![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
growth
|
quantitative increase in the size of a system
|
|
|
development
|
qualitative change in the complexity or configuration of a system
|
|
|
sustainable development
|
-Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
-increasing value while maintaining or increasing biodiversity |
|
|
what are three factors that need to change before sustainable development will be achievable
|
-values at the core of human fabric that drive our collective behavior need to change; long therm sustainability must replace short term personal gain as the primary human motivation
-growth oriented economic systems that drive human existence must be replaced by steady state economic systems that accept natural limits to our artificial economies -human population growth must slow, stop and eventually reverse |
|
|
Potential impacts of tourism
|
-disruption of social structures
-negative cultural impacts -negative economic impacts -modification of ecosystems |
|
|
ecotourism
|
nature based tourism that adheres to a set of standards that help ensure environmental protection, cultural integrity and community benefit
|
|
|
5 areas ecotourism can support conservation in
|
-financing for biodiversity conservation
-alternative livelihoods for local people -constituency and stewardship for biodiversity -providing an economic justification for protecting areas -creating an impetus for private conservation |
|
|
Integrated conservation and development projects
|
seek to conserve biodiversity, especially in protected areas by enhancing benefits adjacent communities derive from biodiversity. Target enhancing biological conservation and economic and social development that is compatible with conservation in local communities.
|
|
|
Integrated conservation and development projects (conceptual diagram)
|
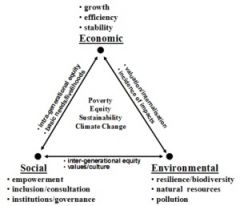
|
|
|
Ecological principles of sustainability
|
-nature is an irreplaceable source of knowledge
-issues of environmental deterioration and human oppression and violence are linked -Humility must guide our actions, good stewardship begins with restraint -Place and locality are the foundation for all durable economies, solutions are local and scale dependent -sufficiency must replace economic efficiency, must distinguish between needs and wants -community is essential for survival, global community should reflect and encourage diversity while being independent -Biological and cultural diversity must be preserved, defended and encouraged |

