![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
131 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
14 CFR Part 101 |
FAA regulations for recreational drone use. |
|
|
|
14 CFR Part 107 |
FAA commercial regulations for drone use. |
|
|
|
Less than 55 lbs. |
Part 107 sUAS weight limit |
|
|
|
Unmanned aircraft |
Without possibility of direct human intervention within or on aircraft. |
|
|
|
Emergency reporting protocol |
Upon request of FAA, send written report. |
|
|
|
Maximum altitude, no building |
400 feet AGL |
|
|
|
Maximum altitude, building |
Within 400' of structure, 400' AGL higher than building |
|
|
|
Speed limit (mph) |
100 |
|
|
|
Speed limit (knots) |
87 |
|
|
|
Visibility minimum distance |
3 statue miles |
|
|
|
Ceiling minimum height |
500 AGL above predicted flight altitude. For 400' maximum AGL, that means 900'. |
|
|
|
Right of way |
Must yield to all manned aircraft. |
|
|
|
See and avoid requirements |
Only eyeballs |
|
|
|
Operations over people |
Are not allowed for "non-participants". |
|
|
|
VLOS |
Visual line of sight |
|
|

Remote operation from vehicle |
(A) Compliant |
|
|
|
Moving vehicle requirements |
Not driver VLOS Sparsely populated Not from within aircraft |
|
|
|
Drop items from drone |
- Precautions taken to avoid damage to person or property -same state -cannot operate from moving vehicle |
|
|
|
Hazardous materials |
Cannot be carried by drone, except if providing active power, as in the case of a battery. |
|
|
|
Alcohol requirements |
Not within 8 hours Under influence .04% Affects mental or physical capabilities |
|
|
|
Alcohol test |
Must submit to request for testing or lose certificate |
|
|
|
Change of address |
Within 30 days after moving |
|
|
|
CoW |
Certificate of Waiver |
|
|
|
Advance notice of filing CoW to FAA |
90 days |
Days |
|
|
Regulatory (controlled) airspace |
A, B, C, D, E |
Letters |
|
|
Non regulatory airspace |
G, military |
Letters |
|
|
Chart Supplemental U.S. |
Resource to determine type of airspace |
|
|
|
NOTAMs |
Notice to airmen |
|
|
|
TFR |
Temporary flight restrictions |
|
|
|
Section Aero Aeronautical Chart |
Most used for determining airports, airspace |
|
|
|
TAC |
Terminal Area Chart |
|
|
|
Most comprehensive info given on airport |
Chart Supplement |
Document |
|
|
How to check NOTAMs? |
Faa.gov, flight service station (FSS), 1800WXbrief.com |
|
|
|
NTAP |
Notices to airmen publication |
|
|
|
NTAP contents |
All current NOTAMs |
Notices to airmen publication |
|
|
AIM |
Aeronautical Information Manual |
|
|
|
AIM purpose |
Official guide to basic flight info and ATV procedures. |
Aeronautical Information manual |
|
|
Class A |
18000 feet MSL to FL 60 (60,000') |
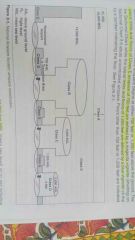
|
|
|
Class A map |
Not listed on sectionals |
|
|
|
Class B |
Varies. Requires ATC clearance |
|
|
|
Class B map |
Blue, with delimiting arcs, radials, and altitudes |
|
|
|
Class B primary |
Large airports. Pilot requires private pilot certificate |
|
|
|
Class C |
Two circles. - Inner 5 NM miles from surface to 4000 AGL - Outer 10 NM 1200 AGL to 4000 |

|
|
|
Class C map |
Solid magenta lines |
|
|
|
Class D |
Surface to 2500 AGL 4 NM radius Actual space defined on sectional |
|
|
|
Class D map |
Dashed blue Numbers showing ceiling |
|
|
|
Class D weather restrictions |
Ceiling less than 1000' Visibility less than 3 statute mile |
|
|
|
Class E |
700 or 1200 feet. 14500 to 17999 feet. |
|
|
|
Class E map, 700 feet AGL |
Magenta shading |
|
|
|
Class E map, 1200 feet |
No shading, or blue next to glass G. |
|
|
|
Airway |
Class E from 1200 feet up. 4nm side of centerline. Blue. |
|
|
|
Class G |
Surface to class E if no ATC responsibility |
|
|
|
Restricted area |
No entry without permission. |
|
|
|
MOAs |
Military operations areas Contact controlling agency |
|
|
|
National park restrictions |
2000 feet above surface requested |
|
|
|
MTRs |
Military training route Below 10000' MSL >250 knots |
|
|
|
MTRS below 1500 AGL |
Four digits, VR1351 |
|
|
|
MTRS above 1500' |
Three numbers, IR411 |
|
|
|
When ATC clearance is required |
B, C, D, and lateral surface of E |
|
|
|
CTAF |

Common traffic advisory frequency |
|
|
|
Latitude |
Parallel to equator |
|
|
|
Longitude |
Pole to pole |
|
|
|
Airports with control towers, map |
Shown in blue |
|
|

