![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
SSS Postulate |
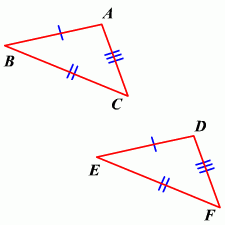
Two triangles are congruent if the 3 sets of corresponding sides are congruent. Stands for Side-Side-Side |
|
|
SAS Postulate |
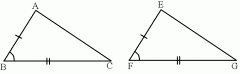
Two triangles are congruent if 2 sides and the angle in between on one triangle are congruent to 2 sides and the included angle of another triangle. Stands for Side-Angle-Side |
|
|
ASA Postulate |
Two triangles are congruent if 2 angles and the side in between them on one triangle are congruent to 2 angles and the side in between of another triangle. Stands for Angle-Side-Angle |
|
|
AAS Theorem |
If 2 angles and a non-included side of one triangle are congruent to 2 angles and a non-included of another triangle. Stands for Angle-Angle-Side |
|
|
HL Theorem |
Two RIGHT triangles are congruent if the hypotenuse and a leg of a right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and a leg of another right triangle. Stands for Hypotenuse-Leg |
|
|
Congruent Figures |
Figures that have the same size and shape. |
|
|
Congruency Transformations |
Transformations that result in congruent figures: Translations, Reflections, and Rotations |
|
|
Corresponding Angles |
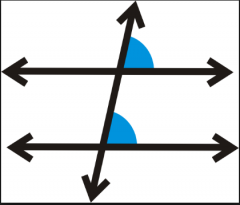
Angle pairs in the same corners but on different parallel lines.
|
|
|
Alternate Interior Angles |
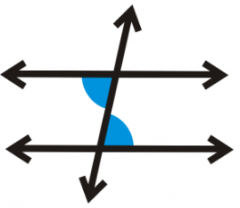
Angle pairs on the inside of the parallel lines and opposite sides of the transversal. |
|
|
Alternate Exterior Angles |
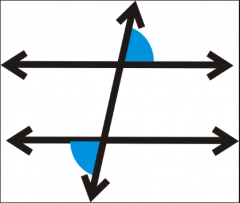
Angle pairs on the outside of the parallel lines and opposite sides of the transversal. |
|
|
Equilateral Triangle |
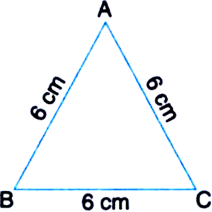
Triangle with three sides of equal length and three angles of equal measure. |
|
|
Isosceles Triangle |
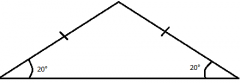
Triangle with two sides of equal measure and congruent base angles. |
|
|
Scalene Triangle |
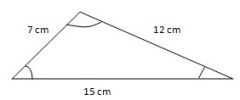
Triangle with 3 different side lengths. |
|
|
Obtuse Triangle |
Triangle with one angle larger than 90°. |
|
|
Right Triangle |

Triangle with one 90° angle. |
|
|
Acute Triangle |
Triangle with three angles less than 90°. |
|
|
Triangle Angle Sum Theorem |
The angles of any triangle add up to 180°. |
|
|
Perpendicular Bisector |
A line that divides a line segment into two equal parts. It also makes a right angle with the line segment. |
|
|
Transversal |
A line that cuts through two or more lines. |
|
|
Supplementary Angles |
Angles whose measures add up to 180°. |
|
|
Complementary Angles |
Angles that add up to 90°. Together they form a right angle. |
|
|
Vertical Angles |
The opposite angles created by 2 intersecting lines are congruent. |
|
|
Adjacent Angles |
Two angles that share a side and vertex. |
|
|
Congruent Angles |
Angles with equal measure. |

