![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
283 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the USPSTF screening recommendations for bladder cancer?
|
do not screen (grade D)
*encourage smoking cessation since 50% of all bladder cancer occurs in current or former smokers |
USPSTF Handbook 2009
|
|
|
Discuss the appraoch to the patient with a renal disorder.
|
Kidney disease may be found:
1. incidentally on routine exam 2. signs/symptoms may indicated kidney dysfunction -nausea -HTN -edema -hematuria Approach → assess cause and severity: 1. acute vs chronic 2. H&P 3. UA 4. GFR |
Current ch22
|
|
|
Define oliguria.
|
abnormally low urine output
|
|
|
|
Define proteinuria.
|
excessive protein excretion in the urine
|
|
|
|
What patient population is usually affected by orthostatic proteinuria and how is it measured?
|
<30y/o
measures 8-hour overnight urinary protein secretion shoud be <50mL |
|
|
|
What are the USPSTF screening recommendations for penile cancer?
|
no recommendations
|
USPSTF Handbook 2009
|
|
|
Define hematuria.
|
blood in the urine
|
|
|
|
Gross hematuria is considered a sign of malignancy until proven otherwise, true or false?
|
True!
|
|
|
|
Describe the etiology, location and character of renal pain.
|
location → ipsilateral CVA
radiation → umbilicus referred pain → ispsilateral testicle in men or labium in women ETIOLOGY & ASSOCIATED CHARACTER: infection → constant obstruction → intermittent intraperitoneal disorder → lie motionless to avoid pain kidney disorder → move about to find comfortable position |
Current ch23
|
|
|
Define hematospermia.
|
blood in the semen
|
|
|
|
Define pneumaturia.
|
air or gas in the urine
|
|
|
|
Define nocturia.
|
need to get up at night to urinate
|
|
|
|
Define urgency.
|
urgent need to urinate
|
|
|
|
What is uremic frost.
|
manifestation of chronic renal failure; urea accumulates in sweat; fine white power remains after sweat evaporates
|
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for bladder cancer?
|
smoking
environmental exposure to solvents or dyes |
Current ch39
|
|
|
Define frequency.
|
frequent need to urinate
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of bladder cancer?
|
hematuria
irritative voiding symptoms → frequency, urgency |
Current ch39
|
|
|
Describe the etiology, location and character of ureteral pain.
|
typically acute and due to obstruction
site of pain often correlates with site of obstruction distension of ureter → dull ache hyperperistalsis/spasm of ureter → colic if upper ureter, may refer to scrotum of male or labium of female if mid-ureter, may refer to ipsilateral lower abdominal quadrant (do not confuse with appendicitis on RT side or diverticulitis on LT side) if lower ureter, may cause vesicle irritability |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of bladder cancer?
|
UA → hematuria
cytology US, CT, or MRI → filling defects biopsy → staging |
Current ch39
|
|
|
Describe the etiology, location, and character of vesicle pain.
|
acute urinary retention → severe suprapubic discomfort
chronic urinary retention → painless acute cystitis → pain referred to distal urethra + associated with urination *suprapubic pain unrelated to urination is rarely vesicular |
|
|
|
What is the pattern of metastasis for bladder cancer?
|
liver → hepatomegaly
lymph → LE lymphedema |
Current ch39
|
|
|
What is the management of bladder cancer?
|
1. if superficial → resection +/-local chemotherapy
2. if invasive but localized → cystectomy, irradiation, chemotherapy 3. if invasive → systemic chemotherapy followed by cystectomy |
Current ch39
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of pneumaturia?
|
fistula between urinary bladder and colon
|
|
|
|
Define azoospermia.
|
absence of sperm in semen
|
|
|
|
Define aspermia.
|
absence of semen
|
|
|
|
Define impotence (AKA erectile dysfunction).
|
consistent inability to attain or maintain an erection
|
|
|
|
What is uremic frost.
|
powdery deposits of urea and uric acid salts on the skin due to excretion of nitrogenous waste in the sweat
|
Stedmans
|
|
|
What is the pattern of metastasis of testicular cancer?
|
lymph
retroperitoneal lung brain |
|
|
|
What is the ddx for uremic frost?
|
chronic renal disease
chronic renal failure uremia |
|
|
|
What are the risk factors of penile cancer?
|
5th or 6th decade
uncircumsized smoking balanitis |
|
|
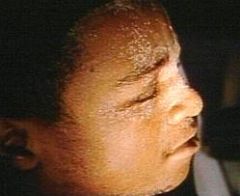
|
uremic frost
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of penile cancer?
|
non-tender ulcer or warty growth under foreskin
itchy or burning sensation beneath foreskin hidden behind erythematous phimosis |
|
|
|
What is the normal range for sodium?
|
136-145 mEq/L
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p120
|
|
|
What is the most abundant cation in extracellular fluid?
|
sodium
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p120
|
|
|
What is the management of penile cancer?
|
1. circumcision
2. resection 3. radiation if young male + noninvasive cancer, resection refused, metastasis 4. chemotherapy if metastasis |
|
|
|
What is another name for vasopressin?
|
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
|
|
|
|
What is the pattern of metastasis of penile cancer?
|
lymph
|
|
|
|
What is the major regulating factor of body fluid balance?
|
sodium
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p120
|
|
|
What is the best treatment for metastatic prostate cancer?
|
decreasing testosterone
|
|
|
|
What is hyponatremia?
|
abnormally low serum sodium
<136 mEq/L |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p122
|
|
|
List 12 signs/symptoms of hyponatremia.
|
lethargy
apathy agitation disorientation hypothermia Cheyne-Stokes respiration nausea anorexia muscle cramps abnormal sensor depressed DTRs seizures |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p122
|
|
|
Does hyponatremia occur in presence of low, normal, or high total body sodium?
|
all
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p122
|
|
|
What are the two main categories of hyponatremia?
|
1. sodium depletion due to fluid loss (e.g. dehydration)
2. sodium dilution due to fluid intake greater than fluid loss |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p122
|
|
|
List 9 signs/symptoms of hypernatremia?
|
lethargy
irritability restlessness thirst muscle twitching hyperflexia seizures coma death |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p125
|
|
|
What should be considered when assessing natremic status?
|
serum sodium
renal function hydration status fluid intake/output |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p122
|
|
|
What is the normal range for potassium?
|
3.5-5.0 mmol/L
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p130
|
|
|
What is the ddx for hyperkalemia?
