![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
199 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name ten techniques for spreading fabrics
(10) |
On the fold; Face up;
Back up; Face to Face; Back to back; Stripes, checks and plaid; One-way design; Mock fur; Velvet; Leather |
|
|
For what reason would you use the on the fold spreading technique?
(1) |
When knits are done in a tube.
|
|
|
Describe the face up spreading technique
(1) |
All plies are spread with the face, or right
side up. |
|
|
Describe the back up spreading technique
(1) |
All plies are placed with the back, or wrong side, up.
|
|
|
Describe the face to face spreading technique
(1) |
The right sides are spread facing each other.
|
|
|
How do you lay-up stripes, checks and plaids?
(2) |
Each lay is started with the same stripe or colour.
Check spikes or cloth clamps are used to keep it in position |
|
|
How do you spread one-way designs?
(2) |
Face up;
Design runs in same direction |
|
|
How do you spread mock fur?
(2) |
Single ply;
wrong side |
|
|
How do you spread velvet?
(2) |
Only 4 - 6 plies;
Face up (One-way) |
|
|
How do you spread leather?
(3) |
Single ply;
Back up, Rotary blade (Cut around odd marks) |
|
|
How do you supply power to electric cutters?
(3) |
Overhead;
From rods or rails; Only enough cable so no coils on table |
|
|
Name the two types of steam irons
(2) |
Reservoir and Flash;
Steam iron |
|
|
How do the reservoir and flash irons work?
(3) |
Water enters iron from 2L tank or reservoir;
Water flows over element; flow of water controlled by thumb knob |
|
|
How do steam irons work?
(1) |
Fed from central steam supply
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of steam irons?
(4) |
Complicated;
Expensive; If a fault arises all irons are unusable; noisy |
|
|
Where are steam irons used?
(1) |
Very large factories
|
|
|
Name three types of pressing machine
(3) |
Pressing machines;
vacuum tables; Fusing presses |
|
|
What are the parts of the pressing machine?
(3) |
table;
buck ; shoe |
|
|
Which part of the pressing machine is stationary?
(1) |
Buck
|
|
|
Which part of the pressing machine is moved and how?
(3) |
Shoe;
hand; foot pedal |
|
|
Which part of the pressing machine houses the element?
(1) |
shoe
|
|
|
What are vacuum tables used for?
(1) |
Drying pressed garments
|
|
|
How do vacuum tables work?
(1) |
Suction draws moisture away
|
|
|
What are the types of fusing presses?
(2) |
Flat;
Roller |
|
|
What are fusing presses used for?
(1) |
Fusing resin fusable interfacing fabrics
|
|
|
What varies when using different types of interfacing fabrics?
(3) |
Time;
Heat; Pressure |
|
|
What problems can occur when fusing interfacing fabrics?
(2) |
Strike through;
Strike back |
|
|
How are problems caused when fusing interfacing fabrics?
(3) |
Incorrect time;
heat; pressure for weight of fabric |
|
|
What is strike through?
(2) |
Resin layer of interfacing fabric melts through fabric;
White markings visible on outside |
|
|
What is strike back?
(2) |
Resin layer deposit forms on shoe or roller;
Fuses onto next garment |
|
|
Why must workflow be carefully planned?
(3) |
Optimal production;
Save time; Save labour |
|
|
What needs to be ensured when designing workflow?
(4) |
Shortest routes;
no delay; no bottling up; no crossing routes |
|
|
Name the five types of equipment in the cutting room:
(5) |
Cutting table,
Cutting machines, Laying-up/Spreading machines, Marking machines and Ticketing machines |
|
|
Name the six requirements for cutting tables:
(6) |
Strong; Sturdy;
Smooth and durable finish; Correct height; Length; Width |
|
|
What is the width of a cutting table determined by?
(2) |
The type of fabric and the
laying-up technique used |
|
|
What is the width of the cutting table needed for knits? Why?
(2) |
Narrow table ;
They are layed-up on the fold |
|
|
What type of fabrics need cutting tables of 160 - 170 cm wide? Why?
(4) |
Fashion fabrics;
Plaids Checks; They are spread on the open. |
|
|
Name the two types of cutting machines:
(2) |
Straight knife/blade ;
Circular blade/Round knife |
|
|
How does the straight knife cutting machine work?
(2) |
They glide on a base which slides underneath the fabric ;
The blade cuts in a vertical motion |
|
|
What are the benefits of the straight knife cutting machine?
(3) |
Handles easily;
Manoeuvrable around sharp tight corners ; cuts nips easily |
|
|
Which type of cutting machine needs its knife removed for sharpening?
(1) |
Straight knife/blade
|
|
|
How does the circular blade cutting machine work?
(2) |
The base slides underneath the fabric;
Cutting is done with a rotary action. |
|
|
What are the drawbacks of the circular blade cutting machine?
(2) |
Not effective around corners;
