![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the function of GP1b for coagulation?
|
Initial slowing and loose binding of the platelet to the collagen and to activated platelets (binds to VWF GP1b binding domain)
This binding activates the platelet |
|
|
What is the function of GP2b/3a for coagulation?
|
(Only activated after plt activation); 2ndary binding of the platelets to the collagen and to activated platelets (binds to VWF GP2b/3a binding domain and fibrinogen)
|
|
|
What is the role of VWF for early coagulation?
|
VWF is found on the surface of platelets and collagen. It has BP1b and GP2b/3a binding domains where the platelets can bind.
|
|
|
Which type of VWD is defined by low levels (but still present) of VWF?
|
Type 1 (80% of total cases of VWD)
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of type 2a VWD?
RCo level? VWF ag level? |
Lack of large (more active) VWFs due to either destruction or accelerated lysis. Results in decreased activity (low RCo). VWF ag level is variable from low to increased (feedback?)
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of type 2B VWD?
|
Increased VWF binding to GP1b
----> increased clearance of VWF (esp. large ones) and plts from circulation ---> lowed VWF ag, lowered RCo |
|
|
How can one distinguish type 2A from 2B VWD?
|
Similar lowering of RCo and VWF ag. Therefore, test ristocetin at 0.5 as well as the usual 1.5 mg/ml. 0.5 will aggregate in 2B due to the gain of function.
|
|
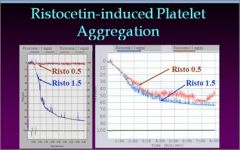
Low VWF ag levels. What type of VWD is it?
|
Type 2B VWD - gain of function
- Large multimers are lost due to premature binding so Ag and RCo are low |
|
|
What is the difference between Type 2B VWD and Platelet type VWD?
|
Show the same on studies. 2B is due to a change in the VWF leading to increased binding. Platelet type is due to defective plt rec causing increased binding.
|
|
|
What is the mechanism and testing manifestations of Type 2M VWD?
|
Decreased ability of VWF to bind platelet (GP 1b).
Normal VWF ag, disproportionately lower RCo |
|
|
What is the mechanism and testing manifestations of Type 2N VWD?
|
Mutations in Factor 8 binding so that VWF binds okay to F-8 but the complex gets cleared quicker then normal. WFF ag = RCo
|
|
|
What is Type 3 VWD?
|
A complete absence of VWF
|
|
|
What population has been found to have a 25-30% lower level of VWF levels than "normal".
|
Blood Group O individuals
|
|
|
How could a type A women with subclinical VWD have child with clinically significant VWD?
|
Type O individuals have lower circulating levels of VWF. She could have a type O child.
|
|
|
What molecular interaction is Ristocetin an indirect measurement of?
|
The GP 1b and VWF interaction
|
|
|
What coagulation disorders (2) show a complete absence of response to Ristocetin?
|
Bernard Soulier syndrome
GP 1b (one b in BSS) absent ristocetin (AR bernARd) also VWD type 3 These can be differentiated by adding normal plasma. VWD will correct while BSS won't. |
|
|
What coagulation disorder show response to ristocetin at 1.5 mg/ml but does not respond to AA, TRAP, collagen, ADP or risto at 0.5 mg/ml?
|
Glanzmann Thromasthenia
|
|
|
What coagulation disorders (2) show a complete absence of response to Ristocetin?
|
Bernard Soulier syndrome
GP 1b (one b in BSS) absent ristocetin (AR bernARd) also VWD type 3 |
|
|
What coagulation disorder shows response to ristocetin at 1.5 mg/ml but does not respond to AA, TRAP, collagen, ADP or risto at 0.5 mg/ml?
|
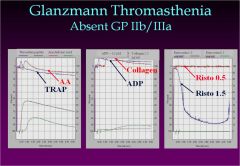
|
|

Name the disorder
|
Aspirin
-Plts fail to aggregate with arachadonic acid. ADP and Collagen responses can often be abnormal also |
|
|
How does a platelet functional defect appear on platelet aggregation studies?
|
Decreased or absent response to ADP. Other studies are pretty much normal
|
|
|
What is the effect of a Factor XIII deficency on PTT and PT?
|
No effect
|
|
|
What must always be done after a prolonged isolated PT or PTT?
|
repeat and 1:1 mixing study
|
|
|
What is the significance of an increased PTT that corrects with a 1:1 mixing study?
|
Factor deficiency
8, 9, 11, 12 or vWF |
|
|
Which coagulation factor is not decreased with liver disease?
|
8
|
|
|
Which common coagulation disease show the highest RR for venous thromboembolism?
|
Homozygous Factor V leiden (80x), heterozygous also shows significant risk
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Factor 5 Leiden?
|
Point mutation of factor 5 at cleavage site for protein C.
|
|
|
What is the normal function of activated protein C?
|
Inactivates Factor V and VIII
|
|
|
Which factor deficiency will result in normal PT and PTT but will have bleeding?
|
Factor 13 (transglutaminase)
|
|
|
What is the specific function of vitamin K for activating factors 10, 9 7 and 2?
|
Adds a diglucuronide moiety allowing the factor to interact with lipid membranes
|
|
|
Patient with prolonged aPPT without history of bleeding. What are the 3 disorders that can result in this? Is it safe to have surgery?
|
Deficiency in factor 12, HMWK or PreK
Should not effect surgery |
|
|
Elevated PT and PTT, normal platelets. Normal D-dimer. Normal PT and PTT before hospitalization.
