![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
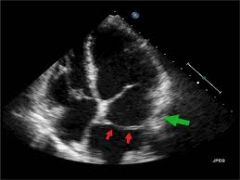
What does this show?
|
cor triatrium
|
|
|
How is cor triatrium described?
|
appearance of three atria
|
|
|
What is causing this appearance?
|
a membrane above the MV
|
|
|
What may occur in severe cases of cor triatrium?
|
supravalvular MS
|
|
|
Which side is usually affected by cor triatrium?
|
left
|
|
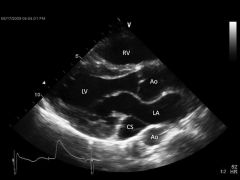
What does this show?
|
dilated coronary sinus
|
|
|
What defect often manifests with dilated coronary sinus?
|
persistent left SVC
|
|
|
Is persistent left SVC common or rare?
|
most common venous malformation
|
|
|
What is best method for confirming the presence of plsvc?
|
contrast injection
|
|
|
Where should contrast be injected when looking for plsvc?
|
left arm
|
|
|
Where does contrast appear and when during study to detect plsvc?
|
coronary sinus first, confirming diagnosis
|
|
|
What is a third type of septal defect after ASD & VSD?
|
atrio ventrical septal defect
|
|
|
What other term is used to describe av septal defect?
|
endocardial cushion defect (ECD)
|
|
|
What condition is it often associated av septal defect?
|
Down Syndrome
|
|
|
What else is Down Syndrome called?
|
Trisomy 21
|
|
|
What are the two types of ECD?
|
1. complete canal
2. partial or incomplete |
|
|
What is seen with complete canal?
|
VSD
ASD common AV valve |
|
|
What is seen with incomplete canal?
|
only an ASD OR a VSD
two AV valves cleft MV |
|
|
What is an anomaly of IAS that is not an actual ASD?
|
interatrial septal aneurysm
|
|
|
How is interatrial septal aneurysm defined?
|
mobile septal protrusion 10-15 mm past IAS plane
|
|
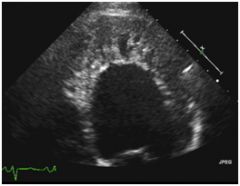
what anomaly is this?
|
non compacted lv
|
|
|
How is the appearance of non compacted lv described?
|
spongy
|
|
|
What is non compacted lv a malformation of?
|
myocardium
|
|
|
What else is present with non compacted lv?
|
significant trabeculation with systolic dysfunction
|
|
|
What other condition might non compacted lv be confused with?
|
dilated cardiomyopathy with lv thrombi
|
|
|
One uncommon anomaly, considered a cyanotic defect is..........and what acronym is used?
|
transposition great arteries
d-TGA |
|
|
What happens with TGA?
|
pulmonary system and venous system are independent instead of interdependent
|
|
|
What is meant by transposition?
|
the aorta comes off of the rv and the pulmonary artery off the lv
|
|
|
What keeps a tga patient alive?
|
pfo and pda and maybe vsds
|
|
|
What path does blood flow follow with tga?
|
system flow returns to RA, RV, aorta & body
pulmonary flow returns to la, lv, pulmonary artery lungs |
|
|
How is tga corrected?
|
anatomic RV becomes systemic ventricle
anatomic LV becomes pulmonary ventricle baffles redirect blood flow in the LA |
|
|
What is the name of the procedure to correct tga?
|
Mustard
|
|
|
What acronym is used to refer to a corrected d-TGA?
|
l-TGA
|
|
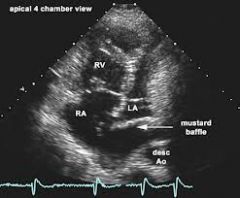
what is shown
|
mustard procedure result
|

