![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the Difference Morphologic Alt V Functional Abn What are the Nuclear Abn? What are the Cytoplasmic Abn? |
Morphologic are problems with appearance such as problems within the nucleus or within the cytoplasm. Functional These generally do not have physical changes to the appearance of the cell but function irregularly. Nuclear - Pelger Huet , Hered Neut Hyperseg Cyto - Alder-Reilly Chediak Higashi May-Hegglin Fx Abn - Chronic Granulomatous Disease Leuk Adh Disorder, Mono/Macro Lysosomal Storage Disease, B/T Lymph Abn, Misc - Job Synd, Lazy Leuk Synd, MPO Def. |
|
|
(Morph)Pelger-Huet Anomaly Morph/Funct? What Cell Line affected? Dom/Rec? How does it occur? *Pseudo-Pelger-Huet Anomaly |
Morphological Abn Decrease Nuclear Segmentation (neuts) BILOBED Autosomal Dom Disorder *MOST COMMON GEN DISORDER Mut. of Lamin B Receptor *It is an occurance when >50% of Segs are affected Seen in Mal. Myeloproliferative Neoplasm. |
|
|
(Morph)Hereditary Neut Hypersegmentation What does the name mean? Dom/Rec? *Break it down* |
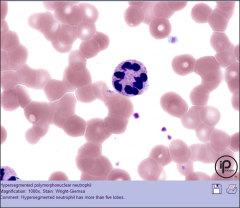
Autosomal Dom Cond. Dom |
|
|
(Morph)Alder-Reilly Anomaly Dom/Rec Appearance of cell? |
Rec Granulocytes are large dark purple resembles Toxic Granulation it is in all leukocytes |
|
|
(Morph)Chediak-Higashi Syndrome Dom/Rec Appearance of Cell? Patient Concerns? |
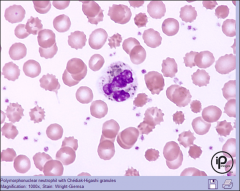
Rec Enlarged Lysosomal Vess, Giant Gray-Green Granules Fatal Disease- Rare, Bleeding Disorders Bact Inf. Albinism and Immunodef associated. |
|
|
(Morph)May-Hegglin Anomaly Dom/Rec Appearance of Cell? Patient Concerns? |
Dom Large Baso Inclusions, Giant Plt, Thrombocytopenia, Leuks Resemble (Dohle Body) Patients are Asymptomatic but can have bleeding disorders, thrombocytopenia |
|
|
Chronic Granulomatous Disease CGD Fx Abn? Dom/Rec Patient Concerns? |
X Linked Recessive Inability to phagocytosis to produce react O2 Spec, WBCs unable to function Pre-Disp to Infections and Formation of Granulomas affects GI and Urinary |
|
|
Differences Between a. Leukocyte Adhesion Disorder b. Job Syndrome c. Lazy Leukocyte Syndrom d. Myeloperoxidase Deficiency e. Diabetes Mellitus |
a. Inability of neuts and monos to bond to endothelial cells (Cell to Tissue Transport) b. Elevated IgE, Skeletal Abn, Bact Inf. c. Rare, Neutropenia poor responses to chemotactic agents. d. Most Common Neutrophil Abn, Mild Sympt e. Type I Inh, Type II Acq Associate with poor Neut func |
|
|
Mono/Macro Lysosomal Storage Disease What are the two divisions? Mechanism? |
Mucopolysaccharide Storage Disease Lipid Storage Diseases Inherited enzyme deficiencies or defects resulting in flawed degradation of phagocytize material. |
|
|
What is lipid storage disease and what are some of the specific diseases associated with it and how do they work? |
Defective Lipid Catabolism Gaucher Disease - most common lipid storage disease Gaucher cells anemia Neimann-Pick Disease - Def in acid sphingomelinase, neurologic problems as infant, marrow contains many macrophages |
|
|
What are B/T Lymphocyte Abn & what is the difference between the each? |
Genetic disorders that result in decreased prod of B/T cells
DiGeorge Syndrome Decreased number of T-Lymphs absence or underdevelopment of thymus Comb B/T Severe Combined Immunodeficiency - Decreased # of T/B cells and lack of NK cells- No Immune system. Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome- X linked mutation patients have immunodeficiency, eczema, and thrombocytopenia |
|
|
What are the 5 quantitative abnormalities |
Neutrophils - Neutrophilia, leukamoid reaction, leukoerythroblastic reaction, neutropenia Eosinophils - eosinophilia Basophils - basophilia Monocytes - monocytosis Lymphocytes -lymphocytosis, lymphocytopenia |
|
|
What are the 3 qualitative disorders |
Granulocytes Lift Shift - Mild, Mod, Marked Monocytes - Imm Monos observer in infection response Lymphocytes - Variant, reactive (confused with blast), atypical |