Cutting nips is not accurate. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the differential grinder in the rotary knife cutter?
(1) |
Keeps the blade sharp
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the safety shield in the rotary knife cutter?
(1) |
Prevents accidents
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the rotary blade in the rotary knife cutter?
(1) |
Cuts through fabric piles
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the base plate in the rotary knife cutter?
(1) |
Guides for cutting accuracy
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the control handle in the rotary knife cutter?
(1) |
For manoeuvrability of the machine
|
|
|
What are the two advantages of laying-up machines?
(2) |
Labour-saving
Accurate |
|
|
What are the five disadvantages of laying-up machines?
(5) |
Expensive;
Needs special tables; Heavy; Fabric is more stretched; Less accurate with striped and check fabrics |
|
|
What is meant by the selvedge grain?
(1) |
The band of more tightly woven fabric that runs up
either side of the fabric's meterage |
|
|
Name the three types of marking machines:
(3) |
Hot drill;
Thread marker; Hot Notcher |
|
|
Where are pocket and dart points marked?
(1) |
1 cm inside the point
|
|
|
How does the hot drill marking machine work?
(3) |
Circular base placed under fabric at position for marking;
Lower the drill down into fabric; A small hole is burned into the fabric pile. |
|
|
Which two types of fabrics can you not use the hot drill on? Why not?
(3) |
Natural fibres;
knits; They will run |
|
|
Why is polyester easily marked by the hot drill?
(1) |
Heat sensitive so melts
|
|
|
What types of fabrics are appropriate to use a thread marker on?
(3) |
Silk,
velvet, very fine natural fabrics |
|
|
What two parts make up a thread marker?
(2) |
spoolpin;
needle |
|
|
How does the thread marker work?
(3) |
A needle is lowered into the fabric;
the stitch is caught underneath and snipped; leaving a thread loop as the needle rises. |
|
|
Which marking machines can be used to mark pocket and dart positions?
(2) |
Hot drill ;
Thread marker |
|
|
What is a hot notcher used for?
(5) |
To mark accurate 2mm nips for;
seam widths; Hem widths; pleats; other match points |
|
|
How does a ticketing machine work?
(2) |
It prints and ;
sticks coded stickers onto garment pieces. |
|
|
Why do garment pieces need to be ticketed?
(5) |
To ensure correct assembly ;
Misplaced parts can be placed in the correct bundle; Garment parts can be checked; Determine when parts go missing; workers can be traced |
|
|
What do the codes printed by ticketing machines show?
(4) |
Size
part colour style |
|
|
What is a marker?
(1) |
A plan of how to lay-out the pattern pieces on the fabric.
|
|
|
What are the eight requirements for a marker?
(8) |
Width is the same as fabric; Parts are economical;
Parts don't overlap; long and straight edges are aligned; Small pieces fit into larger spaces; Keep selvedge grain in mind; Use thin clear making pen to trace parts onto marker paper; check the whole marker again |
|
|
What should you check your marker for?
(4) |
All parts marked;
Parts lie correctly; No waste; Saves time and labour |
|
|
What is another name for a ticketing machine?
(1) |
Sober machine
|
|
|
What methods of transporting work in a factory
(2) |
Plastic crates ;
Conveyer belts |
|
|
Define the term "Chartering Conventions"
(3) |
Policies that are applicable to all processes on flow charts
|
|
|
Name the three chartering conventions
(6) |
Heading; Structure and description (vertical
symbol followed by description); Connection of subdivisions or components indicated by horizontal line at vertical point of connection |
|
|
Name the two methods of arranging workstations
(2) |
Line stations;
Island stations |
|
|
What are line stations?
(1) |
Workstations follow each other in a horizontal line.
|
|
|
What are island work stations?
(1) |
Workstations arranged in groups of 3 or 4 face each other.
|
|
|
When and why are island work stations effective?
(2) |
When processes consist of 3 or 4 operations;
Space is saved from transport lanes. |
|
|
What spaces need to be left around workstations
(4) |
Transport avenue
aisle for supervisor and worker use; Behind and in front of the workflow. |
|
|
Why should workers not sit with backs to the wall?
(4) |
Feel confined;
No avenue for emergency, supervisor or mechanic |
|
|
What are the characteristics of industrial machines?
(7) |
One function; Big;
Mounted on stand; Thick and sturdy tabletop; One horsepower single- or three phase motor; Greater speed; Expensive |
|
|
What is another name for a straight sewing lock stitch machine
(1) |
Plain sewer
|
|
|
How is a lock stitch formed?
(2) |
Formed by a needle and bobbin thread
Hooked through the centre of the fabric ply. |
|
|
