![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Articles of Confederation |
a plan for the national government that was ratified in 1781
|

|
|
|
ratification
|
an act of offical confirmation
|

|
|
|
levy
|
to impose or raise a tax
|

|
|
|
Founders (or Framers) |
a system of government in which power is shared between the national or federal government and the states |

|
|
|
Virginia Plan
|
proposal for a two-house legislature with representation according to each state's population or wealth |
|
|
|
New Jersey Plan |
proposal for a legislature in which ech state would have one vote |
|
|
|
Great Compromise
|
agreement to establish a two-house national legislature, with all states having equal representation in one house and each state having representation based on its population in the other house |

|
|
|
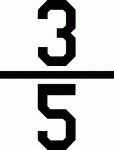
Three-Fifths Compromise
|
agreement that three-fifths of a state's slave population would be counted for representation and taxation |
|
|
|
Executive Branch
|
branch that enforces laws |

|
|
|
Judicial Branch
|
branch that interprets laws |

|
|
|
Legislative Branch |
branch that makes laws |

|
|
|
Checks & Balances
|
the ability of each branch of government to exercise checks, or controls, over the other branches |

|
|
|
Antifederalists
|
people who do not agree with the ratification of the constitution |

|
|
|
Federalists
|
people who agree with the ratification of the constitution |

|
|
|
Federalism |
a government system where power is shared between the national government and the states |

|
|
|
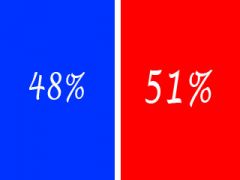
majority rule
|
a government system where more than half of the group holds the power to make decisions including the entire group |
|
|
|
amendment
|
an addition to a document
|

|
|
|
Bill of Rights
|
the first ten amendments to the US Constitution
|

|
|
|
House of Representatives
|
the lower house of the United States government |

|
|
|
Senate |
part of a legislative government |

|
|
|
Congress
|
the national legislative body |

|
|
|
Popular Sovereignty
|
a system where issues are decided by the citizens or voters
|

|
|
|
Republicanism
|
governing the people rather than being the subjects of the head of state
|

|
|
|
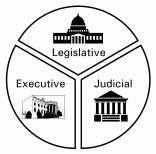
separation of powers
|
serperation of powers into the three branches of government |
|
|
|
limited government
|
a government with restricted limits
|

|
|
|
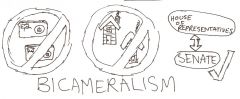
bicameralism |
two branches or houses of the legislative body |
|
|
|
judicial review
|
principle that states that the Supreme Court has the final say in interpreting the Constitution |

|
|
|
impeachment
|
the process of accusing a public offical of wrongdoing |

|
|
|
quorum
|
the minimum number of members that must be present for offical business to take place |

|
|
|
revenue
|
income |

|
|
|
veto
|
to prevent from becoming a law |

|
|
|
naturalization
|
a way to give full citizenship to a person of foreign birth |

|
|
|
elastic clause
|
a statement granting Congress to pass necessary laws for carrying out lists of powers
|

|
|
|
natural born citizen
|
a citizen born in the United States, or parents who are U.S. citizens living outside the country
|

|
|
|
electoral college
|
a cast of votes for the president and vice president |
|
|
|
Supreme Court
|
the highest body in the judical branch
|

|
|
|
suffrage
|
the right to vote
|

|
|
|
due process of law |
the government may not take away the citizens life, liberty, or presuit of hapiness |

|
|
|
bail
|
money paid by an arrested person to guarantee they will return for trial |

|
|
|
Constitution |
a document with the rights of the American citizens
|

|