|
renal failure
renal failure + increased potassium intake glomerulonephritis problem with proximal or distal convoluted tubule obstructive disease of urinary tract (urolithiasis) ↓ aldosterone secretion (Addison's) acidemia meds: -ACE inhibitors -ARBs -K-sparing diuretics surgery: -transplant rejection |
|
|
|
What tests are in an electrolyte panel?
|
sodium
potassium chloride total CO2 |
Antrim
|
|
|
What is the range for normal serum osmolality?
|
280-295 mOsm/kg H2O
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p120
|
|
|
Where is ADH secreted from?
|
magnocellular neurons in supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p120
|
|
|
Names 4 causes for stimulation of ADH secretion.
|
1. thirst
2. hypovolemia (detected by baroreceptors) 3. increased serum osmolality 4. angiotensin II |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p120
|
|
|
Define dysuria.
|
difficult or painful urination
|
|
|
|
Define urinary urgency.
|
strong desire to void
|
|
|
|
What drug turns urine blue-green?
|
amitriptyline
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
What drugs turn urine orange-red?
|
phenazopyridine
rifampin |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
How does renal dysfunction affect lab results?
|
↑ K (hyperkalemia)
↑ PHOS (hyperphosphatemia) ↓ creatinine clearance |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p11
|
|
|
What drugs are nephrotoxic?
|
prolonged course of high-dose aminoglycosides
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p39
|
|
|
How do nephrotoxic drugs affect lab results?
|
↑ CREAT
↑ aminoglycoside trough |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p39
|
|
|
What is the generic name of LASIX
|
furosemide
|
|
|
|
What kind of medication is furosemide?
|
loop diuretic
|
|
|
|
What is the risk of treating a patient with CHF with digoxin and furosemide?
|
furosemide decreases serum K+
hypokalemia increases risk of digoxin cardiac toxicity so treat patient acutely with K+ supplementation |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p41
|
|
|
Which is more accurate in assessing renal function, serum creatinine or urine output + urine creatinine?
|
urine output + urine creatinine
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p42
|
|
|
How can cefoxitin affect lab results?
|
may falsely elevate serum CREAT
if true renal failure, both BUN and CREAT would be elevated |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p42
|
|
|
What is the ddx for high protein in urine?
|
glomerulonephritis
cystitis pyelonephritis HTN HF |
|
|
|
Describe direct inguinal hernia, indirect inguinal hernia, and femoral hernia.
|
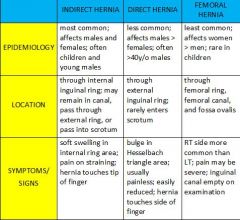
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
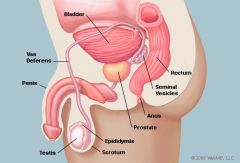
What penile structure surrounds the male urethra?
|
corpus spongiosum
|
|
|
|
What is the function of the penis?
|
1. excretion of urine
2. introduction of semen into vagina |
Mosbys p641
|
|
|
What is the function of the testicles?
|
synthesis of spermatozoa and testosterone
|
Mosbys p641
|
|
|
Define cryptorchordism.
|
undescended testicle(s)
|
|
|
|
What is the function of the epididymis?
|
storage, maturation, and transit of sperm
|
Mosbys p641
|
|
|
Describe the pathway of the vas deferens.
|
begins at tail of epididymis
ascends spermatic cord travels through inguinal canal unites with seminal vesicle |
|
|
|
What is the function of the vas deferens?
|
transportation of sperm from epididymis to ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation
|
|
|
|
What is the function of the seminal vesicles?
|
secrete seminal fluid (part of semen)
-alkaline -helps neutralize acidity of vagina → protecting sperm |
|
|
|
What is the cremasteric muscle and its function?
|
muscle covering the testis that raises and lowers the scrotum to regulate the temperature of the testis and promote spermatogenesis
|
|
|
|
List possible genitourinary complaints.
|
erectile dysfunction
persistent erections unrelated to sexual stimulation prolonged erection difficulty with ejaculation penile discharge penile lesions penile mass testicular mass testicular pain infertility hernia |
|
|
|
Define hypospadias.
|
congenital abnormality where urethral meatus is located on ventral surface of glans penis, shaft of penis, or base of penis
|
|
|
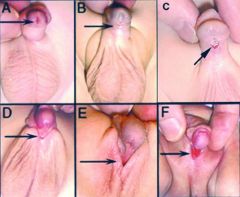
|
hypospadias
|
|
|
|
Describe the procedure for performing a male genitourinary exam.
|
1. introduce self
2. explain purpose of exam 3. wash hands ask about self exams 4. ask patient to raise gown 5. inspect skin and hair distribution around pubic hair, penis, and testicles retract foreskin if necessary 6. palpate shaft of penis down front and sides - size, shape/contour, lesions, induration (hardness), masses, tenderness 7. palpate glans penis and urethral meatus - inflammation, discharge 8. palpate scrotum (hold testicle in hand and palpate with other hands) - size, shape/contour, mass -palpate each testis -palpate each epididymis and spermatic cord -check for inguinal hernias -feel one side and watch opposite side 9. palpate femoral pulse palpate inguinal and femoral lymph nodes inspect and palpate for femoral hernias by placing hand over femoral area, asking patient to cough, feel on one side and look at other side 12. inspect perianal area, feel coccyx ask patient to bear down - hemorrhoids lubricate finger ask patient to bear down insert finger while patient relaxes -palpate prostate - identify lobes and median sulcus, assess size, consistency -sweep finger over all 4 walls -crook finger and sweep again -ask patient to bear down to assess sphincter tone -give patient tissues |
|
|
|
What is the ddx for penile discharge?
|
urethritis
balanitis STIs -trichomonas -gonorrhea -chlamydia -herpes penile cancer foreign body |
|
|
|
Which testicle is often lower, left or right?
|
left
|
Mosbys p649
|
|
|
Describe how to perform a genital self-examination.
|
perform once a month
perform in warm shower 1. hold penis in hand 2. examine head for lesions or discharge 3. examine shaft for lesions, masses -make sure to examine underside 4. examine skin beneath pubic hair for lesions 5. examine scrotum for tenderness, swelling, masses 6. purpose is to have idea of what is normal so notice when something changes |
Mosbys p651
|
|
|
What is the ddx for enlarged penis without enlargment of the testes?
|
precocious puberty
adrenal hyperplasia CNS lesion |
Mosbys p654
|
|
|
How do you elicit the cremasteric reflex?
