![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CPU |
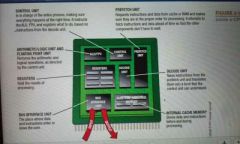
Central processing unit/microprocessor |
|
|
3 computer coding schemes |
ASCII EBCIDIC Unicode |
|
|
ASCII |
Traditionally used on personal computers. 7-bit code, but there are some 8-bit versions. 8-bit = 256 characters. |
|
|
EBCIDIC |
Developed by IBM for mainframe use. |
|
|
Unicode |
Universal international coding standard. Designed to be used for text in any modern or ancient language. Quickly replacing ASCII as primary coding scheme. |
|
|
RAM |
Random Access Memory Chips connected to the motherboard that provide a temporary location for the computer to hold data and program instructions while they are needed. |
|
|
ROM |
Read Only Memory Nonvolatile chips located on the motherboard into which data or programs have been permanently stored. |
|
|
Registers |
High- speed memory built into the CPU that temporarily stores data during processing. |
|
|
BUSES |
An electronic path on the motherboard or within the CPU or other computer component along which data is transferred. |
|
|
Cache |
A group of fast memory circuitry located on or near the CPU to help speed up processing. 3 levels. Level 1 being the fastest. |
|
|
Word size |
Amount of data a CPU can manipulate at one time. Typically 32 or 64 bits |
|
|
Bandwidth |
Amount of data that can be transferred by a BUS in a given time period. |
|
|
Flash memory |
Nonvolatile memory chips that can be used for storage. |
|
|
Pipelining |

Processing with and without pipelining |
|
|
Nanotechnology |
Science of creating tiny computers and components less than 100 nanometers in size. |
|
|
Quantum computing |
Applies the principles of quantum physics and mechanics to computers. * Utilizes atoms or atomic nuclei working together as quibits (quantum bits) * Quibits function as processor and memory - can represent more than 2 states. |

