![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Meningitis Encephalitis Meningoencephalitis Cerebritis Abscess Empyema |
1. Localized to Subarachnoid space 2. Brain tissue infection by virus 3. Meningiits + encephalitis 4. Diffuse bacterial, fungal, parasitic infection of brain tissue 5. Local bacterial, fungal, parasitic infection of brain tissue (acute, active infection) 6. Infection localized to space btwn dura and arachnoid (subtle, chronic presentation) |
|
|
RED FLAGS
|
1. Bacterial (purulent) meningitis: N. Meningitieds, organ failure. 2. Herpetic encephalitis (steroid, DM, immunocompromised) 3. epidural abscess 4. Subdural empyema 5. High opening pressures on LP 6. Opportunistic infections |
|
|
GENERAL S/S (6) |
TRIAD: Headache, fever, neck stiffness (all 3 not always present) Photophobia (nerve palsy), confusion/altered LOC, localized pain = epidural abscess |
|
|
GENERAL PE findings (7)
|
Nuchal rigidity (Brudzinski's, Kernig's)
Maculopapular, bumpy rash (menningocoocal meningitis - RMSF on diff), papilledema, altered mental state, nerve palsy, focal neuro, posturing (decorticate, decerebrate) |
|
|
Approach to bacterial meningitis
|
2. Lab: CSF/LP*, Blood culture, CBC, drug tox, BMP (chem profile) *Contraindicated in head trauma, loss of consciousness, papilledema, focal deficit |
|
|
Bacterial meningitis red flags
|
1. Hx: Older than 60; immunocompromised, history of CNS dx; seizure 2. PE: LOC (commands, answer questions), gaze palsy, abnormal visual fields, facial palsy, arm drift, leg drift, abnormal language = ischemia, edema, mass lesions - GET AN MRI or CT |
|
|
Bacterial meningitis tx
|
START THERAPY ASAP: 18-50 = S. Pneumonia, N. Meningitides = VANC CEFOTAXIME + CEFTRIAXONE 50+ also consider Listeria, group B strep: ADD AMPICILIN Refine treatment after lab results. May add steroids. |
|
|
LP: What are signs/#s of bacterial men.
|
CSF studies: 1. Normal = 0-5 lymphocyte. 200-20K = meningitis. 2. Gram stain >60% 3. Culture >90% 4. Fungal mycobacterium/AFB 5. Decreased glucose .6 CSF/Serum ratio <.4 7. Protein increased 8. PCR - bacterial DNA* 9. Latex agglutination-antibody/antigen response testing. |
|
|
5 most important causes of bacterial meningitis
|
2. Listeria (older/infants): Gram+ rod, bimodal peak, food borne 3. Strep pneumonia (most common)* 4. N. Meningitis* 5. H. Flu: children receive vaccine* *=vaccine available (pneumococcal/meningococcal) |
|
|
S. pneumonia predisposing factors
|
MOST COMMON CAUSE (50%) 20% mortality Vaccine available |
|
|
N. Meningitidis |
2. Epidemic/endemic outbreak, exposure prophylaxis needed. 3. Fulminant presentation - petechial/purpuric rash, immunocompromised pt. 4. Vaccine available |
|
|
Other causes
|
S. aureus, S. epidermitis, Gram neg. /Pseudomonas aueriginosa |
|
|
Chemoprophylaxis |
1. M. Menigitis - at risk for droplet contact, 1+ hour intimate contact. RIFAMPIN, CEFTRIOXONE, CIPRO. 2. Group B strep: treat carrier mother 3. HIB: Unimmunized, RIFAMPIN |
|
|
Acute viral/aseptic meningitis: presentation on LP; 2 causes
|
