![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Connective tissue is made of
|
Cells, fibers, amorphous intercellular substance
|
|
|
Characteristics of Ct?
|
abundant matrix (lots of fibers and amor. ground substance)
Portions of the cell and intercellular substance vary considerably *form basis of classificiation of connective tissu* |
|
|
Embryological orginins of CT
|
Mesoderm>mesenchyme>cT
|
|
|
Mesenchyme is the foundation for all?
|
Connective Tissue
|
|
|
Fibers of connective tissue?
|
Collangeous Fibers
Reticular Fibers Elastic Fibers Amorphous Intercellular Substances |
|
|
Cells of the Connective Tissue?
|
Fibroblasts
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Pericytes Macrophages Plasma Cells Mast cells Fat Cells Mononuclear Wandering Cells |
|
|
Collogenous Fibers physical characterstics
|
1-2 micrometers, Comprised of smaller fibrils, held together by an amorphous material (that is trypsin sensitive) aligned in parallel.
Irregular, undulating shape. Flexible Non-extensible (inelastic) Forms geletan when in boiling H2O Collagen+heavy metal>insolu. prd. Stains with acid dyes Fibrils can be resolved into microfibrils, has a characteristi of cross banding 64nm plus intraband patterns |
|
|
Collogenous fibers chemical
|
Tropocollogen made of 3 alpha polypeptide chains.
Contain lots of glycine, proline,hydroxyproline,hydoxylysine. Sligh variations in AA sequences in Alpha chains are responsible for diff. collogen types. Chains wrap around each other to form a triple helix held together by collagen bonds. |
|
|
Formation of fibrils from tropocollogen occurs??
|
Outside the cell in fibroblast.
|
|
|
Formation of tropocollagen molecules into fibrils occurs how?
|
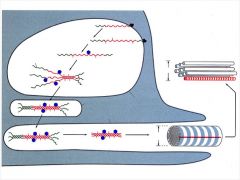
|
|
|
Numerous collogens arise because of?
Where they are found?? And Made?? |
Slight variations in alpha chain sequences due to slight differences of AA. Found in most connective tissue, made in fibroblast
|
|
|
Type IV collogen
|
basement membranse, peanut butter in basal lamina
|
|
|
Reticular Fibers Physical characteristics?
|
Type 3 collagen
Norrower than other coll. fibers Tend to branch forming delicate network Argyrophilic, blacken with silver impregnation. PAS + Similar to collagen except thinner Exhibit 64 nm cross banding |
|
|
Reticular Fibers Chemical comp, location and orgins?
|
More carbohydrate than other types, probably present as a surface coat, why it reacts with PAS
Sparse in Adult loose CT, around muscle, nerves, and epi. structures, glandular organs, lymphatic tissues, embryonic CT, red bone marrow Fibroblats and reticular cells (in lymphatic and hemopoietic tissues) |
|
|
Elastic fibers physical characterisics?
|
Thinner than collogen, branch and anastomose freely, may be flat or round in cross section
Highly refractile, may appear yellowish when present in large masses React poorly with most stains, stain with orcein. 2 components Microfirillar (fibrillin-1) amorphos compon. (elastin) Easily streched breaks at 150% origional length, no cross banding, spiral or kink when broken. |
|
|
Elastic Fibers chemical Composition
|
Elastin (amorphous component)
Fibrillin-1 |
|
|
Elastin
|
high proline, glycine content
2 unusual AA, desmosine and isodesmosine |
|
|
Fibrillin-1 defective
|
Marfan's Syndrom catastrophic rupture of aorta
|
|
|
Marfan's syndrome
|
Catastrophic rupture of aorta
|
|
|
Fibrillin-1
|
Glycoprotein forms fine microfibrils
Chronice sun exposure leads to extensive remodeling and loss of elasticity |
|
|
Reticular fibers location and origin
|
In many CT, loose, irregular etc.
In elastic ligaments (ligamentum flavum in blood vessels, vocal chords origin, fibroblasts' smooth muscle cells |
|
|
Amorphous Intercellular Substance
|
Viscous solution<>thin gel, optically homogenous and transparent.
Has alot of H2O Glycosaminoglycan (GAGs) a. Non sulfated, very viscous in aqueous solution, bound to protein, alternates glucosamine and glucouronate, responsible for many of the physical properties of ground substance, acts as a physical barrier to bacterial invasion, present in synovial fluid of joints; good lubricating properties Sulfated-(something)-sulfate Proteoglygans can aggregate due to all the sulfate groups and are negatively charged in H20. |
|
|
Proteoglycan Aggregate
|
Has ionic bonds to hyaluronic acid core and has keratan sulfates bound to it by linker proteins
|
|
|
Reticular Fibers
|
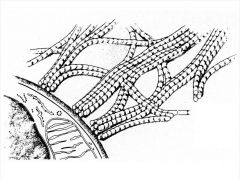
|
|
|
Elastic Fibers
|

|
|
|
Elastics Stretch/Relax
|
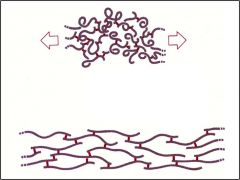
|
|
|
Structural Components of multi-adhesive glycoproteins
|
Fibronectin (most abundant Glycopro)----monomers connected by disulfide links in mesenchynal tissue, extracellular spaces, important in organizing EC matrix, binds to a number of things like fibrinogen, collagen heparin, etc.
