![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
197 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 methods of diagnosis in tcm |
1. observation
2. smelling / hearing 3. inquiry 4. palpation |
|
|
8 principles of TCM
|
excess – deficiency
internal – external hot – cold yin – yang |
|
|
desire to drink indicates...
|
internal heat
qi level |
|
|
malar flush indicates
|
heat
|
|
|
floating and rapid pulse indicates
|
excess, heat
|
|
|
heat felt all day indicates
|
excess, heat
|
|
|
dry stool with no pain indicates
|
deficiency heat
|
|
|
pain indicates
|
excess
|
|
|
tongue diagram
|
KD BL Intestines SP/ST LU HR then GB/LIV on sides
|
|
|
Aspects to consider for tongue diagnosis include...
|
coating
colour shape movement moisture texture |
|
|
colours of the tongue and what they indicate
|
red – heat
pink – normal pale – deficiency blue – cold purple – stasis crimson red |
|
|
tongue coating and what they indicate (those most likely on comprehensive)
1. red and no coat tongue coating |
- yin deficiency, deficiency heat/empty heat
|
|
|
tongue coating and what they indicate (those most likely on comprehensive)
2. yellow, thick tongue coating |
- internal heat
|
|
|
tongue coating and what they indicate (those most likely on comprehensive)
3. yellow, thick, dry tongue coating |
- internal fire consuming fluids
|
|
|
tongue coating and what they indicate (those most likely on comprehensive)
4. yellow, thin coat tongue coating |
- more superficial, evil heat
|
|
|
tongue coating and what they indicate (those most likely on comprehensive)
5. white, thin tongue coating |
- cold
|
|
|
tongue coating and what they indicate (those most likely on comprehensive)
6. black, cracked and dry tongue coating |
- extreme heat, yin deficiency
|
|
|
nose discharge and what that indicates (those most likely on comprehensive)
1. clear nose discharge |
- cold
|
|
|
nose discharge and what that indicates (those most likely on comprehensive)
2. clear and long term nose discharge |
- LU deficiency
|
|
|
nose discharge and what that indicates (those most likely on comprehensive)
thick and turbid nose discharge |
- phlegm
|
|
|
nose discharge and what that indicates (those most likely on comprehensive)
4. yellow and smelly nose discharge |
- LU heat
|
|
|
nose discharge and what that indicates (those most likely on comprehensive)
5. bloody, foul smelling nose discharge |
- toxic heat
|
|
|
10 questions for clients – treatment intake
|
1. cold/fever
2. sweat 3. head and face, ie. Headache/dizziness 4. thirst 5. appetite/digestion, taste in the mouth 6. stool and urination 7. chest/abdomen/limbs or pain in the body 8. sleep 9. mental/mood/emotions 10. menstruation/libido |
|
|
distending pain
|
LIV
|
|
|
stabbing pain
|
– blood stagnation
|
|
|
burning pain
|
– heat
|
|
|
dull pain
|
– deficiency
|
|
|
heavy pain
|
– phlegm/damp
|
|
|
pain worse on pressure
|
– full/excess condition
|
|
|
Pulses on the right
|
– LU, SP, KD Yang
|
|
|
Pulses on the left
|
– HR, LIV, KD Yin
|
|
|
pulses from distal to proximal
|
– cun, guan, chi
|
|
|
What do the following pulses indicate?
choppy pulse |
– blood stasis
|
|
|
What do the following pulses indicate?
slippery |
– damp
|
|
|
What do the following pulses indicate?
superficial |
– exterior
|
|
|
What do the following pulses indicate?
deep |
– internal
|
|
|
What do the following pulses indicate?
strong |
– excess
|
|
|
What do the following pulses indicate?
wiry |
LIV
|
|
|
What do the following pulses indicate?
thin |
– blood deficiency
|
|
|
What do the following pulses indicate?
weak |
– qi deficiency
|
|
|
what are some of the main causes of pain?
|
what are some of the main causes of pain?
Blood stasis trauma cold damp wind heat deficiency/excess qi stagnation |
|
|
what are the shu transporting points and what are their indications?
|
1. Well – heat, emergency, distal
2. spring – heat 3. shu – heaviness in the joints and pain that comes and goes 4. river – voice, asthma 5. he sea – treats organs, reverse flow of qi |
|
|
What do xi cleft points treat?
|
Blood stasis and pain