Cause? |
Vit K deficiency due to antibiotic killing of normal gut flora.
(or patient started on Warfarin) |
|
|
How does factor 13 deficiency present?
|
Normal coag studies. Recurrent soft tissue hematomas.
|
|
|
(Classically) how do you test for a factor 13 inhibitor?
|
Clot lysis testing with 5M urea. Dissolves in < 3 hours (N=>24)---> mix with normal plasma. If still dissolves, then suspect inhibitor. Otherwise, deficiency of 13
|
|
|
If an abnormal PT or PTT does not correct after a mixing study of normal plasma, what should be suspected and what should be done next?
|
Suspect inhibitor is present
Dilute Russell's viper venom test (dRVVT) to test for lupus anticoagulant |
|
|
How is a dilute Russell's viper venom test (dRVVT) interpretted?
|
Venom=clotting, but limited phospholipid (PL) is given. If a Lupus anticoagulant(LA) is present, then it interferes with PL (no clot). If corrected with more PL, suspect LA
|
|
|
Why are many PT and PTT assays sensitive to lupus anticoagulant?
|
They have phospholipid-dependent clotting. Lupus anticoagulant interfers with phospholipids.
|
|
|
What protein does protein S bind to in serum? What normal physiologic state can cause a lowered protein S level?
|
C4b
Pregnancy due to increased C4b levels |
|
|
What is the function of Protein C in coagulation?
|
Activated protein C(APC)/protein S complex inactivates factor 5 and 8. Protein C is activated by the thrombin-thrombomodulin-endothelial protein C receptors complex.
|
|
|
Which liver depended Factors (non-8) are least effected by liver disease.
|
11 and 12 due to long half-lives
|
|
|
Which factor deficiency can be seen post-CABG?
|
Factor 5 - bovine thrombin used during surgery can contain factor 5, which in turn induces antibodies
|
|
|
What do you give a patient with mild VWD for epistaxis?
|
DDAVP (desmopressin acetate) nasal spray --> stimulates release of factor VIII from endothelial cells
|
|
|
VWF multimer analysis shows reduced high molecular weight multimers and normal intermediate weight multimers. What is it?
|
Type 2B VWD or platelet type vWD
2A will show decreased intermediate multimers |
|
|
Suspect vWD but normal PTT
|
Check if the fibrinogen (an acute phase reactant) is elevated since VWF and factor 8 can also be acutely elevated in that state.
|
|
|
vWD with reduced activity vs. antigen but normal multimer analysis.
|
Type 2M vWD
|
|
|
T/F: The prolonged PTT in hemophilia A and B correct with 1:1 mixing studies with normal plasma
|
True - Normal plasma would contain enough factor to correct the deficite.
|
|
|
What is the effect of vWD on PFA-100 closer time? PTT?
|
PFA-100 closure time is increased
PTT remains normal |
|
|
What is the mutation seen in Factor V leiden?
|
Arg 506 --> Gln
|
|
|
What 3 thrombotic disease can cause arterial thrombosis?
|
Homocysteine
antiphospholipid antibody Elevated factor 8 |
|
|
What is the defect seen in gray platelet syndrome?
|
Lack of alpha granule proteins
|
|
|
What disease is caused by a deficiency of a disintegrin and metalloprotease with a thrombospondin type motif?
|
TTP
A disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin 13 type motifs (ADAM TS 13) |
|
|
What is the mechanics of thrombocytopenia in TTP?
|
ADAM TS 13 is a vWF cleaving protease. Deficiency causes buildup of large vWF multimers -> microscopic thrombosis
|
|
|
What is the genetics of Hemophilia A?
Hemophilia B? |
X-linked recessive
X-linked recessive |
|
|
T/F Hemophilia A causes severe bleeding for levels 10% or less?
|
False
Mild 5 to~50% Mod 1-5% Severe <1% |
|
|
What test is used to screen for factor 13 deficiency?
|
5M urea test
|
|
|
What are the genetics of antithrombin 3 deficiency?
|
Autosomal dominant
|
|
|
Patient with skin necrosis after receiving warfarin. What is a likely genetic cause?
|
Protein C deficiency
Wait till after acute episode to measure levels |
|
|
What is the most common reason for activated protein C resistance?
|
Factor 5 Leiden- resistant to APC cleavage but still functional
|
|
|
T/F antiphospholipid syndrome is caused by an anticardiolipin antibody and is associated with SLE, AIDS, drugs or LP disorders.
|
T
|
|
|
Which coagulation factor is the first to show decrease with severe liver disease?
|
Factor 7. It has the shortest half-life of all the liver dependant coag factors (all but 8).
|
|
|
What are the last two coagulation factors to be effected by liver disease? Which factor is not effected?
|
11 and 12- longest half-lives
8 - not produced in liver |
|
|
Which factor deficiency can be seen post-CABG?
|
Factor 5 - Due to use of bovine thrombin which induces factor 5 antibodies.
|
|
|
What is the antibody in HIT syndrome?
|
PF4 (platelet factor 4) - causes activation of platelets
|

