![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Competition |
Where different firms are trying to sell a similar product |
|
|
|
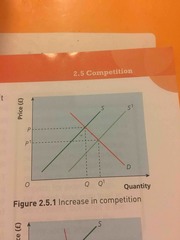
What happens if there is an increase in competition? |
Supply increases Quantity rises Decrease in price |
|
|
|
Monoply |
Sole producer or seller of that good or service |
|
|
|
Oligopoly |
Small number of firms control a large part of the market share E. G Asda |
|
|
|
Why do producers compete? |
To enter a market To survive a market To make profit |
|
|
|
Barriers to entry examples |
Legal barriers Greater efficiency Location |
|
|
|
Impact on consumers |
Lower prices - reducing costs Improved quality and range of goods and services Rise in standard of living |
|
|
|
Price competition |
Lower prices attracts more consumers and increases market share |
|
|
|
Impact on competition on producers |
Improved efficiency which leads to reduced costs Innovation for example computers can lead to higher productivity which can cause higher economic growth Increase in demand |
|
|
|
Competitive market |
Small Many Price is lower quantity is greater Lead to economic efficiency |
|
|
|
Legal barriers |
Laws prevent certain firms from operating e.g Royal Mail is the only firm allowed to handle letters |
|
|
|
Copy right |
Copy right claims prevent firms from duplicating that specific production so competition isn’t a problem. Only that firm can provide that design |
|