LU 6 – acute asthma wind heat blood disorders LI 7 – sore throat face px swelling px in LI channel ST 34 – breast issues, acute epigastric pain SP 8 – blood stagnation in uterus/lower abdo – impt gyne HR 6 – hr px, reckless bleedg SI 6 – severe px along SI channel (sh scap arm), acute contractn and sprain of lumbar BL 63 – acute cystitis, vomiting diarrhea epilepsy intense px obstruction KD 5 - menstrual probs dt def or blood stagnation PC 4 – severe chest px, reckless bleeding in upper jiao, blood stasis chest and hr SJ 7 – not much clinically GB 36 – px skin esp lower limbs, rabies LV 6 – acute cystitis, blood stag or px lower abdo |
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
Radial side of the wrist? |
LI 5 LI 3 LU9 LU7 and local ah shi points
|
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
Low back pain? |
BL23, BL26, BL40, cupping, massage and tuina
|
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
Carpal tunnel syndrome? |
PC7
|
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
Knee pain? |
Xiyan and Heding,
|
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
IT band? |
GB 31 32 33,
|
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
Hip pain? |
GB 29 30, ST 41, peripheral, shu stream
|
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
Tennis elbow? |
LI 11, LI 10,
|
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
Golfers elbow? |
HR 3, SI 8
|
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
Whiplash |
– Du14, bailao, SI3
|
|
|
which points would you use to treat...
Shoulder injury? |
LI 15, SJ 14, SI 10, jian qian, ashi
|
|
|
Which of the channels go to the teeth?
|
LI top
ST lower |
|
|
what is the extra jing well point for KD?
|
Medial side of baby toe
|
|
|
what happens 8 cun above the medial malleolus?
|
LIV crosses over SP
|
|
|
Name the yin channels of the foot from anterior to posterior at the ankle
|
LIV SP KD
|
|
|
Name the yin channels from radial to ulnar
|
LU PC HR
|
|
|
What is the order of the great qi circuit?
|
LU LI ST SP HR SI BL KD PC SJ GB LIV and back to the start
|
|
|
qi flows where it starts thus from:
|
LU to LIV from the middle jiao
|
|
|
where do all yang meridians meet?
|
DU 14
|
|
|
name the channels of the foot
|
yin – KD SP LIV
yang – GB BL ST |
|
|
name the channels of the hand
|
yin – PC HR LU
yang – SJ LI SI |
|
|
what is the common location for yang channels?
|
all yang channels meet (start or end) in the head
|
|
|
what do channels connect with?
|
Zang fu organs
|
|
|
cold bi involves:
|
– very severe pain
– very fixed – worse with cold |
|
|
chest bi includes:
|
– dull pain
– weakness – low back pain |
|
|
Bi due to blood stagnation:
|
– stabbing pain
– stiffness – nodules |
|
|
Heat bi symptoms are:
|
– worse with heat
|
|
|
Wind bi symptoms are:
|
– moving pain
|
|
|
Damp bi symptoms are:
|
– heaviness,pain
– swollen – fixed – numbness |
|
|
Treatment for the following case – man shovels snow in the cold – symptoms would be cold and blood stasis
|
– moxa, cupping, tuina and acupuncture
|
|
|
what are the main needling techniques ?
|
1. 5 needling
- LU, superficial, treats skin 2. leopard spot - poke to bleed, HR, blood vessels/vessels 3. joint needling - joints, rheumatic pain and tendons, LIV 4. valley-union – Hegu - flip needle directions, treats muscles 5. shu point / transport - treat bone and kidneys, touch the bone?! |
|
|
what is NADA protocol, and what points are involved
|
– auricular acupuncture for addiction
– 5 pts – shen men, LIV, KD, sympathetic and LU2 |
|
|
what are the indications for electrical stimulation?
|
– pain
– inflammation – depression/psychological – paralysis/flaccidity |
|
|
what are the functions of moxabustion?
|
– warming
– dispel cold – strengthen yang – tonify/disperse – move blood |
|
|
what barriers can be used for moxabustion?
|
– salt
– ginger – garlic – cakes |
|
|
what are indications for cupping?
|
– blood stagnation
– pain – damp cold |
|
|
what are ci in terms of bleeding?
|
– pregnancy
– blood deficiency – haemophilia |
|
|
what are indications for bleeding?
|
– loss of consciousness
– heat – blood stagnation |
|
|
ci for pregnancy
|
– LI4 SP6 BL67 GB21 BL60, abdominal and low back area
|
|
|
ci for treatment
|
– hungry
– drunk – exhaustion after a big meal |
|
|
no dai qi sensation?
|
– not on point
– improper depth – poor manipulation – deficiency |