|
stroke medial thigh with a tongue blade → cremasteric muscle should contract and scrotum should rise
|
|
|
|
*notes on genitourinary and rectal exam
|
1. focus on 1 testicle at a time
2. cup testicle with one hand while examine with other 3. can find epididymis easier if start with spermatic cord 4. when checking for inguinal hernias, feel on one side and look at opposite side (not all hernias are palpable, but may be visible!) 5. check for femoral hernia by placing hand flat over femoral area and having patient cough (feel on one side and look at opposite side) 6. during rectal, feel coccyx area for induration 7. put finger against anus and ask patient to bear down and then insert 8. touching prostate makes patient feel like they have to urinate 9. boggy prostate might indicate infection?? 10. remember to curl knuckle |
|
|
|
What equipment is needed for the male genitourinary and rectal examination?
|
gloves
lubrication fecal occult card and developer penlight for transillumination |
|
|
|
Where does a femoral hernia occur?
|
fossa ovalis where femoral artery exits abdomen
|
Mosbys p656
|
|
|
Are femoral hernias more common in males or females?
|
females
|
Mosbys p656
|
|
|
Describe condyloma acuminatum lesions.
|
soft, reddish lesions
|
Mosbys p659
|
|
|
What is another name for foreskin?
|
prepuce
|
Mosbys p659
|
|
|
What are the complications of condyloma acuminatum?
|
squamous cell carcinoma
|
Mosbys p659
|
|
|
What is condyloma acuminatum commonly known as?
|
genital warts
|
|
|
|
Describe molluscum contagiousum lesions.
|
pearly gray, smooth, dome-shaped, umbilicated, with discrete margins
usually located on glans penis |
Mosbys p660
|
|
|
What is Valsalva maneuver?
|
forcible exhalation against closed airway (i.e. when closing your mouth and pinching your nose)
|
|
|
|
Define pyuria.
|
urine that contains pus
|
|
|
|
Define epispadias.
|
congenital abnormality where urethral meatus is located along dorsal shaft of penis
|
|
|
|
Hypospadias increases the risk of what disorder?
|
cryptochordism
|
Mosbys p657
|
|
|
What is the treatment for hemorrhoids?
|
increase water intake
increase fiber intake NSAIDs for pain surgery if non-responsive to above treatment |
|
|
|
What are the physical exam findings of external hemorroids?
|
rectal pain, pruritus, bleeding with defecation, often visible while straining, may become thrombosed
|
|
|
|
What are the physical exam findings of internal hemorroids?
|
no rectal pain unless thrombosed, prolapsed or infected; bleeding with or without defecation; not palpable; not visible unless prolapsed through anus
|
|
|
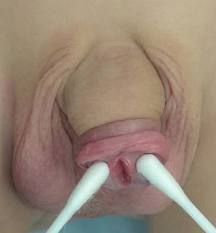
|
epispadias
|
|
|
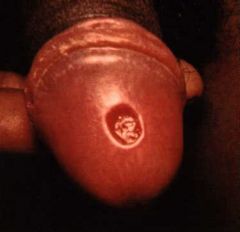
|
chancre of 1° syphilis
|
|
|
|
What is the etiology of nephrolithiasis?
|
stones may be composed of:
calcium oxalate (70-80%) calcium phosphate (5-10%) uric acid (5-10%) struvite (5-10%) cystine (1-5%) men:women 3:1 3rd-4th decades high temperature and humidity (SW united states) sedentary occupation decreased water intake genetics |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of nephrolithiasis?
|
nausea and vomiting
flank pain colic pain → sudden, severe, intermittent, radiation to anterior abdomen, ipsilateral testis or labium, patient constantly moving irritative voiding symptoms if stone lodged lower down → frequency, urgency |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of nephrolithiasis?
|
UA → hematuria, +/- infection
stone analysis CT first line also KUB, US, IVP if first stone → electrolytes, calcium, phosphate, uric acid if recurrence → 24 hour urine, PTH |
|
|
|
What is management of nephrolithiasis?
|
1. double fluid intake → during meals, 2 hours after meals, before going to sleep, during night
2. calcium stone absorptive disorder → type I, II, or III; cellulose phosphate, dietary calcium restriction, or orthophosphates respectively resorptive disorder → secondary to hyperparathyroidism → surgery renal disorder → thiazide diuretics 3. uric acid stone → potassium citrate to break up stone, dietary purine restriction, allopurinol 4. struvate stone → associated with UTI → antibiotics 5. cystine stone → difficult to treat → increase fluid intake, alkalinize urine, etc. |
|
|
|
What is the patient education for nephrolithiasis?
|
stay hydrated
restrict sodium to 100 mEq/d restrict protein to 1g/kg/d |
|
|
|
Which kidney stones are radiopaque and which are radiolucent?
|
RADIOPAQUE:
calcium oxalate calcium phosphate struvite RADIOLUCENT: uric acid (unless mixed with calcium oxalate) cystine |
|
|
|
Smooth edged ground glass appearance is characteristic of what type of kidney stone?
|
cystine
|
|
|
|
Which kidney stones have urinary pH <5.5 and which have urinary pH >7.2?
|
pH <5.5 = uric acid, cystine
pH >7.2 = struvite |
|
|
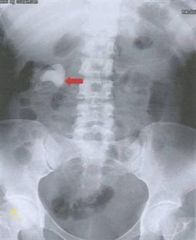
|
calcium oxalate kidney stone
|
|
|
|
What is the etiology of interstitial cystitis?
|
unknown
associated with: severe allergies IBS IBD diagnosis of exclusion → URNC negative, cytology negative, no vaginitis, urethral diverticulum, genital herpes, chemical/radiotion cystitis 18-40y/o white Jewish women hx of childhood bladder problems |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of intestitial cystitis?
|
pain with bladder filling that is releived by emptying
irritative voiding symptoms → frequency, urgency, nocturia |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of interstitial cystitis?
|
UA/URNC → negative for infection
cytology → negative for malignancy urodynamic eval → excludes detrusor instability cystoscopy → +/- submucosal petechiae or hemorrhage biospy |
|
|
|
What is the management of interstitial cystitis?
|
1. symptomatic relief only
2. hydrodistension 3. amitryptiline etc. |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of acute cystitis?
|
infection of bladder
most commonly due to coliform bacteria (E. coli) occasionally due to gram-pos bacteria (enterococci) associated with sexual activity in women rare in men |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of acute cystitis?
|
usually afebrile
irritative voiding symptoms +/- gross hematuria suprapubic tendernes otherwise physical exam unremarkable |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of acute cystitis?