Height, in MSL and AGL |
3130 MSL 1089 AGL |
|
|
|
LOA |
Letter of Agreement Establishes UAS operating procedures with ATC. |
Letter of Agreement |
|
|
Recommended entry point for airtraffic pattern |
45° to the midpoint of downwind leg at traffic pattern altitude |
|
|
|
Traffic pattern, draw |
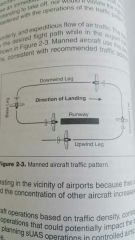
|
Counter clockwise |
|
|
SIDA |
Security identification display area |
|
|
|
SIDA requirements |
Airport-approved ID. |
Security identification display area |
|
|
Threshhold |
Beginning of suitable landing surface |
|
|
|
Displaced threshhold |
Threshhold not at the start of the runway. |
|
|
|
Displaced threshhold markings |
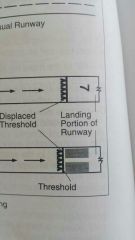
Arrows |
|
|
|
Stopway |
Emergency runway ending |
|
|
|
Stopway markings |

Chevron |
|
|
|
Closed runway marking |
X |
|
|
|
Taxiway marking |
Continously yellow centerline |
|
|
|
Holding position marker |
Four yellow lines Two solid Two dashed |
|
|
|
Mandatory instruction sign |
Red background, white text |
|
|
|
Location sign |
Black background, yellow text |
|
|
|
Direction sign |
Yellow backgrouns, black text. At intersection. |
|
|
|
Destination sign |
Yellow backgrouns, black text, and arrow |
|
|
|
Information sign |
Yellow background, black text |
|
|
|
Runway distance sign |
Black background, white number |
|
|
|
Runway 9 is on a heading of: |
90 magnetic |
|
|

|
B - West |
|
|

|
C |
|
|

|
A |
|
|
|
Purpose of runway hold position sign |
Denotes intersecting runways |
|
|
|
Document showing airport signs and markings |
AIM |
|
|
|
Most midair collisions occur during what weather? |
Clear days |
|
|
|
Antenna tower avoidance |
2000' horizontally |
Feet |
|
|
Bird collision reporting |
ATC |
|
|
|
Every physical process of weather is accompanied by |
Heat exchange |
|
|
|
What causes variation in altimeter settings? |
Unequal heating of earth's surface |
|
|
|
Where do thermal currents develop? |
Dry fields or areas |
|
|
|
Effects of building on wind gusts |
Change direction and speed (turbulence) |
|
|
|
Front change includes change in |
Wind direction. |
|
|
|
What is primary concern with cold front? |
Thunderstorms and heavy rain. |
|
|
|
Stable air mass effect on visibility |
Poor surface visibility |
|
|
|
Moist unstable air characteristics |
Turbulent and showers |
|
|
|
Stable air |
Poor visibility and steady precip |
Visibility and precip |
|
|
Actual lapse rate |
Measurement to determine stability of atmostphere. |
|
|
|
What decreases stability of air mass? |
Warming from below |
|
|
|
Minimum visibility requirement |
3 miles |
|
|
|
Minimum cloud distance requirement |
500' below 2000' horizontal |
|
|
|
Cumulus stage of thunderstorm danger |
Updrafts |
|
|
|
Mature stage of thunderstorm |
Rain Updrafts and downdrafts Most intense stage |
|
|
|
Dissipating stage of thunderstorm |
Downdrafts |
|
|
|
Squall line thunderstorms |
Most hazardous thunderstorms to UAV |
|
|
|
Nonfrontal, narrow band of active thunderstorms |
Squall line |
|
|
|
Landing hazard near thunderstorms |
Wind sheer |
|
|
|
Duration of microburst |
Seldom longer than 15 mins |
|
|
|
Ice pellets at surface is evidence that |
There is a temperature inversion. |
|
|
|
Requirements for structural icing |
Visible water 32F or colder |
Two things |
|
|
Highest ice accumulation rate |
Freezing rain |
|
|
|
Radiation fog |
Caused by warm, moist air over low flatland areas on clear, calm nights. |
|
|
|
Advection fog |
Moist air moves over colder ground or water. Common in coastal areas. |
|
|
|
Upsloap fog |
Moist air is cooled to dew point as it moves upsloap, pushed by wind. |
|
|
|
Low level turbulence and icing caused by - fog. |
Steam fog |
|
|
|
Steam fog |
Cold, dry air passes over warm water |
|
|
|
Steam fog hazards |
Turbulence, icing. |
|
|
|
High density altitude effects |
Decreased effectiveness |
|
|
|
OAT |
Outside air temperature |
|
|
|
Warmer OAT effects |
Higher altitude pressure |
Outside air temperature |
|
|
Standard temp and pressure for sea level |
15C (59F) and 29.92" Hg (1013.2 mb) |
|
|
|
What increases density altitude? |
Increase in ambient temp |
|
|
|
Standard briefing |
Complete weather overview |
|
|
|
ASOS |
Automated Surface Observing System |
|
|
|
AWOS |
Automated Weather Observing System |
|
|
|
METAR |
International weather reporting code |
|
|
|
Lateral dimensions of Class D airspace is based on |
Instrument procedures for which the controlled airspace is established. Differs based on airport. |
|