|
|
what are the 5 basic dai qi sensations?
|
– heaviness
– achiness/dull pain – soreness – numbness – distending |
|
|
Main angles of the needle
|
– perp – 90 degrees
– oblique – 45 degrees – transverse – along the skin |
|
|
name the parts of the needle
|
tail, handle, root, body, tip
|
|
|
needling techniques – tonification and sedation
– with or against the channel |
with is tonifying, vs is reduction
|
|
|
needling techniques – tonification and sedation
– twirling |
reinforcing is twirling slowly, reduction is fast
|
|
|
needling techniques – tonification and sedation
– thrust |
tonification -heavy thrust, lift slowly
sedation - slow thrust, force when lifting |
|
|
needling techniques – tonification and sedation
– in and out |
tonification - slow in, fast out
sedation - fast in, slow out |
|
|
needling techniques – tonification and sedation
– inhalation – |
tonification - insert needle exhale
sedation - insert needle inhale |
|
|
needling techniques – tonification and sedation
– open /close hole |
tonification - close
sedation - open |
|
|
needling techniques – tonification and sedation
– burn mountain, cool heaven |
– tonification is 9x thrust and lift light,
- for sedation it is 6x thrust light and lift with force |
|
|
the emotions related to the organs
anger |
LIV
|
|
|
the emotions related to the organs
joy |
HR
|
|
|
the emotions related to the organs
sadness |
LU
|
|
|
the emotions related to the organs
anxiety/worry |
SP
|
|
|
the emotions related to the organs
fear |
KD
|
|
|
what are the external pathologies?
|
wind, fire, damp, dry, summer heat, cold
|
|
|
names of the extraordinary organs
|
– uterus
– bones – GB – marrow – brain – blood vessels |
|
|
what are the four seas and related area?
|
1. blood – LIV
2. marrow – brain 3. water and grain – ST 4. qi – chest |
|
|
describe jing fluids
|
– thin
– saliva – moistens skin and muscles – clear – sweat and tears |
|
|
describe ye fluids
|
– thick
– stored in the joints and orifices |
|
|
the 2 types of fluid are:
|
ye, jing
|
|
|
what are the pathologies of blood?
|
– stagnation
– escape – deficiency – heat/cold – dryness |
|
|
what is post heaven?
|
– brought into the body
|
|
|
what is pre-heaven?
|
– genetic/dna
|
|
|
what are the functions of KD?
|
– water passages
– lower orifices – essence – growth – pre heaven – gate of vitality |
|
|
which organ is involved?
– stores blood? |
LIV
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– pre heaven? |
KD
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– dredge and discharge? |
LIV
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– post heaven? |
SP
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– controls blood in the vessels? |
HR
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– grasping? |
KD
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– controls contraction? |
LIV
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– house of hun? |
LIV
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– transporting/transforming? |
SP
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– raising function? |
SP
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– strength and skills? |
KD
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– holding blood in the vessels? |
SP
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– controls muscles? |
SP
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– house of Ye? |
SP
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– governs qi? |
LU
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– willpower? |
KD
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– circulation? |
HR
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– diffuse and descending? |
LU
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– house of shen? |
HR
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– governs blood? |
HR
|
|
|
which organ is involved?
– house of Po? |
LU
|
|
|
relationship between qi and blood includes:
|
1. qi moves blood
2. blood is the mother of qi 3. qi holds blood (qi is the commander of blood) 4. qi produces blood |
|
|
functions of blood include:
|
moisten / nourish
mental activities |
|
|
name 4 qi pathologies
|
sinking
prolapse rebellious stagnation |
