![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does Boyles law refer to?
|
the relationship between volume and pressure (inverse)
As one increases the other decreases |
|
|
What range of frequencies is the auditory mechanism most sensitive to?
|
1000 - 4000 Hz
|
|
|
What is SPL?
|
Sound pressure level, this refers to the given pressure a sound wave exerts on an object (tympanic membrane)
|
|
|
what does 0dBHTL refer to?
|
0dB Hearing Threshold level, this refers to Audio-metric Zero, perfect hearing should have a 0dB threshold for all Hz's on a audiometer
|
|
|
If you know the frequency of a sound wave, how do you calculate the period?
|
1/f (f = Hz)
|
|
|
What is atmospheric pressure? (#)
|
14.7 psi
|
|
|
What is the smallest amount of pressure that can move the TM? (dynes and micro-pascals)
|
.0002dynes/cm2
20uPa |
|
|
What are the two ways we measure pressure?
|
dynes and micro-pascals (uPa)
|
|
|
CPS stands for what?
|
Cycles per second
|
|
|
What is the formula for calculating pressure?
|
Pressure = force/area
|
|
|
What are the measurements used for Period?
|
sec, msec (time)
|
|
|
What are the measurements used for a wavelength?
|
cm, m (distance)
|
|
|
What are the measurements used for volume?
|
cc (cubic centimeter), ml - 3d measurements
|
|
|
What are the upper and lower frequency limits of audibilty
|
20Hz - 20,000Hz
|
|
|
At how many decibels would one start to feel pain?
|
140dB SPL
|
|
|
What is the average velocity of sound?
|
340m/sec
|
|
|
What does HTL and HL stand for?
|
Both stand for Hearing threshold level
|
|
|
How many decibels are required for audibility?
|
0dB SPL
|
|
|
What is the range of frequencies used in audiometric testing?
|
250Hz - 8000Hz (though some go down to 125Hz)
|
|
|
What is type of relationship between period and frequency?
|
Reciprocal
|
|
|
Frequency and wavelengths have what type of a relationship?
|
Inverse
|
|
|
When measuring number of repetitive cycles in one second what label do we use?
|
Hz
|
|
|
If you know the time, how do you calculate frequency?
|
1/t (1/time)
|
|
|
What is the formula for calculating density?
|
D = m/v (density = mass/volume)
|
|
|
What are the 3 properties necessary to produce a sound wave?
|
A force (disturbance), a vibrating mass (molecules), an elastic medium (gas, liquid, or solid)
|
|
|
Define Frequency
|
Number of times it disturbs the molecules of the medium in one second. One back and forth movement of the molecules makes up one cycle of vibration.
|
|
|
What are cycles per second? (CPS)
|
Cycles of vibration measured in time (sec/ms). 120Hz = 120cps
|
|
|
What are frequencies above and below the human range of hearing?
|
Above = ultrasound
Below = infrasound |
|
|
Define Period
|
the amount of time consumed by each cycle in a wave. If a wave has a freq of 10, then the period of each cycle is 1/10th of a second. Therefore, they have an inverse relationship, as frequency increases there are more cycles in a second, and the period of each cycle is shorter. On the other hand, if frequency decreases, each cycle has a longer period.
|
|
|
What is a periodic wave?
|
A wave where the characteristics are equal for all cycles, can be a pure tone or a combination of one or more pure tones.
|
|
|
Can a human create a pure tone?
|
No, the vocal tone is a complex mix of pure tones
|
|
|
Can humans create periodic speech sounds?
|
Yes: singing, vowels, etc.
|
|
|
What is an aperiodic wave?
|
A wave in which individual cycles do not take the same amount of time to occur. This wave is perceived as noise (white noise).
|
|
|
Vowels are what type of wave? Also, what type of air flow is present for their creation?
|
Periodic, Laminar airflow (no use of articulators to disrupt airflow besides tongue)
|
|
|
Consonants are what type of wave? Also, what type of air flow is present for their creation?
|
Aperiodic, turbulent air flow (articulators are used to disrupt airflow)
|
|
|
In a wave, what are three results of more frequent cycles?
|
Higher frequency, shorter duration, shorter length of cycle
|
|
|
What is wavelength? Also, how do you mathematically find it?
|
The measurement of the distance traveled by one complete cycle of a wave (m, cm, mm).
