![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Order, response to stimuli, reproduce, grow and develope, regulation, homeostasis, energy processing |
Properties of life |
|
|
Dumb King penises carry off ******* giant spiders |
Domain kingdom phylum class order family genus species |
|
|
What are the three domains |
Archaea bacteria and Eukarya |
|
|
Proteins are made up of |
Amino acids |
|
|
Enzyme is a |
Protein |
|
|
DNA and RNA are made up of |
Nucleotides |
|
|
Cells are classified into |
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes |
|
|
Organelles that degrade macromolecules |
Perform photosynthesis and cellular respiration |
|
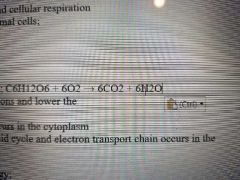
Formula for? |
Respiration |
|
|
Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions and lower |
Activation energy |
|
|
Where does glycolysis occur |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
Where does the citric acid cycle and electron Transportation chain occur |
The mitochondria |
|
|
Cell energy is ATP which loses a |
Phosphate to release energy |
|
|
What are the two stages of photosynthesis |
The light reaction on the thylakoids, and the Calvin cycle in the stroma |
|
|
A somatic cell contains two matching sets of chromosomes and it's known as |
Diploid |
|
|
Sex cells have one set of chromosomes are known as |
Haploid |
|
|
Matching pairs of chromosomes in a diploid organism are called |
Homologous chromosomes |
|
|
What is a duplicated chromosome called |
Sister chromatid |
|
|
The cell cycle includes |
Interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis |
|
|
The three stages of interphase are |
G1, s, G2 |
|
|
Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase |
Mitosis |
|
|
Meiosis consists of one round of blank and two rounds of blank |
1, chromosome duplication 2, nuclear division |
|
|
Homologous pairs separate in |
Meiosis 1 and the cell become haploid |
|
|
Sister chromosomes separate in |
Meiosis 2 |
|
|
Crossing over results in new combinations of |
Genes or variations |
|
|
Independent assortment occurs during |
Metaphase 1 |
|
|
homologous chromosomes occur in...a |
anaphase 1 |
|
|
Sister chromatids are separated in |
Anaphase 2 |
|
|
Monohybrid cross results in a |
3:1 phenotypic ratio |
|
|
Dihybrid cross results |
9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio |
|
|
Alleles refer to |
Different variants for the same gene |
|
|
Incomplete dominance leads |
1:2:1 phenotypic ratio |
|
|
DNA is made up of |
Polymers of nucleotides |
|
|
DNA bases consist of |
A t c g |
|
|
RNA bases are |
Aucg |
|
|
Transcription leads to |
Messenger RNA |
|
|
The MRNA is transported into the |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
Transcription takes place in |
Nucleus |
|
|
Translation involve synthesis of |
Amino acid using the MRNA |
|
|
Each amino acid is defined by a three nucleotide sequence called the |
Triplet codon |
|
|
The three steps of polymerase Chain Reaction are |
Denaturing, annealing, and extension |
|
|
Plasmids with foreign DNA inserted into them are called |
Recombinant DNA |
|
|
Restriction enzymes are used to cut the |
DNA of the plasmid and the foreign DNA |
|
|
Dolly the sheep was the result of |
Nuclear transfer |
|
|
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells and can develop |
Many different types of cells |
|
|
Using a virus to get the correct gene into a cell is |
Gene therapy |
|
|
When two species evolve in different directions from a common point is called |
Divergent evolution |
|
|
The sum of all alleles in a population is |
Gene pool |
|
|
The wing of bird and an arm of man are examples of |
Homologous |
|
|
Mutation is a primary source for |
New unique genes |
|
|
Evolution that occurs as a result of a chance events is called |
Genetic drift |
|
|
Biogeography describes the distribution patterns |
Living things around the world |
|
|
The evolutionary history and relationships among a species or group of species |
Phylogeny |
|
|
A branch point in a phylogenetic tree describes a |
New lineage implies evolution |
|
|
When two lineages arise from the same Branch went there called |
Sister taxa |
|
|
Genes for ribosomal RNA are used to determine the relationships between different |
Species like Archaea and bacteria |
|
|
Shared derived traits are important to |
Cladistics |
|
|
Transformation, transduction, and conjugation are the three types of |
DNA transfer |
|
|
DNA comparisons of shown that fungi more closely related |
Animals than plants |
|
|
The vegetative body of a fungus is called |
Thallus and can be unicellular or multicellular |
|
|
The vegetative stage of fungi is made up of mass of thread-like structures called |
Hyphae |
|
|
Fungi produce spores in both |
Sexual and asexual reproduction |
|
|
A cap of cells at the shoot tip or root tip that divide continuously throughout the life of the plant |
Apical meristem |
|
|
Transports water and nutrients |
Xylem tissue |
|
|
Transports sugars proteins and other solutes |
Phloem tissue |
|
|
Stamen, anther, and filament |
The male flower parts |
|
|
Carpel, stigma, style, and ovary |
female flower parts |
|
|
Endosperm tissue serves as a food source for the |
Plant embryo |
|
|
Ectoderm mesoderm and endoderm |
Three germ layers, AKA triploblastic |
|
|
Cnidarians have two distinct body plans |
Polyp and Medusa |
|
|
Evolution significance of amniotic membrane |
Less dependence on water and able to survive on dry land |
|
|
Functional units of the kidneys |
Nephrons |
|
|
Nobody can leave these big bitches alone |
Nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli |
|
|
The concentration of smooth muscles that moves food down the esophagus |
Peristalsis |
|
|
For the digestion of proteins, fats and carbohydrates is |
Small intestine |
|
|
Capillary exchange of gases occurs in |
Lung alveoli from diffusion |
|
|
The heart has |
To atriums and two ventricles |
|
|
Reverse transcriptase enzymes help in synthesizing |
DNA from viral RNA |
|
|
Cell mediated immune response is controlled by |
T cells |
|
|
Humoral immune response is controlled |
B cells |
|
|
T cells undergo maturation in the |
thymus gland |
|
|
B cells secrete proteins called blank that bind to and inactivate antigens |
Antibodies |
|
|
T cells directly attack |
Foreign particles |
|
|
Semen includes sperm and secretions from |
Prostate gland, seminal vesicles, and bulbourethral gland |
|
|
GnRH causes the release of FSH and LH hormones from |
Anterior pituitary |
|
|
A binds to T or U in RNA, C binds to G |
Yeee |