Name two types of lock stitch machine
(2) |
Straight sewing lock stitch machine
Zig-zag lock stitch machine |
|
|
How does a zig-zag lock stitch machine differ from the plain sewer?
(1) |
The needle bar swings left and right, forming a zig-zag
|
|
|
Name two types of chain stitch machine
(2) |
Single thread chain stitch machine
Double chain stitch machine |
|
|
What are single thread chain stitches used for?
(1) |
Decorative stitchings
|
|
|
What is a double thread chain stitch machine used for?
(1) |
Seams in trousers
|
|
|
How does the double thread chain stitch machine differ from the single thread one?
(3) |
More elastic
Stronger Subjected to more strain |
|
|
Name three types of general function machine
(3) |
Lock stitch machine
Chain stitch machine Double and multi-needle machines |
|
|
What are the two ways that double needle machine can work
(2) |
Two bobbins
Two spreaders |
|
|
Which stitch do double needle machines that use bobbins use?
(1) |
Lock stitch
|
|
|
Which stitch do double needle machines that have spreaders use?
(1) |
Chain stitch
|
|
|
What fabric is usually sewn using a chain stitch double needle machine?
(1) |
Denim
|
|
|
Name five special function machines
(5) |
Buttonhole machines
Bar tacking machines Button sewing machines Blind stitch machines embroidery machines |
|
|
Name two types of buttonhole machines
(2) |
Double bar (Shirt) buttonhole machine
Key hole buttonhole |
|
|
Describe how the Double bar buttonhole machine functions.
(5) |
Uses a bobbin and bobbin case
Sews a zig-zag stitch Blade cuts hole open Automatic thread cutter The stitch length, width and density are adjustable |
|
|
Describe how the keyhole buttonhole machine functions.
(4) |
Double thread chain stitch
Blade cuts hole open Automatic thread cutter Size is adjustable |
|
|
What are the requirements of thread for a buttonhole machine?
(2) |
Strong
Correct twist |
|
|
What do you need to do when you change the buttonhole size being made by a buttonhole machine?
(1) |
Change the blade
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a bar tacking machine?
(4) |
Attaching belt carriers (loops)
Reinforcing fly base, pocket ends, pleats |
|
|
What stitch does the bar tacking machine use?
(1) |
zig-zag
|
|
|
How does the button sewing machine function?
(3) |
Chain stitch
One needle and spreader Button held in spring clamp |
|
|
What kind of buttons can a button sewing machine sew on?
(6) |
Two holes
Four holes With attachment: hooks, eyes, press studs and buttons with a shank |
|
|
What is another name for a blind stitch machine?
(1) |
Blind hemmer
|
|
|
What stitch does a blind stitch machine use?
|
Chain stitch
|
|
|
Describe the needle in a blind stitch machine?
(2) |
Curved
positioned horizontally |
|
|
What is the width of hems that a blind stitch machine can sew?
(1) |
5mm - 8mm
|
|
|
What stitch does an embroidery machine use?
(1) |
Chain stitch
|
|
|
How many heads can operate on an embroidery machine?
(1) |
12 - 25
|
|
|
How many colour threads can each head of an embroidery machine sew with at once?
(1) |
three
|
|
|
Name two finishing machines
(2) |
Serging machine
Overlocker |
|
|
How does a serging machine function?
(2) |
Two threads
One needle and one looper |
|
|
For what purpose would you use a serging machine?
(1) |
Serging long seams
|
|
|
What is the benefit of a serging machine?
(1) |
Cheaper than overlocking
|
|
|
How many threads can overlockers function with?
(1) |
3 - 4
|
|
|
How do the mechanics of a three and four thread overlocker differ?
(2) |
Three threads = 1 needle and 2 loopers
Four threads = 2 needles and 2 loopers |
|
|
For what reason would you use a differential feed overlocker?
(2) |
Gathers
Knits |
|
|
Name three labour saving devices?
(3) |
Feeders
Feet Folders |
|
|
What are the benefits of using a feeder?
(3) |
Fast
Accurate Leaves operator's hand free |
|
|
What are folders?
(4) |
Attachments with a groove for folding
waistbands neck bands cuffs |
|
|
What are the benefits of folders?
(2) |
Accurate
Saves manual labour |
|
|
Name three types of feet
(3) |
Hemming feet
Binders Gathering feet |
|
|
What is the purpose of hemming feet?
(1) |
Feet fold hems evenly and neatly.
|
|
|
What widths are hemming feet available in?
(1) |
3mm - 5mm
|
|
|
What size rolled hems are hemming feet able to sew?
(1) |
6mm
|
|
|
What are the benefits of hemming feet?
(2) |
Saves time
Saves labour |
|
|
What do binders do?
(2) |
Fold and
attach bias binding |
|
|
What is another name for gathering feet?
(1) |
Shirring feet
|
|
|
What does a gathering foot do?
(2) |
Retards feeding action
so gathers fabric |
|
|
What are the requirements of work surfaces in the pattern room?
(2) |
Depends on pattern maker's preference
Smooth, flat surfaces for tracing blocks and making markers |
|

