![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A. Loose Connective Tissue, Areolar
B. Gel like matrix with all three fiber types C. Wraps and cushions organs D. Under Epithelia of body E. Dots- Fibroblast nuclei, thin dark fibers- elastic fibers, thicker lighter fiberst are elastic fibers |

A: What kind of tissue is this?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? E. What are the dots and the different types of fibers? |
|
|
A. Loose connective tissue, adipose
B. Closely packed adipocytes with nucleus pushed to the side C. Provides reserve fuel D. Under skin, around kidneys and eye balls; within abdomon and beasts |
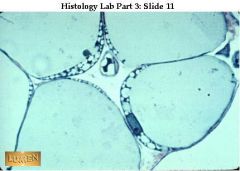
A. What kind of tissue is this?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Loose connective tissue, reticular
B. Network of reticular fibers C. Supports white blood cells, mast cells and macrophages D. Lymphoid organs |
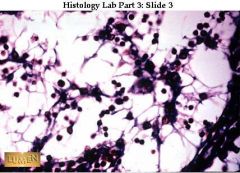
A. What kind of tissue is this?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Dense regular connective tissue
B. Parallel collagen fibers; major cell type fibroblast C. Attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; bones to bones; withstands stress when applied in one direction D. Tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses |

A. What kind of tissue is this?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A: Dense irregular connective tissue
B. irregularly arranged collagen fibers, some elastic; major cells are fibroblast C. Withstand tension exerted in many directions D. Dermis of skin, submucosa of digestive tract, organs and joints |
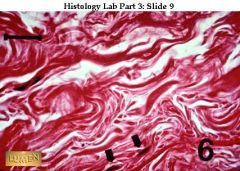
A: What kind of tissue is this?
B. Description? C: Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Hyaline Cartilage
B. Collagen fibers form an imperceptible network, chondroblasts produce the matrue and when mature lie in lacunae C. Supports and reinforces, resists compression and stress D. Covers ends of long bones in joint cavities, cartilage of ribs, nose, trachea and larynx |
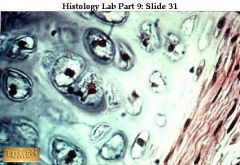
A. What kind of tissue is this?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Elastic Cartilage
B. More elastic fibers then hyaline C. Maintains shape and structure while allowing flexibility D. External Ear and epiglottis |
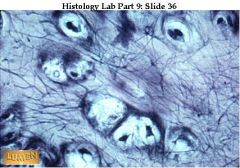
A. What tissue is this?
B Description? C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Fibrocartilage
B. Similar to hyaline with more thick collagen fibers C. Tensile strength, absorbs compressive shock D. Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint |
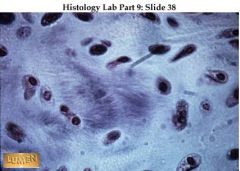
A. What kind of tissue is this?
B. Description C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Bone, osseous tissue
B, Hard, calcified matrix, many collagen fibers; osteocytes (tree) C. supports and protects, provides levers for muscle, stores calcium D. Bones |

A. What kind of tissue is this?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Blood
B. Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix C. transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes and other D. Contained in blood vessels |
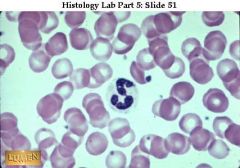
A. What kind of tissue?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Nervous tissue
B. Neurons are branching cells C. transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and effectors which control their activity D. Brain, spinal cord, nerves |
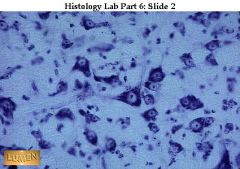
A. What kind of tissue?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Skeletal muscle
B. long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells, obvious striations C. Voluntary movement D. skeletal muscle attached to bones |
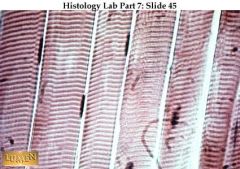
A. What kind of tissue is this?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? |
|
|
A. Cardiac Muscle
B. Branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells C. propels blood through circulation D. Walls of the heart |
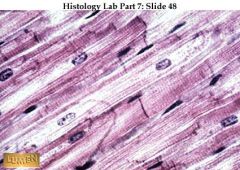
A. What type of tissue is this?
B. Description? C. Function? D. Location? |