|
UA → pyruria, bacteriuria, +/- hematuria
URNC → positive |
|
|
|
What is the management of acute cystitis?
|
single dose therapy or 3 day regimen
fluoroquinolones ( or nitrofurantoin |
|
|
|
What is the prevention of acute cystitis?
|
if women + >3 episodes per year:
1. prophylactic antibiotics → TMP-SMX, nitrofurantoin, or cephalexin 2. take single dose at bedtime or before sexual activity if catheter-related: 1. use catheter only when necessary 2. use proper insertion technique 3. remove catheter when no longer necessary 3. antimicrobial catheters in high-risk patients 4. external collection devices for men 5. postvoid residual |
|
|
|
What is acute cystitis?
|
infection of the bladder
|
|
|
|
Acute cystitis is common in men, true or false?
|
false!!!
think infected stone, prostatitis, or chronic urinary retention! |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup for UTI in men?
|
figure out underlying problem
think infected stone, prostatits, chronic urinary retention abdominal US cytoscopy CT if anatomic abnormality, pyelonephritis, recurrent infection |
|
|
|
What is a post-void residual?
|
measure of urine remaining in bladder after attempt to empty it completely
measured via US no risk or adverse effects |
|
|
|
What organism is the most common cause of uncomplicated UTI?
|
E. coli
|
|
|
|
What is the etiology of pyelonephritis?
|
commonly gram-negative bacteria (E. coli, proteus, klebsiella, enterobacter, pseudomonas)
less commonly gram-positive bacteria (enterococcus faecalis, staph aureus) |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of pyelonephritis?
|
fever and chills
nausea and vomiting flank pain → constant irritative voiding symptoms → dysuria, frequency, urgency tachycardia CVA tenderness |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of pyelonephritis?
|
CBC → leukocytosis, left shift
BMP → kidney function UA → pyuria, WBCs, WBC casts, bacteriuria, +/- hematuria URNC → positive BC → +/- positive if sepsis |
|
|
|
What is the management of pyleonephritis?
|
1. if young, uncomplicated → treat as outpatient:
fluorquinolone (ciprofloxacin x 21 days) or nitrofurantoin 2. if elderly, living alone, complicated (severe, signs of sepsis) → hospitalize: IV ampicillin + IV gentamicin (aminoglycoside) narrow-spectrum antibiotics based on BC results |
|
|
|
Discuss recurrent UTI.
|
consider drug resistance or anatomical abnormality
|
|
|
|
Define significant bacteriuria.
|
presence of any bacteria (>1 bacterium/oil power field) on gram-stain of uncentrifuged urine
if asymptomatic 100,000 CFUs/mL urine if symptomatic 1000-10,000 CFUs/mL urine |
|
|
|
What patient populations are commonly affected by asymptomatic bacteriuria.
|
pregnancy
elderly DM spinal cord injury |
|
|
|
What are the treatment guidelines for asymptomatic bacteriuria?
|
treat pregnant women
do not treat elderly, diabetics, spinal cord injury, catheters |
|
|
|
Define asymptomatic bacteriuria.
|
CLEAN-CATCH SPECIMEN:
1. for women → 2 specimens, isolation of same organism, >100,000 CFUs per mL of urine 2. for men → 1 specimen, isolation of 1 organism, >100,000 CFUs per mL urine CATHETER SPECIMEN: women or men, one specimen, one organism isolated, >100 CFUs per mL of urine *CFU = colony forming unit |
|
|
|
Define incontinence.
|
involuntary loss of urine
|
|
|
|
Define total incontinence.
|
loss of urine at all times and all positions
|
|
|
|
Define stress incontinence.
|
loss of urine associated with activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure (coughing, sneezing, laughing, standing up, lifting, exercising)
|
|
|
|
Define urge incontinence.
|
strong urge to void followed by involuntary loss of urine
|
|
|
|
Defue overflow incontinence.
|
chronic urinary retention resulting in involuntary loss of urine
|
|
|
|
What are the 4 categories of incontinence?
|
total
stress urge overflow |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of total, stress, urge, overflow, and mixed incontinence?
|
TOTAL:
often due to urinary fistula → due to trauma, radiation, surgery treat with foley catheter or surgery STRESS: common in women impaired urethral spincter tone → due to childbirth, decreased estrogen, gyn surgery treat with pelvic muscle exercises or surgery URGE: common in elderly detrusor overactivity → uninhibited bladder contractions → due to idiopathic, CNS lesion (stroke), stone, infection, tumor associated with frequency and nocturia OVERFLOW: common in men chronic urinary retention → due to bladder outlet obstruction or atonic bladder → urethral stricture, BPH, or prostate cancer if male; cystocele if female associated with urge, straining, post-void dribbling MIXED: urge + stress common in women combination of detrusor overactivity + impaired urethral sphincter function |
|
|
|
What are the indications for a post-void residual?
|
incontinence
|
|
|
|
Define mixed incontinence.
|
stress + urge incontinence
|
|
|
|
What is bladder outlet obstruction (BOO)?
|
blockage at base of bladder that prevents flow of urine
|
|
|
|
What is the etiology of BOO?
|
urethral stricture
bladder stone BPH tumor (uterus, cervix, prostate, rectum) |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of BOO?
|
unable to void
weak stream feeling of incomplete void palpable bladder +/- abdominal pain |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of BOO?
|
foley catheter
US KUB CT |
|
|
|
Define hydrocele.
|
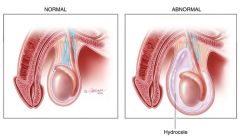
cyst due to fluid accumulation in tunica vaginalis of scrotum
|
|
|
|
Define paraphimosis.
|
inability to return foreskin to normal position after retracting it behind glans penis
|
Mosbys p657
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of a hydrocele?
|
smooth, firm, nontender scrotal mass that transilluminates
10% of testicular tumors associated with hydrocele |
|
|
|
Define priapism.
|
prolonged erection
|
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of hydrocele?
|
positive transillumination
|
|
|
|
Define phimosis.
|
inability to retract foreskin
|
Mosbys p648
|
|
|
What is the treatment for a hydrocele?
|
usually resolves spontaneously
|
|
|
|
Define balanitis.
|
inflammation of the glans penis
*only occurs in uncircumsized males |
Mosbys p648
|
|
|
In what patient population does a hydrocele most commonly occur?
|
infants
|
|
|
|
What is the most common etiology of balanitis?