Wavelength = speed/frequency Mainly, the average speed of sound is used and then divided by the frequency of the wave - so a 100hz wave would have a wavelength of 340meters/sec / 100 = 3.4meters |
|
|
What happens to wavelength when frequency is increased or decreased? What type of relationship is this?
|
frequency increased - wavelength decreased
*inverse relationship |
|
|
Define phase
|
Relative timing of compressions and rarefactions of waves
|
|
|
How do phase angles work?
|
A complete cycle of a wave is said to make a 360 degree revolution. The angles refer to the place along its cycle that a wave is, 90* is the highest point, 270* is lowest point.
|
|
|
When are waves in Phase and what happens?
|
waves are in phase when their peaks and troughs match up in a way that they are able to add together.
|
|
|
When are waves out of phase and what happens?
|
When waves are 180* out of phase, they are opposite at any given time such as one wave is peaked while the other is trough-ed, this causes the waves to completely cancel each other out.
|
|
|
What happens when two waves combine that are neither in-phase or out of phase?
|
They create an entirely new wave with a mix of the original waves characteristics.
|
|
|
What is the Fourier Analysis and who came up with it?
|
Jean Babtiste, a french mathematician and physicist. It proves that complex periodic waves can be broken down into their single waves (each unique frequency).
|
|
|
WHat is a continuous spectrum?
|
a line spectrum that instead of having the individual lines showing hz, there is one horizontal line that is meant to connect all the component frequencies in the sound
|
|
|
Define Harmonics
|
A set of natural frequencies that are systematically related to each other. The lowest frequency is the fundamental/ first harmonic and all that follow are mathematically related to this first one (whole number multiples)
|
|
|
Define Fundamental Frequency (Fo) (also known as first harmonic)
|
the lowest frequency of a natural set
|
|
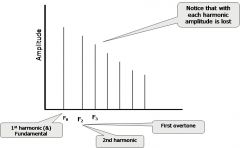
|
just know it
|
|
|
If the Fo of a wave is 250Hz, what are frequencies of remaining harmonics? What is the math for finding this? What about a 500Hz Fo?
|
Fo x 1 = F1 + first harmonic, Fo X 2 = F2, etc
(250Hz) - 500Hz, 750Hz, 1000Hz, 1250Hz, etc (500Hz) - 1000Hz, 1500Hz, 2000Hz, etc |
|
|
• Name one way you can you lower the frequency of the notes played on a guitar.
• Hint: you can not make the strings any longer or shorter |
Make the string more dense
(Reducing its tension) - this changes the speed of the medium |
|
|
There are four pure tone waveforms with frequencies of 1000Hz, 1500Hz, 2000Hz, and 2500Hz..
Will the result be a complex periodic or aperiodic waveform? Is the 1000hz tone the fundamental? Will you be able to hear the fundamental? |
1. Resulting wave will be a complex periodic waveform (the frequencies are mathematically related).
2. No, the fundamental is actually 500Hz, the rest of the tones are whole number multiples of this number. 3. Yes, because of the anatomy of our ears - our cochlea and brain will "fill in the blank" of whats missing |
|
|
Boundaries - what is the incident wave?
|
The wave that hits a boundary - could be a voice, music, etc
|
|
|
Boundaries - what is absorption?
|
The damping of a wave, diminishing changes in air pressure due to friction. There are soft materials that absorb the energy of the sound waves.
|
|
|
Will the frequency of a wave change when it hits a boundary?
|
No, only the amplitude will change
|
|
|
Boundaries - what is reflection? Fixed? Free?
|
The portion of the sound wave not transmitted and not absorbed is reflected back in the opposite direction. This depends on the boundary itself,
Fixed - a wall, something that is fixed between two like mediums (tympanic membrane) Free - a change of one medium to another |
|
|
Boundaries - what happens when a wave reflects off a boundary that is fixed/more dense? Free/less dense?
|
fixed/more dense - reflected wave inverts
free/less dense - wave doesn't invert |
|
|
What is ANSIS12.60?
|
Acoustical requirements for good speech intelligibility in the classroom
Addresses reverberation Background noise Reverberation in the classroom “smears” the acoustic signal (Teachers voice) affecting intelligibility |