What is this machine?
(1) |
Straight knife / blade
|
|

What is this machine?
(1) |
Circular blade / Round knife / Rotary
|
|

What is this machine?
(1) |
Handheld round knife cutter
|
|
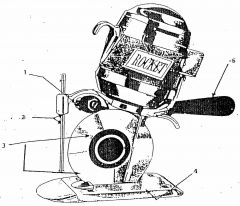
What is 1?
(1) |
Differential grinder
|
|
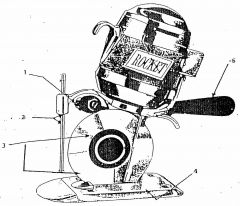
What is 2?
(1) |
Safety shield
|
|
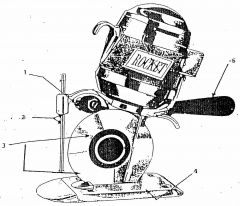
What is 3?
(1) |
Rotary blade
|
|
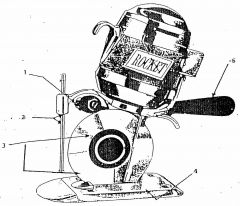
What is 4?
(1) |
Base plate
|
|
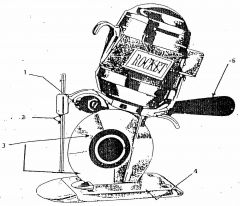
What is 5?
(1) |
Control handle
|
|