|
uncircumsized male + poorly controlled DM + candidal infection
|
Mosbys p648
|
|
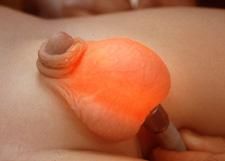
|
hydrocele
|
|
|
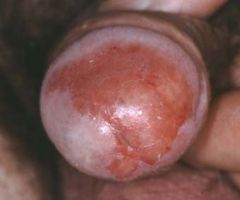
|
balanitis
|
|
|
|
What is the ddx for testicular swelling?
|
testicular trauma
testicular torsion orchitis epididymitis hydrocele spermatocele varicocele testicular tumor hernia |
|
|
|
What is peyronie's disease?
|
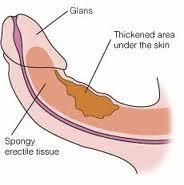
disorder characterized by a fibrous band in the corpus cavernosum resulting in abnormal curvature in the penis during erection
|
Mosbys p660
|
|
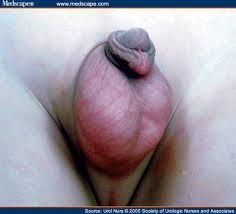
|
RT hydrocele
|
|
|
|
What is the etiology of peyronie's disease?
|
unknown
associated with dupuytren's contracture |
Mosbys p660
|
|
|
What are the complications of peyronie's disease?
|
painful erection
inability to insert penis into vagina erectile dysfunction |
Mosbys p660
|
|
|
What is the ddx for priapism?
|
1. trauma
-genitourinary trauma -spinal cord trauma 2. infection -urethritis -cystitis -prostatitis 3. blood disorder -sickle cell anemia -thalassemia -other hemoglobinopathy 4. cancer -neoplasm -leukemia 5. neurologic disorders -multiple sclerosis -neurosyphilis -diabetic neuropathy 6. foreign body 7. medications -impotence 8. cocaine 8. idopathic (most common) |
|
|
|
What are the complications of paraphimosis?
|
urinary retention
impaired circulation → edema or gangrene of glans penis |
|
|
|
How does penile squamous cell carcinoma present?
|
painless non-healing ulceration usually originating in foreskin or glans penis
|
Mosbys p660
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of peyronie's disease?
|
abnormal curvature of the penis during erection
painful poor erection distal to curvature may result in inability to insert penis into vagina may result in erectile dysfunction palpable fibrous plaque involving tunica albuginea (sheath surrounding corpus cavernosus penis) |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of peyronie's disease?
|
if severe, radiograph may confirm ossification and calcification
|
|
|
|
What is the management of peyronie's disease?
|
1. refer to urologist
2. 50% resolve spontaneously 3. trial of p-aminobenzoic acid powder/tablets or vitamin E tablets x several months 4. surgery → graft or prosthetic |
|
|
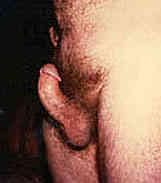
|
peyronie's disease
|
|
|
|
What is the etiology of phimosis?
|
normal during first few years of life
risk factors include chronic balanoposthitis |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of paraphimosis?
|
often iatrogenic → foreskin retracted to insert catheter and not returned to normal
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of phimosis?
|
inability to retract foreskin
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of paraphimosis?
|
inability to return retracted foreskin to normal position
|
|
|
|
What are the complications of phimosis?
|
balanitis
urinary retention |
|
|
|
What is the management of paraphimosis?
|
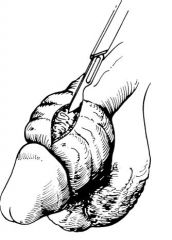
1. attempt manual reduction
-squeeze glans penis firmly for 5-10 minutes to reduce its size -move foreskin distally while glans penis is pushed proximally 2. if manual reduction unsuccessful → make dorsal slit of foreskin 3. refer to urologist for circumcision to prevent recurrence |
|
|
|
What is the prevention of phimosis and paraphimosis?
|
good hygiene
circumcision |
|
|
|
What is the management of phimosis?
|
IF ASSOCIATED WITH IRRITANT BALANITIS:
1. cleansing with foreskin retracted 2. 0.5% hydrocortisone cream 3. sitz baths IF ASSOCIATED WITH FUNGAL BALANTITIS: 1. good hygiene 2. topical antifungal cream |
|
|
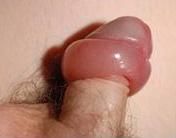
|
paraphimosis
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of balanitis?
|
fungal infection → malodorous, purulent, excoriated and tender glans penis
bacterial infection → erythema, warmth, and edema of foreskin, glans penis, and shaft |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of balanitis?
|
wet mount for yeast?
|
|
|
|
What is the management of balantitis?
|
IF FUNGAL INFECTION:
1. clean with mild soap and allow appropriate drying time 2. apply topical antifungal cream → nystatin or clotrimazole 3. oral antifungal → fluconazole 4. circumcision IF BACTERIAL INFECTION: 1. broad-spectrum antibiotic → 1st or 2nd generation cephalosporin 2. + fungal treatments if refractory → culture or biopsy |
|
|
|
What is the prevention of balanitis?
|
good hygiene
circumcision |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of balanitis?
|
associated with foreskin
usually caused by poor hygiene or irritation which results in candidal infection also may result in bacterial infection (Gardnerella, anaerobes) if recurrent, consider DM |
|
|
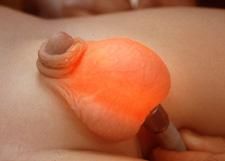
|
hydrocele
|
|
|
|
In what patient population does penile carcinoma most commonly occur?
|
uncircumsized men who practice poor hygiene
|
Mosbys p660
|
|
|
What is the treatment for a hydrocele?
|
usually resolves spontaneously
|
|
|
|
What is the ddx for orchitis?
|
*orchitis is uncommon
complication of mumps complication of prostatic infection |
Mosbys p662
|
|
|
Define varicocele.
|
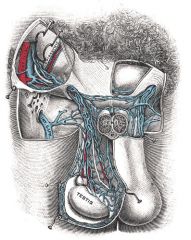
condition where the veins of the pampiniform plexus in the spermatic cord are abnormally dilated and tortuous
|
Mosbys p662
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of a varicocele?
|
commonly on LT side
often only visible while standing → usually dimish in size or disappear when supine "bag of worms" appearance may be painful |
Mosbys p662
|
|
|
What are the complications of a varicocele?
