![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
RAS Location |
in the brain stem occupies central portion of medulla, pons, 4th ventricle and cerebral aqueduct |
4 places MP4A |
|
|
Formation of RAS |
neurons, processes of nuclei and pathways |
|
|
|
properties of RAS |
poorly defined, polysynaptic, has ascending and descending components |
|
|
|
median column |
•serotonergic •next to paramedian zone •Raphei nuclei •extend from medulla upto midbrain in vertical sheers |
|
|
|
medial column |
•lateral to media column •large cells - gigantocellular,pontine tegmental, cuneiform and sub cuneiform nuclei |
|
|
|
lateral column |
•lateral to medial column •small cells - parvocellular •visceral functions |
|
|
|
afferent connections of Reticular formation
|
1.spinal cord from all ascending tracts 2. CN + vesitbular 3.Superior n inferior colliculi through tectoreticular fibers 4.Cerebellum 5.basal ganglia 6.neocortex 7. limbic lobe + amygaloid and hippocampus |
7 connections |
|
|
efferent connection of reticular formation |
descending and ascending |
2 types |
|
|
Descending Efferent connection of Reticular formation |
1. spinal cord via ? 2. brain stem cn via reticulobulbar fibres 3. cerebellum 4. red nucleus, subthalamus and hypothalamus 5.corpus striatum, neocortex and limbic node
|
5 to's |
|
|
subdivision of descending reticulospinal tracts |
1. descending facilitatory reticular prj 2. descending inhibitory reticular prj |
one up one down |
|
|
Excitation of Reticular excitatory area |
1. peripheral sensory signals 2. + feedback signals from cortex 3. stimulation of thalamus centre |
3 |
|
|
formation of bulboreticular facilitatory area |
pons and mesencephalon |
P + M |
|
|
fx of excitatory reticular substance released by bulboreticular facilitatory area |
•maintain tone of anti gravity muscles •control activity levels of spinal cord reflexes |
muscle n spinal |
|
|
reticular inhibitory area |
location: medial and ventral in med fx:decrease activity in the superior portion of the brain by excitation of serotonergic neurons |
|
|
|
ARAS location and projections |

|
|
|
|
types of ascending signal passing through thalamus |
1. rapid - acth, milisec 2. by intralaminar + reticular nuclei over surface of thalamus |
|
|
|
Properties of ARAS |

|
|
|
|
Factors affecting arousal reaction |

|
|
|
|
ARAS cortical stimulation |
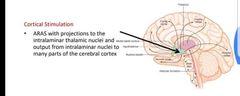
|
|
|
|
ARAS Complex polysynaptic pathway |

|
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters of reticular formation |
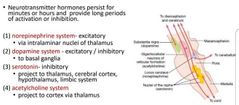
|
|
|
|
Describe norepinephrine system |
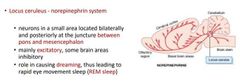
|
|
|
|
Describe Dopamine system |
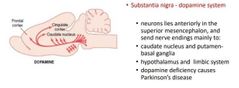
|
|
|
|
Describe serotonin system |
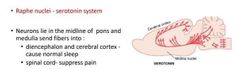
|
|
|
|
Describe Acetylcholine system |

|
|
|
|
Importance of RAS activity |

|
|
|
|
General fx of reticular formation |

|
9 fx |
|
|
Role of reticular formation in sleep and wakefulness |

|
|
|
|
Role of reticular formation on muscle tone |

|
|
|
|
Role of reticular formation on endocrine control |

|
|
|
|
Role of reticular formation in visceral fx |

|
|
|
|
Role of reticular formation in EEG and learning |

|
|
|
|
RAS activation from cortex. Explain. |

|
|
|
|
Reticular formation response to emotion and muscular activity |

|
|
|
|
Drug exciting Reticular formation |

|
3 drugs type |
|
|
Drug inhibit reticular formation |

|
Makes u slow and and dont feel pain |