|
|
name 6 main functions of qi
|
1. promotion – growth/development
2. warming 3. defending 4. transporting blood 5. transforming food into qi 6. consolidation – controlling gates like sweat |
|
|
describe qi production
|
we have congenital qi – yuan qi, and acquired qi – zong ying and wei qi – both depend on each other for production and nourishment
i) yuan qi stimulates functional activities of the zang fu organs and associated tissues – that produces acquired qi --- * yuan qi is the material foundation for the production of acquired qi ii) acquired qi nourishes and supplements congenital qi ...also have done a diagram |
|
|
what is qi?
|
Fundamental substance, foundation of functional activities
|
|
|
cycles with healthy relationships and cycles with unhealthy relationships
|
cycles with healthy relationships
generating and controlling (restoring) cycles with unhealthy relationships insulting (counteracting) and overacting so generating is to over-restraining as controlling is to counteracting |
|
|
name and the respective element of the zang fu organs
|
5 zang organs
1. LIV – wood 2. HR – fire 3. SP – earth 4. LU – metal 5. KD - water 6 fu organs 1. GB – wood 2. SJ – fire 3. SI – fire 4. ST – earth 5. LI – metal 6. BL – water |
|
|
4 fundamental aspects of the yin/yang relationship are:
|
1. transformation
2. interdependent 3. opposite 4. balance |
|
|
what is yang?
|
Functional, dynamic
up, outside spring and summer rising hollow |
|
|
what is yin?
|
Structure, static
material deep descending solid |
|
|
FOR ALL of the following points, need to know location and depth and angle – just one depth and angle per pt required
KI 3 |
**VERY IMPT PT** - depression midway btwn the tip of the medial malleolus and the attachment of the achilles lvl with the tip of the medial malleolus
-- yuan source pt ANY KD prob -perp .5-1 |
|
|
KI 6
|
depression 1 cun below the tip of the medial malleolus
-- chronic sore throat from KD yin def, ankle px oblique superior .3-.5 |
|
|
KI 7
|
- 2 cun above KI 3 on ant border of achilles tendon
-- metal pt, mother of water and low back px can regulate sweating w/ LI4 perp .5-1 |
|
|
KI 10
|
- medial side of popliteal fossa when knee is flexed btwn semitendonosus and semimembranosus mx tendons, lvl with BL54
-- tonify yin, knee px, water pt of kidney perp 1-1.5 |
|
|
ST 25
|
- at the level of the umbilicus, 2 cun lateral...
perp 1-1.5 |
|
|
ST 36 zusanli (leg three miles)
|
below knee 3 cun inf to ST 35 one finger width lateral to ant crest of the tibia on tib ant mx
he sea pt, earth pt, gao wu cmd, pt of sea of water and grain said to cure 1000 ailments, strong immune pt, ST, strong spleen, qi yang blood yin px clears fire calms spirit consciousness perp 1-1.5 |
|
|
ST 40
|
lower leg midway btwn the tibiofemoral jt line and the lat malleolus, two fingerbreadths lat to anterior crest of the tibia
- perp 1-1.5 |
|
|
ST 41 jiexi (stream divide)
|
jing river and fire pt
dorsum of foot, midpt tv crease of ankle joint approx lvl with tip of lat mall in a dep btwn ext digitorum longus and hallucis longus tendons calms shen, ST heat and fu, luo vessels px, frontal headaches, tonification, ankle perp .5 or ob below tendons to join with SP 5 med or GB 40 lat |
|
|
LI 4 – Hegu (joining valley)
|
yuan source, cmd pt for the face, ma dan yang heavenly star pt, entry
dorsum hand btwn 1st and 2nd metacarpal bones at mdpt of 2nd metacarpal bone and close to its radial border releases exterior, expels wind, regulates face eyes nose mouth ears, defense qi, promotes labour perp .5-1 ci pregnancy |
|
|
LI 11 – quchi (pool at the crook)
|
he sea, earth pt, sun si miao ghost pt, ma dan yang heavenly star pt
btwn lat epic and LU 5 clears heat cools blood bye wind and damp and itching, high fever throat hypertension px in arm and ankle perp 1-1.5 very powerful for fever heat skin hypertension arm probs |
|
|
LI 20 – yingxiang (welcome fragrance)
|
meetg LI and ST, exit
naso labial groove at the midpoint of the lateral border of the ala Nasi tv medio superiorly .3-.5 |
|
|
BL 13
|
– 1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the third thoracic vert
oblique insertion twd spine .5-1 cun |
|
|
BL 17
|
