![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are some familial syndromes that increase the risk of colon cancer?
|
Familial adenomatous polyposis.
Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (aka Lynch syndrome). Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. |
|
|
Which sites does colorectal cancer tend to spread to?
|
Liver, lungs, lymph nodes, and peritoneum.
|
|
|
List important staging imaging for rectal cancer.
|
Endorectal US or pelvic MRI.
|
|
|
List the "T" stages in the TNM staging for colorectal cancer.
|
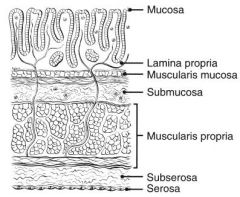
T0 – No evidence of primary tumour.
Tis – Carcinoma in situ: intraepithelial or invasion of lamina propria. The terms “high grade dysplasia”, and “severe dysplasia” are synonymous with in situ carcinoma and in situ adenocarcinoma. T1 – Tumour invades submucosa T2 – Tumour invades muscularis propria T3 – Tumour invades through the muscularis propria into pericolorectal tissues T4a – Tumour penetrates to the surface of the visceral peritoneum T4b – Tumour directly invades or is adherent to other organs or structures |
|
|
During surgical resection of colorectal cancer, how many lymph nodes should the surgeon aim to obtain for staging purposes?
|
At least 12 lymph nodes.
|
|
|
Why is it important to distinguish colon cancer vs. rectal cancer?
|
Adjuvant therapy for colon cancer is mainly achieved through chemotherapy, while for rectal cancer it is achieved through both radiation and chemotherapy.
In addition, rectal cancer is often treated initially with neoadjuvant radiation ± chemotherapy. |