|
reduced fertility
|
Mosbys p662
|
|
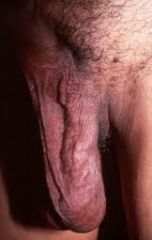
|
LT varicocele
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of epididymitis?
|
ACUTE:
fever scrotal pain → may radiate along spermatic cord or to flank epididymis enlarged and extremely tender, distinguishable from testis early in course scrotum erythematous and enlarged if associated urethritis → pain at tip of penis, urethral discharge if associated cystitis → irritative voiding symptoms if associated prostatits → possible tenderness positive prehn sign → elevation of scrotum above pubic symphysis provides relief (not reliable sign) |
Mosbys p663
Current ch23 |
|
|
What is testicular torsion?
|
disorder characterized by twisting of the spermatic cord, reducing blood supply to scrotum
|
|
|
|
What are the physical exam findings of testicular torsion?
|
acute onset
nausea and vomiting scrotal erythema, swelling, and extreme tenderness absence of cremasteric flex on affected side lack of voiding symptoms (compared to epididymitis) |
Mosbys p663
|
|
|
What patient population is most commonly affected by testicular torsion?
|
adolescents
10-20y/o |
Mosbys p663
|
|
|
Which is more common, indirect or direct hernia?
|
indirect
|
Mosbys p650
|
|
|
When palpating the testis, what should they feel like?
|
smooth
rubbery free of nodules sensitive but non-tender |
Mosbys p650
|
|
|
If a scrotal mass is identified, how can you determine if it is cystic or solid?
|
perform transillumination
if light shines through → cystic if light doesn't shine through → solid |
|
|
|
Define orchitis.
|
inflammation of the testicle
|
|
|
|
Define epididymitis.
|
inflammation of the epididymis
|
|
|
|
Where does a direct hernia occur?
|
through external inguinal ring
|
|
|
|
Where does an indirect hernia occur?
|
internal inguinal ring
|
|
|
|
Define spermatocele.
|
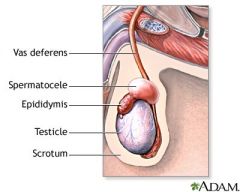
cyst due to spermatozoa accumulation in epididymis
|
|
|
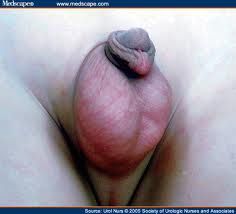
|
RT hydrocele
|
|
|
|
What is the ddx of epidiymitis?
|
UTI
STI TB (if chronic epididymitis) |
Mosbys p663
|
|
|
What are the physical exam findings of a testicular tumor?
|
irregular nontender mass fixed to testis that does not transilluminate
|
Mosbys p664
|
|
|
What disorders of the spermatic cord, scrotum, and testes are emergencies?
|
orchitis
testicular torsion |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of epididymitis?
|
if acute → usually infectious
may also follow heavy lifting or trauma STI: <40 y/o associated urethritis gonorrhea or chlamydia Non-STI: older men associated UTI or prostatitis gram-negative rods Route → via urethra to ejaculatory duct, then down vas deferens to epididymis |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of epididymitis?
|
CBC → leukocytosis, shift to the left
if STI: URNC GCCHDNA → positive if non-STI: UA → puria, bacteriuria, +/- hematuria URNC → positive |
|
|
|
What is the management of epidiymitis?
|
1. best rest with scrotal elevation
2. if STI → antibiotics x 10-21 days; treat partner 3. if non-STI → antibiotics x 21-28 days |
|
|
|
What is the prognosis for epididmyitis?
|
if prompt treatment → outcome favorable
if delayed treatment → possible orchitis, abscess formation, or decreased fertility |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of orchitis?
|
associated with mumps (viral)
associated with epididymitis (bacterial) |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of orchitis?
|
mild or severe scrotal pain
MUMPS: fatigue, fever, HA, myalgias occurs 4-7 days following parotitis testicular pain and swelling (sparing epididymis) scrotal skin may be erythematous or edematous 70% unilateral EPIDIDYMITIS enlarged, tender epididymis boggy, tender prostate |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of orchitis?
|
Doppler U.S. to differentiate between mumps orchitis and testicular torsion
|
|
|
|
What is the management of orchitis?
|
MUMPS ORCHITIS:
1. symptomatic treatment only 2. analgesics 3. hot or cold packs 4. scrotal elevation EPIDIDYMO-ORCHITIS: 1. treat same as epididymitis |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of hydrocele?
|
positive transillumination
|
|
|
|
Which type of inguinal hernia may descend into the scrotum, direct or indirect?
|
indirect
|
|
|
|
List conditions related to the prostate.
|
prostatodynia
non-bacterial prostatitis acute bacterial prostatitis chronic bacterial prostatitis benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) prostate cancer |
|
|
|
Define prostatodynia.
|
prostatic pain
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of acute bacterial prostatitis?
|
high fever
irritative voiding symptoms +/- obstructive voiding symptoms suprapubic, sacral, or perineal pain warm and EXQUISITELY tender prostate |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of acute bacterial prostatitis?
|
CBCDP → leukocytosis, shift to the left
UAC → pyuria, bacteriuria, +/- hematuria URNC → positive |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of acute bacterial prostatitis?
|
Infection via:
ascent up urethra reflux of infected urine into prostatic ducts hematogenous (rare) lymphatic (rare) Possible organsims: usually gram-neg rods (E coli, pseudomonas) rarely gram-pos cocci (enterococci) |
|
|
|
List irritative voiding symptoms.
|
dysuria
frequency urgency nocturia |
|
|
|
List obstructive voiding symptoms.
|
hesistancy
decreased force of stream intermittency post void dribbling |
|
|
|
What is the management of acute bacterial prostatits?
|
OUTPATIENT: ??
refer if chronic prostatitis or urinary retention admit if sepsis or urinary drainage required HOSPITALIZATION: 1. order BC 2. treat empirically with IV ampicillin + IV gentamicin until BC results available, then switch to narrow-spectrum antibiotics 3. if afrebrile 24-48 hours → oral antibiotics → quinolones x 4-6 weeks 4. after therapy complete → order URNC and examine prostatic secretions 3. |
|
|
|
What are the complications of acute bacterial prostatits?
|
sepsis
*prostatic massage is contraindicated |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of chronic bacterial prostatitis?
|
may result from acute bacterial prostatitis, but many men have no history of acute infection
history of UTI routes same as acute organisms same as acute |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of chronic bacterial prostatitis?
