![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what sp of neospora is of vet significance and what sp of animals and diseases does it cause.
|
Neospora Caninum ( IMH cattle - abortion and FH dog- fatal disease )
also causes disease in wild canids and some deer species note neospora caninum is the main cause of abortion of cattle in the UK |
|
|
how does the lifecycle of neospora compare to toxoplasma
|
same except different host.
|
|
|
describe the lifecycle of neospora caninum in a pregant cow
|
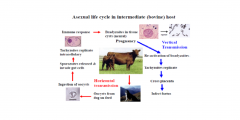
same as toxoplasma except different hosts- reactivated tachyzoites cross placenta and infect foetus.
|
|
|
what is the outcome of infection of a non pregnant cow with nespora caninum
|
no real symptoms or pathology
|
|
|
are calves infected in the last trimester of pregnancy a risk to the farmer.
|
yes. if they become immuno-compromised or pregnant then there will be reactivation of the bradyzoites. this is a major rout of transmition in cattle.
|
|
|
other than being infected from birth what other routs might cattle be infected with neospora caninum
|
ingestion of oocysts from dogs faeces ( horizontal transmition ) or ingestion of sporpzoites from cattle faeces.
|
|
|
how do the final hosts ( dog, wild canid and deer ) become infected with nespora caninum.
how isneospora similar to toxoplasma in the FH |
like the cat and toxoplasma except no infection of rodents....ingetion of bradyzoites from offal or placenta ( imp source) or bradyzoites /tachyzoites from an aborted foetus.
neospora caninum and toxoplasma gondii both have a sexual ( shizogony -gametogeny ) and asexual phase ( tachyzoites - bradyzoites) however in Neospora in the dog the foetus of pups may be infected or born with neurological signs whereas congenital toxoplama infection is uncommon in cats. note this also occurs in cattle infected with neospora caninum. |
|
|
what are the clinical sings of a dog infected with neospora caninum and what is the treatment.
|
disease more common in pups ( neonatal death common if not treated)
hind limb ataxia and paralysis ( adults and pups) behaviour change lesions around mouth and eyes ( rare) bitch infected for life and transmits vertically to pups NO ABORTION treatment: difficult. drugs ( sulphonamides). there is a better chance of success if older than 16 months |
|
|
how do you diagnose cattle and dogs with neospora caninum
|
CATTLE- ELISA detects Ab in serum- if positive examine neural tissue in foetus for lesions ( non superative encephalitis)./immunofluorescence antibody test (IFAT) of aborted foetal fluid
DOGS- PCR from muscle biopsy/ clinical signs |
|
|
You are called to a farm by a farmer reporting reduced numbers of conceptions and he/she reports that the farm dog was found with an aborted foetus.
What would you ask about recently born calves and why ? Where could the infection be coming from? How would the infection be introduced to the farm? |
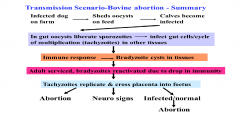
ask what the calf was born like as infection of foetus with tachzoites in ...
1st trimester - abortion. 2nd trimester- calf born with neurological damage. ( survives as some immune response) 3rd trimester- normal calf but bradyzoites in tissue.( due to strong immune response) the infection could be coming from oocysts being shed in the dogs faeces or sporozoites being shed by infected cattle or from trans placental transmition from the mother. the kea issue is transplacental transmission . in N america - Complicates attempts to control as offal of deer left by hunters- eaten by coyote who then infect cattle feed. In UK foxes are seropositive but have not been shown to produce oocysts as a final host . Red & Roe deer are also seropositive. |
|
|
in which animals and body part are sarcocysts commonly found
|
Heart and skeletal muscle of sheep
|
|
|
describe in detail the lifecycle of Sarcocystis in a dog and cow
|
FH -DOG ( carnivore )- ingests muscle of cow containing sarcocyst containing bradyzoites./ the bradyzoites are released and invade SI epi and immediately form micro and macro gametes which fuse in the SI to form the oocyst. the oocyst then sporulates and is passed out in the faeces.
IMH ( rum./pig/horses -sheep esp in UK)- infected by ingestion of sporocysts. the sporozoites are released in the SI and invade the endothelial cells of the mesenteric arteries. theys devide asexually by producing shcizonts which contain merozoites. the merozoites rupture from the cells and invade the endo cells of capillaries. Again they produce more schizonts containing merozoites and rupture the cell to release the merozoites which then invade mononuclear leukocytes. Again each merozoites produces a schizonts with more merozoites inside it. these rupture the cell and finally the free merozoites invade striated muscle cells and form bradyzoites within a sarcocyst. this takes 2-3 months. |
|
|
in which animal and how does sarcocystis cause pathology and what are the clinical signs
|
disease is only significant in the IMH.
it is associated with the second stage schizont. ACUTE- death ( widespred haemorage/ CHRONIC- emaciation/ reduced milk yield/ carcus condemned. CLINICAL SIGNS- fever, increased metabolism, anaemia, sub mandibular oedema, shivering, loss of appetite, weight loss, muscle wasting, lethargy. some cases may see death of recently lambed ewe or vague neurlogical disease and hind limb paralysis. AT PM - petechial hemorrhage and lymphadenopathy. |
|
|
what is the outcome for infection of a farm with neospora caninum
|
sporadic abortions or abortion storm
|