2. Aseptic on LP (inflammation w/o agent) 3. SYPHILIS as spirochete phase can cause 4. Erhilchiosis = TICK BORNE |
|
|
Acute viral/aseptic meningitis: S/S
|
S/S: Acute onset severe headache, fever, photophobia, meningismus. NO PERSONALITY change. |
|
|
Acute viral aseptic meningitis: Dx
|
1. CSF PCR for enterovirus, HSV, ZVZ 2. IgM for west nile virus 3. CSF for fungus, mycobacterium 4. Viral culture: CSF, throat 5. Serology: Viral Ab, IgM, Titer rise in IgG, HIV DDX: Bacterial meningitis, parameningeal focus of infection, slow/non-culturable organism, chronic/subacute meningitis, neoplastic meningitis. |
|
|
Acute viral meningitis LP findings
|
2. WBC 25-2K (normal 0-5) 3. Protein 50+ 4. Normal-low glucose 5. No organism on grain stain |
|
|
Acute viral meningitis treatment
|
2. No IV antibiotic 3. Consider antiviral agents 4. Supportive/symptomatic care: Rest, fluid, analgestic/antipyretic, atiemetic |
|
|
Chronic Meningitis presentation
|
1. Chronic headache 2. Neck pains 3. Double vision, hearing loss 4. Sphincter dysfunction 5. Falling PE: 2. CN defect 3. Delerium 5. Myelopathy, radiculopathy |
|
|
Causes of chronic meningitis
|
2. Bacterial: Syphillis, Lyme dx 3. Helminthic- tapeworm 4. Fungal - cryptoccus, coccidiodes, histoplasma *Mollaret's: Benign, recurrent, aseptic meningitis. Repeated fever 104+, meningismus, severe headache. HSV1/2, EBV possibly? |
|
|
Viral encephalitis - what is encephalitis
|
3. Meningitis may also be present - meningoencephalitis 4. If spinal cord also: Encephalomyelitis |
|
|
Encephalitis presentation
|
2. Fever, headache, stiff neck, focal neuro, SEIZURE, change in MOOD/PERSONALITY |
|
|
Encephalitis cause
|
Arthropod (La crosse, WNV, St Louis) 2. Zeka, Rabies, Equine, Powassan, CMV, enterovirus, mumps, tick fever |
|
|
HSV in encephalitis; S/S, Dx, Tx
|
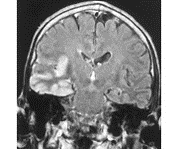
1. MOST COMMON 70% mortality, but treatable if early, mental deficit if not. 2. S/S: 1-7 days upper resp symptoms, sudden onset headache, fever, delirium, behavior changes, *SEIZURE, EEG, MRI. 3. Dx: CSF PCR, culture, IgG, IgM titers for WNV, HSV. PCR, MRI, EEG. 4. Tx: Acyclovir IV |
|
|
Brain abscess: S/S, cause, Tx
|
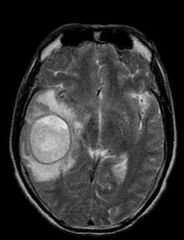
1. Blood borne from distant sites of infection (lung, endocarditis) 2. Sinusitis/Otitis media 3. Similar to other space occupying lesions 4. ENCAPSULATED on MRI Cause: Multiple organisms. Anaerobes, Microaerobic strep, staph, candida, aspergillius. Tx: ABX, drainage |
|
|
Subdural empyema
|
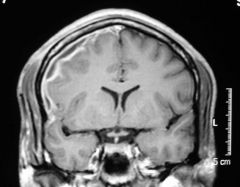
2. Infection in space btwn dura and arachnoid 3. 20% of intracranial infection 4. Complication of sinusitis, otitis media 5. MRI 6. Treatment: Surgical drainage, IV ABX |
|
|
CNS opportunistic infections
|
2. Toxoplasmosis 3. Primary CNS/lymphoma 4. Crypto 5. TB 6. PML 7. Neutropenia 8. Mold 9. Bacterial brain abscess 10. VZV |
|
|
Cranial epidural abscess
|
2. Complication of fracture/craniotomy 3. From sinus, ear, mastoid, orbit infection 4. Fever, headache, nuchal rigidity, seizure, focal deficit. Insidious 5. Cranial MRI with enhancement 6. Neurosugical drainage + ABx by drainage |

