population or wealth
|

|
|
|
New Jersey Plan
|
proposal for a legislature in which each state would have one vote
|

|
|
|
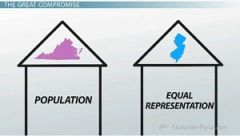
Great Compromise
|
agreement to establish a two-house national legislature, with all states having equal representation in one house and each state having representation based on its population in the other house |
|
|
|
Three-Fifths Compromise |
agreement that three-fifths of a state's slave population would be counted for representation and taxation |

|
|
|
Executive Branch
|
government department that enforces laws |

|
|
|
Judicial Branch
|
government department that interprets laws |
|
|
|
Legislative Branch
|
government department that makes laws |

|
|
|
Checks & Balances
|
the ability of each branch of government to exercise checks, or controls, over the other branches |

|
|
|
Antifederalists |
people who opposed ratification of the Constitution |
|
|
|
Federalists |
people who supported ratification of the Constitution |

|
|
|
Federalism |
system of government in which power is shared between the national government and the states |

|
|
|
majority rule
|
system of government in which more than one half of a group holds the power to make decisions binding the entire group |

|
|
|
amendment |
addition to a document |

|
|
|
Bill of Rights
|
first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution |

|
|
|
House of Representatives |
the lower chamber of Congress |

|
|
|
Senate
|
the upper house of the legislature of certain countries |

|
|
|
Congress
|
the national legislative body of the U.S., consisting of the Senate, or upper house, and the House of Representatives, or lower house, as a continuous institution |

|
|
|
Popular Sovereignty
|
a doctrine, held chiefly by the opponents of the abolitionists, that the people living in a territory should be free of federal interference in determining domestic policy, especially with respect to slavery. |

|
|
|
Republicanism
|
the principles or policy of the Republican Party.
|

|
|
|
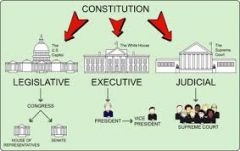
separation of powers
|
power is seperated so one branch is not too powerfull |
|
|
|
limited government
|
restricted with reference to governing powers by limitations prescribed in laws and in a constitution |

|
|
|
bicameralism
|
having two branches, chambers, or houses, as a legislative body. |

|
|
|
judicial review
|
principle that states that the Supreme Court has the final say in interpreting the Constitution |

|
|
|
impeachment
|
the presentation of formal charges against a public official by the lower house, trial to be before the upper house. |

|
|
|
quorum
|
the number of members of a group or organization required to be present to transact business legally, usually a majority |

|
|
|
revenue
|
the income of a government from taxation, excise duties, customs, or other sources, appropriated to the payment of the public expenses. |

|
|
|
veto
|
the power or right vested in one branch of a government to cancel or postpone the decisions, enactments, etc., of another branch, especially the right of a president, governor, or other chief executive to reject bills passed by the legislature. |

|
|
|
naturalization
|
to introduce or adopt |

|
|
|
elastic clause
|
a statement in the U.S. Constitution (Article I, Section 8) granting Congress the power to pass all laws necessary and proper for carrying out the enumerated list of powers |

|
|
|
natural born citizen
|
citizen that was born in the country that they are citizens of |

|
|
|
electoral college
|
a body of electors chosen by the voters in each state to elect the president and vice president of the U.S. |
|
|
|
Supreme Court |
the highest court of the U.S.
|

|
|
|
suffrage |
the right to vote, especially in a political election. |

|
|
|
due process of law |
process before the law is due |

|
|
|
bail
|
property or money given as surety that a person released from custody will return at an appointed time. |

|
|
|
Constitution |
the system of fundamental principles according to which a nation, state, corporation, or the like, is governed |

|