|
asymptomatic
irritative voiding symptoms suprapubic, sacral, and perineal discomfort → dull, poorly localized physical exam often unremarkable normal, boggy, or indurated prostate |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of chronic bacterial prostatitis?
|
CBC
UAC → normal URNC → positive prostatic secretions → leukocytosis |
|
|
|
What is the management of chronic bacteiral prostatitis?
|
1. trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole x 6-12 weeks
2. symptomatic relief with NSAIDs (ibuprofen, indomethacin), hot sitz baths 3. difficult to cure 4. refer if persistent |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of non-bacterial prostatitis?
|
unknown
most common form of prostatitis |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of non-bacterial prostatitis?
|
irritative voiding symptoms
suprapubic or perineal discomfort positive expressed prostatic excretions identical to presentation of chronic bacterial prostatitis except no history of UTIs |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of non-bacterial prostatits?
|
CBC
UAC URNC → negative prostatic secretions → leukocytosis |
|
|
|
What is the management of non-bacterial prostatitis?
|
1. trial of antibiotics → erythromycin x 14 days
2. continue x 3-6 weeks if favorable response, otherwise discontinue 3. symptomatic relief with NSAIDS and sitz baths 4. recurrence common but no serious sequelae |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of BPH?
|
obstructive voiding symptoms → straining, hesitancy, decreased force of stream, post-void dribbling, double voiding (voiding a second time within 2 hours), sensation of incomplete bladder emptying
irritative voiding symptoms → frequency, urgency, nocturia +/- enlarged prostate → smooth, firm, elastic |
|
|
|
What is the prevalence of BPH based on age?
|
41-50y/o → 20%
51-60 y/o → 50% >80 y/o → 90% |
|
|
|
What is BPH?
|
benign tumor of the prostate
|
|
|
|
What is the ddx for obstructive voiding symptoms in men?
|
BPH
UTI urethral stricture neurogenic bladder prostate cancer bladder cancer |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of BPH?
|
UA → to exclude infection and hematuria
PSA → controversial |
|
|
|
Define prostatitis.
|
inflammation of the prostate
|
|
|
|
Define premature ejaculation.
|
peristent or recurrent ejaculation with minimal stimulation before a person desires (associated with distress)
|
|
|
|
Define retrograde ejaculation.
|
ejaculation of semen into urinary bladder instead of out through urethra
|
|
|
|
What is the prevalence of erectile dysfunction?
|
affects 30 million American men
affects 52% of men 40-70y/o |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of male infertility?
|
1. decreased/absent sperm count → ejaculatory duct obstruction, retrograde ejaculation, androgen insufficiency
2. abnormal sperm motility → abnormal flagella, partial ejaculatory duct obstruction, varicocele, antisperm antibodies, infection 3. abnormal morphology → varicocele, infection, environmental exposure |
Current ch23
|
|
|
What is the intial workup of suspected male infertility?
|
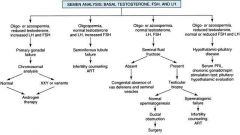
WORKUP IF >6 MONTHS UNPROTECTED SEX
HISTORY: 1. testicular insults (trauma, torsion, cryptochordism) 2. testicular infections (mumps orchitis, epididymitis) 3. environmental exposures (excessive heat, pesticides, chemotherapy, radiation) 4. medications (anabolic steroids etc) 5. drugs (alcohol, tobacco, marijuana) 6. sexual habits (frequency and timing of sex, use of lubricants) 7. both partners previous fertility experiences 8. PHM (thyroid disease, liver disease, diabetic neuropathy, pituitary tumor, hernia repair, retroperitoneal or pelvic surgery) PHYSICAL EXAM: 1. features of hypogonadism (body habitus, diminished male hair pattern, gynecomastia, underdeveloped secondary sexual characteristics) 2. estimate testicular size 3. evaluate scrotal contents 4. palpate epididymis, vas deferens, prostate 5. varicoceles? DIAGNOSTIC WORKUP: 1. semen analysis on 2 separate occasions -must be collected after 2-3 of no ejaculation -must be evaluated within 1 hour 2. endocrine evaluation if low sperm count -initially order FSH and testosterone -if FSH or testosterone abnormal, order LH and prolactin 3. other possibilites include urine (for suspected retrograde ejaculation), genetic testing, imaging |
Current ch23
|
|
|
Define azotemia.
|
retention of BUN and CREAT
|
|
|
|
Define oligospermia.
|
low concentration of sperm in the semen
|
|
|
|
Define vasectomy.
|
method of contraception where vas deferens is surgically cut and tied to prevent sperm from entering ejaculatory stream
|
|
|
|
Define impotence.
|
inability to achieve or maintain an erection during sexual performance
|
|
|
|
List the methods of male birth control.
|
CONDOMS:
worn on penis made of latex or animal membrane prevents pregnancy 98% of time with perfect use prevents STIs including HIV temporary cost ranges from free to $1 VASECTOMY: outpatient surgical procedure vas deferens severed and sealed through scrotal incision under local anesthesia azoospermia may take 2-6 months other forms of contraception must be used until 2 sperm-free ejaculations confirm sterility complications rare and generally due to infection 100% effective cost $350-1000 permanent but can be reversed WITHDRAWAL METHOD: pulling out 75-95% effective PILL may be coming soon! |
|
|
|
What is the etiology of priapism?
|
60% idiopathic
penile trauma spinal cord trauma pelvic infection pelvic tumor sickle cell disease leukemia medications → sildenafil citrate, tadalafil, alprostadil |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation fo priapism?
|
erection >4hr
corpus cavernosum engorged while corpus spongiosum and glans penis flaccid |
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic workup of priapism?
|
none
|
|
|
|
What is the management of priapism?
|
if reversible cause:
1. terbutaline PO or IM 2. aspiration of blood from corpus cavernosum + compression dressing 3. if due to alprostadil → aspirate + inject alpha-adrenergic agent (phenylephrine) 4. if traumatic or refractory → urologic consult 5. can lead to ischemia 6. commonly results in erectile dysfunction |
|
|
|
What is the prevention of priapism?
|
discontinue offending medications
|
|
|
|
What is the etiology of male sexual dysfunction?
|
LOSS OF LIBIDO:
androgen deficiency LOSS OF ERECTION: arterial venous neurogenic medications → anti-hypertensives, antidepressants psychogenic |
|
|
|
Discuss the physiology of an erection.
