![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define a process |
An operating system abstraction to represent what is needed to run a program |
|
|
What does a process consist of? (2 things) |
Sequential Program Execution Stream (includes state of CPU registers) Protected resources: memory state, I/O state |
|
|
The current state of the process is held in the... |
PCB - Process Control Block |
|
|
How do you multiplex processes? |
Allocate CPU time to to them using suitable scheduling policies: preemptive: SRT, RR non-preemptive: FCFS, SJF |
|
|
What is a thread? Draw a simple diagram. |
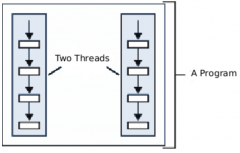
An independent sequence of execution within a program. |
|
|
State 4 reasons a thread is similar to a process. |
- Both have a single sequential flow of control with a start and end - At any time a thread has a single point of execution - A thread has its own execution stack & program counter - Sometimes a thread is called a lightweight process |
|
|
State 3 differences between threads and processes |
- A thread cannot exist on its own; it exists within a process - Usually created and/or controlled by a process - Threads can share a process' resources, including memory and open files [Threads of the same process run in a shared memory space, whilst processes run in separate memory spaces] |
|
|
Define sequential programming |
- Constructing a program containing one process using a (sequential) computer language - The program is supposed to execute on a single processor architecture |
|
|
How is the CPU linked to RAM and I/O devices? |
By buses |
|
|
What are stored in RAM? |
Program instructions, runtime data, and the program counter. |
|
|
The CPU repeatedly executes the cycle of... |
- Fetching decoding and executing the next instruction (Which is referenced by the current value of program counter (PC)) |
|
|
The CPU can execute how many instructions at any given time? |
Only one |
|
|
Draw a diagram of single processor architecture |
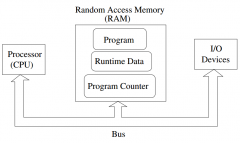
|
|
|
When executing a sequential program, what is the execution sequence? |
The sequence of values of the program counter. |
|
|
What does deterministic mean? |
There can be only one possible sequence of execution. The same input results in the same output |
|
|
What does a sequential program give the system? |
Strict instructions on the order of executing the statements in the program |
|
|
How would the sequential program P; Q; R be executed? |
P => Q => R P must precede Q, and Q must precede R |
|
|
On the System Level of Execution, each statement may be compiled into... |
several machine instructions |
|
|
Given statement Q(y = x + 3), how many machine instructions is this stored as, and what are they?
|
q1: load the value of x into a CPU register q2: increment the value of this register by 3 q3: store the value in this register at the address of y |
|
|
Define total ordering. When is it used? |
Single threaded computation; no overlap in the execution of the statements. Used during sequential programming. |
|
|
Sequential programming is the same as what? |
Finding a strict sequence of steps to achieve the desired end. |
|
|
What is concurrent programming? |
Constructing a program containing multiple processes/threads that execute in parallel |
|
|
Processes executed in parallel may run on... |
A multi processor system OR A single processor system |
|
|
State 3 reasons for using concurrent programming. |
- To improve efficiency in program execution using multi-CPU hardware - To improve CPU utilisation via multi-tasking on a uni-CPU system (OSs) - Because some applications are inherently non-deterministic and concurrent (e.g. embedded traffic lights controller) |
|
|
Why are some applications inherently non-deterministic and concurrent? |
- The order of program operations is determined by external events (e.g. sensor triggered by a coming vehicle) - Impossible to predict the order of these events. e.g. a car from the north comes first, then one from the east, etc. |
|
|
What is a Parallel Computer system and what can it implement? |
A computer with multi-CPUs/cores; it can implement parallel computation. |
|
|
Maximum Parallel Computation means... |
Each task is computed by its own CPU |
|
|
True or false: maximum parallelism is always possible |
False; it may not be |
|
|
True or false: a uni-CPU system can support multi-tasking / multi-threading. |
True. |
|
|
Each process/thread in a uni-CPU system has... |
its own program counter |
|
|
How does the PC act in a uni-CPU system? |
Forks to produce many process/thread counters, which later re-join |
|
|
In a uni-CPU system, what occurs during each CPU cycle? |
A process is non-deterministically chosen and its next command is loaded and executed. There my be many different possible paths. |
|
|
The CPU sharing technique is known as... |
Interleaving |
|
|
The total possible interleavings is: (the complexity of interleaving) |
(n + m)! ------------ n!m! where n and m are the number of statements per process. |
|
|
What is the main issue in Concurrent Programming? What are two others? |
The concurrent processes must interact with each other in order to share resources or exchange data. Synchronisation and distribution. |
|
|
What is synchronisation? |
When, how, and with what language abstractions can we synchronise computation to eliminate unacceptable interleavings, and thus unacceptable outputs? |
|
|
What is distribution? |
How can we distribute processes among a number of processors, and how can a process on one processor interact with another process on a different processor? |
|
|
Processes are strictly _______. There's no what? |
Sequential; concurrency. |
|
|
What are the preemptive scheduling policies? |
- SRT - RR |
|
|
What are the non-preemptive scheduling policies? |
- FCFS - SJF |