– 1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the seventh thoracic vert
- oblique insertion twd spine .5-1 cun |
|
|
BL 18
|
– 1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the ninth thoracic vert
oblique insertion twd spine .5-1 cun |
|
|
BL 20
|
– 1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vert
oblique insertion twd spine .5-1 cun |
|
|
BL 23
|
– 1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 2nd lumbar vert
oblique insertion twd spine 1-1.5 cun |
|
|
BL 40
|
– back of the knee on the popliteal crease in a depression midway btwn tendons of biceps femoris and semitendinosus
- perp 1-1.5 cun |
|
|
GB 21
|
– midway btwn the spinous process of C7 / DU 14 and the acromion process at the highest pt of the traps
- post oblique .5-1 |
|
|
GB 30
|
- VERY IMPT PT – at junc of lat 1/3 and medial 2/3 of the distance btwn the greater troc and the sacral hiatus (DU 2)
-- sciatica - perp twds genitals 2-3.5 |
|
|
GB 31
|
- VERY IMPT PT – 7 cun above the transverse popliteal crease on he lat midline of thigh where the tip of the middle finger touches when the client is standing and hands at their sides
-- calming, headaches - perp 1-2 |
|
|
GB 34
|
– in a depression anterior and inferior to the head of the fibula
-- rib px shao yang back px - perp 1-1.5 |
|
|
GB 38
|
– lat aspect of the lower leg, 4 cun sup to the prominence of the lateral malleolus at the anterior border of the fibula
- perp .7 to 1 cun |
|
|
LV 3
|
– dorsum of the foot in a depression distal to the jnc of the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones
- direction of KD 1, .5-1.5 cun |
|
|
LIV 8
|
– when knee is flexed, above the medial end of the transverse popliteal crease, post to the medial epicondyle of the tibia in a depression on the ant border of the insertions of semimemb and semitend mx
- perp 1-1.5 |
|
|
LIV 13
|
– lat side of abdo below the free end of the 11th rib
-tv or oblique .5-1cun |
|
|
SI 3
|
ulnar border of hand, dep prox to head of fifth metacarpal bone
perp .5-2 directed twd LI 3 |
|
|
SI 9
|
on post aspect of sh, 1 cun sup to post axillary crease when arm hangs in adducted posn, this pt lies in the depression just below post border of deltoid mx
perp 1-1.5 cun |
|
|
Ba Xie
|
loose fist made, pts are on the dorsum of the hand, prox to the margins of the webs btwn all 5 fingers – 8 pts ttl
- perp along the line btwn the shafts of the metacarpal bones .5-1 |
|
|
BA FENG
|
dorsum of the foot, prox to the margins of the webs btwn all 5 toes, jnc of red and white skin
- oblique prox, .5-1 |
|
|
LU 5
|
cubital crease – depression at the readial side of biceps brachii tendon
needle slightly flexed to avoid cubital vein perp .5-1 caution cephalic vein |
|
|
LU 7
|
lat forearm, 1.5cun prox to wrist crease
caution cephalic vein radial artery and vein - transverse insertion prox or dist .5-1 cun |
|
|
LU 9
|
wrist btwn radial artery and abd poll long tendon
perp .5-1 careful radial artery and vein |
|
|
HR 3
|
midway btwn PC3 and med epi of humerus at medial end of transverse cubital crease when elbow flexed
ob .5 to 1.5 cun |
|
|
HR 7
|
wrist jt, rad side of flex carp uln in depression at prox border of pisiform bone
perp .3-.5 |
|
|
PC 3
|
on the transverse cubital crease at the ulnar side of the biceps brachii tendon
-- good for elbow px tendons tremors water point of pc -perp .5-1 cun |
|
|
PC 6
|
2 cun above the transverse crease of the wrist PC7 btwn the palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis tendons, on the line connecting PC3-7
-- good for hiccups, chest and stomach px -perp .5-1 cun |
|
|
SJ 5
|
IMPT PT on the dorsum of the forearm, 2 cun above SJ4 btwn radius and ulna
-- arm px paralysis px of sh and back - slightly oblique twd the ulnar side or oblique prox or distal insertion twd the elbow or wrist - .5-1.5cun |
|
|
SP 6
|
meeting pt of SP LV KD - med side of ankle 3 cun directly above tip of med mall on post border of tibia
ci pregnancy perp or ob prox 1-1.5 |
|
|
SP 10
|
knee flexed 2 cun sup to sup border of patella on bulge of med portion of vastus medialis mx, dir above SP 9
- perp or ob 1-1.5 |
|
|
Cycle of qi production
|
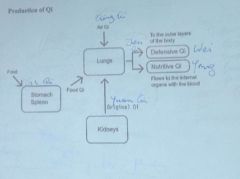
|
|
|
Differentiation of the 8 principles by pattern
|