What is this machine?
(1) |
Laying up machine
|
|

What is this machine?
(1) |
Cloth drill marker
or hot drill |
|

What is this machine?
(1) |
Thread marker
|
|

What is this machine?
(1) |
Hot notcher
|
|

What is this machine?
(1) |
Pattern perforator
|
|

What is this machine?
(1) |
Ticketing machine
or sober machine |
|

What is this?
(1) |
Adjustable cloth clamp
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Cloth clamp
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Reservoir or flash iron
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Utility press
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Vacuum table
|
|
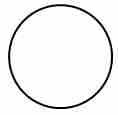
What does this symbol indicate on a workflow chart?
(1) |
Process or work activity
|
|
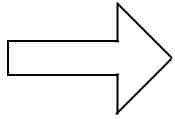
What does this symbol indicate on a workflow chart?
(1) |
Transport: movement of workers; materials or products
|
|
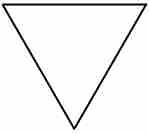
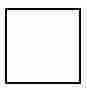
What does this symbol indicate on a workflow chart?
(1) |
Permanent storage
|
|
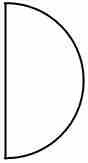
What does this symbol indicate on a workflow chart?
(2) |
Temporary storage
or delay |
|
What does this symbol indicate on a workflow chart?
(1) |
Inspection
|
|
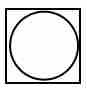
What does this symbol indicate on a workflow chart?
(2) |
Combined activity
Outside symbol is dominant activity |
|
What is this?
(1) |
Industrial lock stitch machine
|
|
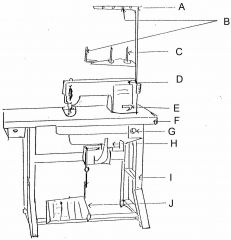
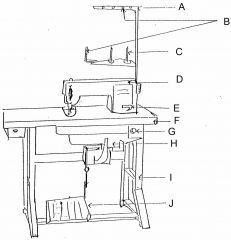
What is at A?
(1) |
Thread guide arm
|
|
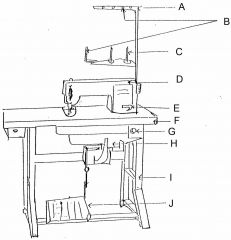
What is at B?
(1) |
Thread guide
|
|
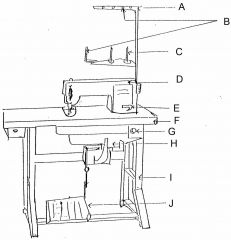
What is at C?
(1) |
Spool pin
|
|
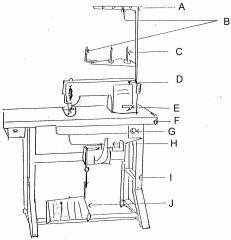
What is at D?
(1) |
Machine head
|
|
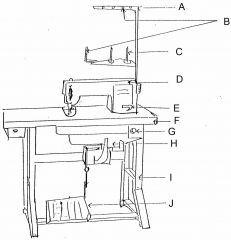
What is at E?
(1) |
Reverse lever
|
|
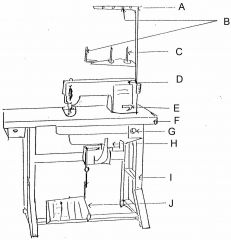
What is at F?
(1) |
Table top
|
|
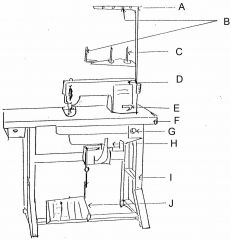
What is at G?
(1) |
Switch
|
|
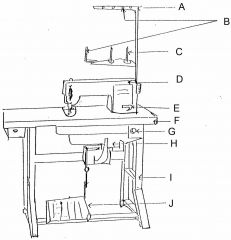
What is at H?
(1) |
Motor
|
|
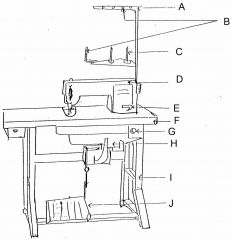
What is at I?
(1) |
Stand
|
|
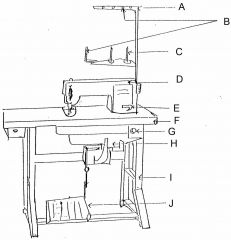
What is at J?
(1) |
Foot controller
|
|
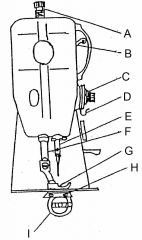
What is at A?
(1) |
Presser bar adjusting scree
|
|
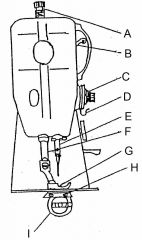
What is at B?
(1) |
Take up lever
|
