![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adding two 1s in the same column. |
Sometimes binary addition will require you to carry over values to the next colour. If you come across the situation where you will need to add 1+1, you create 10. |
|
|
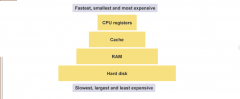
Cache. |
Cache is a small amount of memory which is a part of the CPU. Closer to the CPU than RAM. It temporarily holds instructions and data that the CPU is likely to reuse. |
|
|
Level 1 cache. |
Level one cache is the smallest and fastest to access, around 8 to 64KB. |
|
|
Level 2 & 3 cache. |
Level 1 & 2 cache are larger then level 1. They are built between the CPU and RAM and take slightly longer to access. |
|
|
Processor types. |
CISC & RISC. |
|
|
CISC Processors. |
CISC (Complex instruction set computing) CPUs |
|
|
RISC Processors. |
RISC (Reduced instruction set computing) CPUs Combine simple operations from their reduced instruction set, are smaller, slower and consume less energy. |
|
|
Front-side bus (FSB) types: Address bus. |
The address bus sends information about where data needs to go by sending an address to the memory. It only send data from the CPU to RAM in a single direction. |
|
|
Front-side bus (FSB) types: |
This sends data to the memory or receives data from the memory. Data can flow both ways along the data bus. |
|
|
Data types. |
CPU registers |