|
|
|
Excess heat vs deficiency heat - examples
|
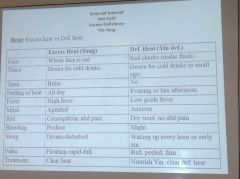
|
|
|
Excess vs deficiency cold
|
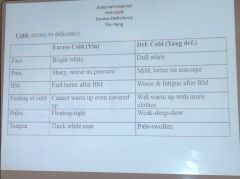
|
|
|
Excess vs deficiency traits
|
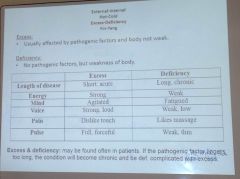
|
|
|
4 qualities for tongue diagnosis and what they indicate
|

|
|
|
5 tongue body colours and what they indicate in detail
|

|
|
|
5 tongue body colours and what they indicate in detail
|

|
|
|
Common pulse categories
|

|
|
|
More common pulse categories
|

|
|
|
Diagram of typical jing well to he sea pts
|
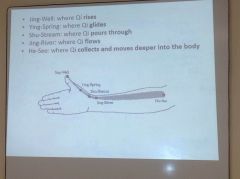
|
|
|
Treatment of acute injuries from 24 hrs to 8 days +
|

|
|
|
Treatment principles for chronic stage of injury
|

|
|
|
Treatment principles for fractures
|

|
|
|
Treatment principles for the different stages of dislocations
|

|
|
|
Yin yang times
|
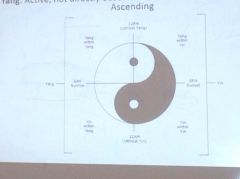
|
|
|
Points at the same level of the lumbar spine and sacrum
|
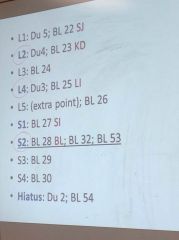
|
|
|
Areas of the spine and what they treat
|

|