|
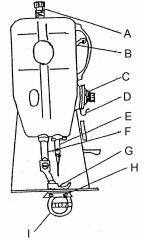
What is at C?
(1) |
Needle thread tension assembly
|
|
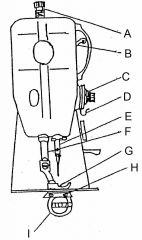
What is at D?
(1) |
Check spring / Take up spring
|
|
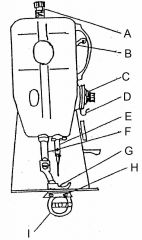
What is at E?
(1) |
Needle bar and needle
|
|
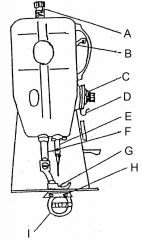
What is at F?
(1) |
Presser bar
|
|
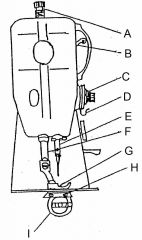
What is at G?
(1) |
Presser foot
|
|
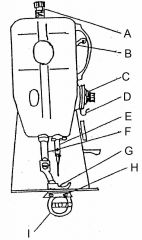
What is at H?
(1) |
Feed dog
|
|
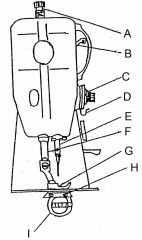
What is at I?
(1) |
Sewing implement
|
|
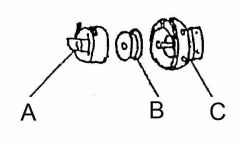
What is at A?
(1) |
Bobbin case
|
|
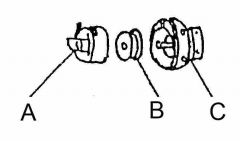
What is at B?
(1) |
Bobbin
|
|
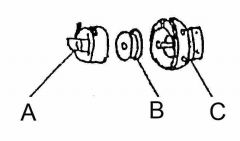
What is at C?
(1) |
Rotary hook
|
|
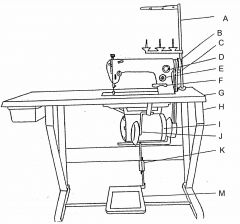
What is at A?
(1) |
Thread stand
|
|
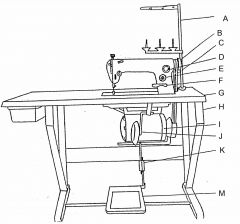
What is at B?
(1) |
Machine handwheel
|
|
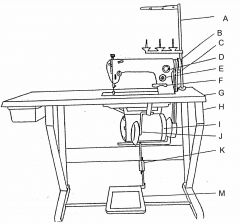
What is at C?
(1) |
Vee belt
|
|
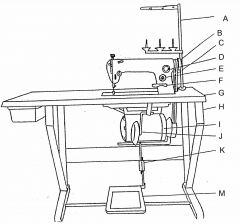
What is at D?
(1) |
Oil flow window
|
|
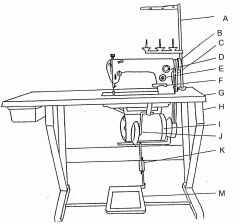
What is at E?
(1) |
Stitch length regulator
|
|
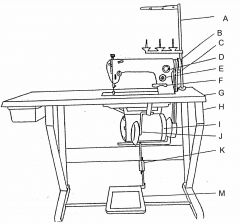
What is at F?
(1) |
Reverse feed lever
|
|
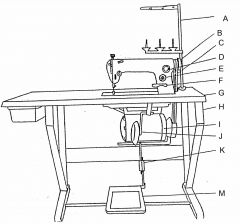
What is at G?
(1) |
Table top
|
|
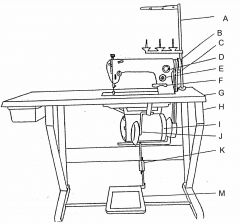
What is at H?
(1) |
Machine stand
|
|
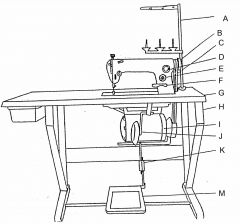
What is at I?
(1) |
Clutch motor
|
|
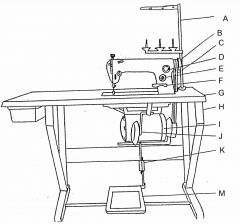
What is at J?
(1) |
Knee lifter (machine foot)
|
|
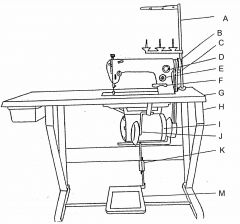
What is at K?
(1) |
Pitman rod
|
|
|
What is at M?
(1) |
Treadle
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Hemming foot
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Binder foot
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Gathering foot
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Elastic shirring foot
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Grading machine
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Perspex tailor's square
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Needlepoint tracer
|
|
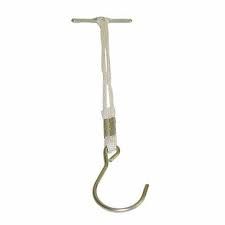
What is this?
(1) |
Pattern hook
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Pattern punch
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Pattern notcher
|
|

What is this?
(1) |
Collar turner
|