Laminin-confined to basement membranes and external laminae where it is a structural and adhesive functions |
|
|
Proteglycan aggregate which has a hyaluronic core with keratan sulfates bonded to it with linker proteins this allows it to be negatively charged in H2O
|
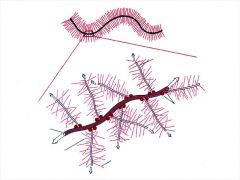
|
|
|
Laminin can bind to different proteins
|
|
|
|
Functions of Ground substance and its origins
|
Efficient space filler, permits passage of gases, ions and small particles, helps to immobilize larger objects.
Fibroblasts make them all except laminin |
|
|
Fibroblasts are?? and differnce between active and inactive?
|
The most common cell type in loose CT
Active Cell-Large, somewhat flattened ovoid with branching processes, oval nuclei (somewhat flattened with weakly staining chromatin particles, distinct nucleolus, basophilic cyto. Inactive-- small nuclues, less distinct nucleoli, cytoplasm is slightly acidophilic |
|
|
Active and inactive Fibroblasts
|
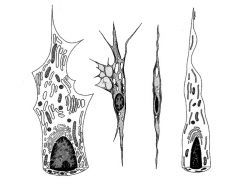
|
|
|
Fibroblast functions??
|
Produtions of fibers, productions of intercellular substances
|
|
|
Disturbances in Collagen metabolism??
|
Scurvy-degredation of CT by deficiency of Vitamin C, need Vitamin C to hydroxylation of proline+lysine
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome-short stature stretchable skin, hypermobility of joins and tendency for joint dislocations.. Due to lack of enzyme to make collagen from procollagen Osteogenesis imperfecta-brittle bone disease. No type 1 collagen |
|
|
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Pericytes
Traits and uses |
Relatively primitive, undifferntiated cells, (look similar to small young fibroblast. Usually seen in Blood vessel(capillaries)
Can make-Fibroblasts, fat cells, chondrocytes, osteroblastes SM cells, epith |
|
|
Macrophages appearance, movement, and location???
|
2nd most common loose CT
Irregular shape with blunt processes Rounder, smaller, darker nucleas than fibroblast, cyto. stains lightly **when active gets bigger with larger nucleus and nucleolus many granuales an vacuoles in cyto. Moves by ameboid movement (normally fixed) but can move to site of inflammation. Numbers increase in areas of inflammation. multiplation of existing cells, movement of many cells there. MONOCYTES LEAVE BLOOD TO BECOME MACROPHAGE |
|
|
Macrophage function??
|
Phagocytosis-permits IDing, inject dye that enters these cells. Phago=eating cellular remains, microorganism and inert particles forms phagosomes! which combine with 1* lysosome to make 2* lysosomes.
Create foreign body giant cells- fusion of large # of macro. multi nucleated, object needs many things to eat it. Membranse have Fc receptors and C3 complement. Immune response |
|
|
Plasma cells commonality and appearance
|
Not particularily common in CT normally
Except: in lamina propria in digestive tract, greater omentum, reticular CT of blood forming organs. #'s increase in areas of chronic inflamation Nucleus is spherical and eccentrically placed and resemples a wagon wheel, cyto is basophilic only area near golgi isn't. ER is large so is Golgi, |
|
|
Plasma Cell origins and functions distrunces related to # of plasma cells?
|
Come from B-Lymphocytes
Acts to produce humoral antibodies (circulating immunoglobulins) found in R-ER. Hyperglobulinea, agammaglobulinemia Multiple myeloma |
|
|
Hyperglobulinea
|
excess circulating antibodies;high concentrations of plasma cells
|
|
|
agammaglobulinemia
|
complete failur of antibody synthesis, plasma cells do not develop at sites of antigenic stimulation
|
|
|
multiple myeloma
|
neoplasm of plasma cells
|
|
|
Typical Plasma cell, note wagon wheel nucleus
|
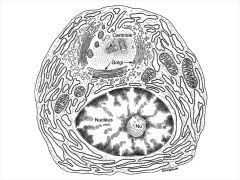
|
|
|
Mast cells places, appearance, origins
|
Common in Blood Vessels
Large ovoid cells, nucleus sm. ovoid, cyto. numerous cyto. granules, water soluble, not seen in H and E selections, granules are basophilic, cospicuous golgi, with membrane bound secretory particales that contain heparin and histamine... Made by mesenchymal-like cells |
|
|
Mast cell Functions
|
Heparin-gives staining properties
Histamine-causes smooth mucle of bronchi to constrict, dilates blood capillaries (vasodilator) increases permiability |
|
|
Anaphylaxis?
|
Occurs when host recieves an antigenic insult a second time
1.Antibodies form as a result of initial insult go to Fc (Ig#) receptors on mast cells. 2. 2nd insult attach to antibodies, stimulate degranulation and release histamine (vasodilation) 3. Respiratory failure |
|
|
FAT CELLS
|
Occur Around loose CT.