|
Normal male erection is a neurovascular phenomenon relying on an intact autonomic and somatic nerve supply to the penis, smooth and striated musculature of the corpora cavernosa and pelvic floor, and arterial blood flow supplied by the paired pudendal arteries. Erection is caused and maintained by an increase in arterial flow, active relaxation of the smooth muscle elements of the sinusoids within the paired corpora cavernosa of the penis, and an increase in venous resistance. Contraction of the bulbocavernosus and ischiocavernosus muscles results in further rigidity of the penis with intracavernosal pressures far exceeding systolic blood pressure. Nitric oxide is a pivotal neurotransmitter that initiates and sustains erections; however, other molecules contribute, including acetylcholine, prostaglandins, and vasoactive intestinal peptide.
|
|
|
|
What is the initial workup of male sexual dysfunction?
|
1. distinguish between problems of erection, libido, orgasm, ejaculation, and deformity
2. erection during sleep or in morning? if yes → psychogenic cause if no → organic cause 3. gradual loss of erection? if yes → likely organic cause 4. severity of ED → achieving vs maintaining; situational, intermittent, chronic 5. associated disease → pelvic trauma, peyronie's disease, HTN, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, CKD, DM, endocrine disorder, neurogenic disorder, depression, alcohol, tobacco, drugs, chemotherapy, radiation therapy 6. CBC, GLUC, LIPID, testosterone, prolactin 7. if testosterone or prolactin abnormal → FSH, LH |
|
|
|
What is the management of erectile dysfunction?
|
1. oral medications → sildenafil citrate, tadalofil
2. injectable medications → alprostadil 3. vacuum erection device 4. penile prosthetic 5. if arterial disorder → vascular reconstruction 6. if hormonal disorder → hormone replacement |
|
|
|
Sildenafil Citrate (Viagra): indications, contraindications, patient education
|
INDICATIONS:
erectile dysfunction pulmonary arterial HTN CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity to sildenafil concurrent use of nitrates PATIENT EDUCATION: take 1 tablet 1 hour before sexual activity do not take >1 tablet per day absorption delayed by consumption of food (especially high-fat) avoid excessive alcohol consumption → may cause hypotension do not take nitrates may experience HA, flushing, vision changes, nasal congestion, epistaxis, dyspepsia, myalgia, insomnia discontinue if serious side effects → erection >4hr, vision change, hearing changes |
Pharmacology p341
Lexi-Comp p1368 |
|
|
Tadalafil (Cialis): indications, contraindications, patient education
|
INDICATIONS:
erectile dysfunction CONTRAINDICATIONS: concurrent use of nitrates PATIENT EDUCATION: take 1 tablet 1 hour before sexual activity do not take >1 tablet per day avoid excessive alcohol consumption → may cause hypotension do not take nitrates may experience HA, flushing, nasal congestion, dyspepsia discontinue if serious side effects → erection >4 hours, vision changes, hearing changes |
Pharmacology p341
Lexi-Comp p1422 |
|
|
Compare sildenafil citrate (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis).
|
SILDENAFIL CITRATE:
quicker onset (<1 hour) shorter duration (4 hours) absorption delayed by food consumption TADALAFIL: slower onset (1 hour) longer duration (36 hours) absorption NOT delayed by food consumption |
Pharmacology p341
|
|
|
Alprostadil (Caverject, Muse): indications, contraindications, patient education
|
INDICATIONS:
erectile dysfunction CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity to alprostadil anatomical deformity of penis conditions predisposing to priapism → sickle cell disease, multiple myeloma, leukemia penile implant pregnancy PATIENT EDUCATION: get trained on how to inject into penis or urethra only use appropriate dose do not use >1 time per day do not use >3 times per week do not reuse needles avoid concurrent alcohol use may experience penile pain, urethral burning or bleeding, testicular pain, HA, dizziness, HTN discontinue if serious side effects → erection >4hr, signs of penile fibrosis (angulation, fibrosis, peyronie's disease) |
Lexi-Comp p70
|
|
|
List drugs to treat erectile dysfunction and whether they are oral or injections.
|
ORAL:
sildenafil citrate tadalafil INJECTION: alprostadil (may be injected into corpus carvernosum or urethra) |
|
|
|
Describe the male sexual response cycle.
|
sexual stimulation → increased production of nitric oxide → increased acitivity of guanylyl cyclase → increased cGMP → increased relaxation of smooth muscle of corpus cavernosum → increased blood flow → erection
|
Pharmacology p342
|
|
|
What are the pharmacologic agents used to treat BPH?
|
finasteride
prazosin terazosin |
|
|
|
What are the pharmacologic agents used to treat prostate cancer?
|
treatment → flutamide
palliative treatment → leuprolide |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of finasteride?
|
decreased libido
sexual dysfunction |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of prazosin and terazosin?
|
vertigo
orthostatic hypotension tachycardia sexual dysfunction |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of flutamide?
|
decreased libido
sexual dysfunction gynecomastia |
|
|
|
Flutamide: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
INDICATIONS: metastatic prostate cancer CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity severe hepatic impairment ADVERSE EFFECTS: gynecomastia decreased libido impotence nausea and vomiting increase AST and LDH DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATIONS: |
|
|
|
Finasteride: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
INDICATIONS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATIONS: |
|
|
|
Prazosin: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
INDICATIONS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATIONS: |
|
|
|
Terazosin: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
INDICATIONS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATIONS: |
|
|
|
What is a semen analysis?
|
includes semen volume, sperm count, sperm morphology, and sperm motility
|
|
|
|
What are the indications for ordering a semen analysis?
|
suspected infertility
post-vasectomy |
|
|
|
What are the collection requirements for a semen analysis?
|
semen collected in urine container following masturbation and 3 days of abstinence from ejaculation
sample must be kept at room temperature and examined within 1 hour |
|
|
|
What are the indications for ordering a PAP?
|
intermediate and high-risk prostate cancer
may be helpful in determining who needs more aggressive treatment |
|
|
|
What is a PAP test?
|
blood test that measures an enzyme produced by the prostate called prostatic acid phosphatase
|
|
|
|
What does PAP stand for?
|
prostatic acid phosphatase
|
|
|
|
What is the sensitivity of PSA?
|
40%
PSA has a low sensitivity since it is specific for the prostate but not for prostatic carcinoma It can be elevated by urinary retention, urethral instrumentation, prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostatic instrumentation (e.g. rectal exam, prostatic needle biopsy) It cannot be relied on as the sole prostatic cancer screening method |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p3-4, p42
|