Signet ring shape, lots of apparent empty space because lipid is dissolved. Nucleus forms slight buldge at cell surface, thin rim of cytoplasm, each cell has a fine network of reticular fibers. Can see golgi, mito, by Electon Micro Come from undifferentiated mesenchymal Functions::: storage of neutral fats/TG, carb and fat metabolism, release of leptin and adiponectin |
|
|
Mononuclear Wandering Cells (visitors from the blood)
|
Monocytes
lymphocytes eosinophils neutrophils |
|
|
Mast Cells
|
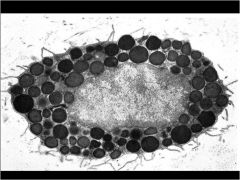
|
|
|
Release of histamine
|
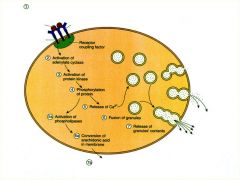
|
|
|
Fat cell
|
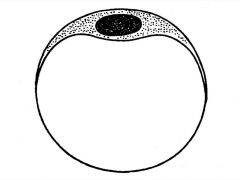
|
|
|
Monocytes
|
Ameboid. migrate from blood to CT and become macrophages
Phago. properties and antigen presenting cells, cell volume increases, so does golgi |
|
|
lymphocytes
|
ameboid, go to inflamtion
Look small round cells dark stain nucleus that takes up most of the cell, thin rim of cytoplasm Acts as 1. T-lymphocytes(long lived, initiate Cell mediate Immune Response. 2.B-lymp(long or short life) related to humoral antibody mediated immune responses, comes out under antigenic stimulus creat plasma cells. 3. NK lymph. cytotoxic killing mechanism |
|
|
Eosinophils
|
Ameboid, common in mamary gland, lung, lamina propria of SI.
bilobed nucleus, large crystalline material in granules. Fights parasites, allergic hypersenitivity. Appear to destroy immune complexs, control local responses to allergic reactions |
|
|
neutrophils
|
ameboid, multilobed nucleus granular cytoplasm,
First line of cellular defense against invasive organisms Active Phagocyte |
|
|
Mononuclear phagocyte Systems
|
Widespread system of phagocytic cells, uses to identify cells compromising immune system.
Arise frome common stem cell in one marrow, have FC and complement receptors, macros. of spleen, lymph nodes, thymus, bone marrow, CT, Kupffer cells (liver) microglia **CNS)** Langerhans cells of skin, osteoclast of bone. ALL PHAGOCYOSIS and ANTIGEN PRESENTATION (APC's) |
|
|
Vital staining
|
phagocytic cells take up dye particles and thus become identifiable
|
|
|
Mesenchyne??
|
Precursor of all connective tissue in the body
|
|
|
Adult connective tissue
|
Loose (areolar) CT
Dense CT Adipose CT Reticular Connective tissue |
|
|
Loose (areolar) CT
|
Irregularly arranged, looks cobwebby with loose interlacing fibers, has spaces (areolae) cause of ground substances
Constituents Most common cellsFibroblasts and marcrphages Key for many Collagenous fibers lesser extent elastic +reticular. Also present in amorphous ground substance. Fills in many otherwise unoccupied spaces, binds to muscle, surrounds blood vessels and nerves |
|
|
Dense Connective tissue types?
|
Irregular and regular
|
|
|
Dense connective tissue can be
|
Irregular and Regular
|
|
|
Irregular dense CT?
|
Costituent fibers that are irregularily arranged
Made of: Fibers (coarse collagenous mostly) with some elastic and reticular present. They are primarily parts of fibroblasts or macrophages and have ground substances. dermis of skin, periosteum, capsules of certain organs |
|
|
Regular Dense CT
|
Collagenous or elastic fibers are lined up in // arrays. Hold tension well in one way. Fibroblast is predominant cell, lies between fibers
Predominantly Collagenou: Tendons, ligaments, fibroblast nuclui are really long and flattened btw fiber Pred. elastic:vocal cords, ligamenta flava, suspensory ligaments of penis. Fibroblast has rounded or oval nuclei between fibers |
|
|
Adipose Connective Tissue
|
Numerous fat cells in lobes or groups, surrounded by fine collagenous, reticular, and elastic fibers.
Found in; subcutaneous CT, kidneys, emesenteries, bone marrow, etc. Absent: eyelids, ears, penis, dorsum of hands FUNCTION: Nutritional, mechanical functions, heat conservation, endocrine |
|
|
Reticular CT
|
Provides a fibrillar network of lymphoid tissues
Retucular cells are stellate shapped(may be multipotential) produce reticular fibers. |

