![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is gestational age and how is gestational age calculated?
|
estimated age of fetus
calculated from first day of last (normal) menstrual period (LMP) and expressed in completed weeks |
|
|
|
What is the estimated date of confinement (EDC) and how is it calculated?
|
estimated due date
1. 280 days (or 40 weeks or 9 months) from 1st day of LNMP +/- 2 weeks 2. 266 days (or 38 weeks) from last ovulation (requires normal 28 day menstrual cycle) 3. subtract 3 months from month of LNMP, add 7 days from 1st day of LNMP, add 1 year *if LNMP is 07/16/10, EDC is 4/23/11 4. fetal doppler → fetal heart sounds heard at 10-12 weeks 5. fetoscope → fetal heart sounds heard at 17-20 weeks 6. ultrasound → transabdominal or transvaginal |
|
|
|
Define presumptive, probable, and positive diagnoses of pregnancy.
|
PRESUMPTIVE:
signs and symptoms that may indicate pregnancy but could also be caused by something else examples include amenorrhea, nausea and vomiting, mastodynia, Montgomery Tubercle enlargement, colostrum secretion, secondary breast enlargement, frequency, nocturia, UTI, increased body temp, striae, spider telangiectasias, linea nigra, chloasma, fetal movement (quickening) PROBABLE: signs and symptoms that indicate pregnancy a majority of the time examples include same symptoms as presumptive, enlarged abdomen, changes in pelvic bones, ligaments and organs (Chadwick's sign, Hegar's sign), leukorrhea, Braxton Hicks contractions POSITIVE: signs that cannot be mistaken for anything other than pregnancy examples include palpation of fetus, fetal heart sounds, fetus present on ultrasound, positive pregnancy test |
|
|
|
CHORIONIC VILLUS SAMPLING (CVS):
|
cells obtained from placental chorionic villi and analyzed by variety of techniques including chromosomal analysis if FH with potential risks
used to detect chromosomal abnormalities (down syndrome) and genetic disorders (CF) (does not detect neural tube defects) performed at 11-14 weeks performed transabdominally with needle and ultrasound (similar to amniocentesis) or transcervically with catheter and ultrasound (more common) 99% accurate Increases risk of miscarriage |
|
|
|
AMNIOCENTESIS:
|
fetal cells obtained from amniotic fluid and grown in culture for chromosome analysis, biochemical analysis, and molecular biologic analysis following abnormal triple or quad screen
used to detect chromosomal abnormalities (downs syndrome), genetic disorders (CF), neural tube defects (spina abifida), paternity, lung maturity performed >15 weeks performed with needle and ultrasound testing takes 10-14 days 99% accurate increases risk of miscarriage |
|
|
|
When should a triple or quad screen be performed?
|
16-18 weeks
|
|
|
|
What is included in a triple or quad screen?
|
TRIPLE:
BHCG maternal serum AFP maternal serum estriol QUAD: tests listed above + inhibin-A |
|
|
|
What are the recommended screening tests during pregnancy and when should they be performed?
|
1. 1st prenatal visit → CBC, ABORHB, rubella antibody titer, HEPB antigen, RPR, HIV (can opt out), urine dip (glucose, protein, leukesterase, nitrites), URNC, PAP, GCCHDNA, optional serum or urine HCG, varicella antibody titer, PPD, CF, or down syndrome testing
2. 16-18 weeks → triple or QUAD screen 3. 26-28 weeks →1-hour GTT (50g) (3-hour GTT (100g) if 1-hour GTT abnormal) 4. 28 weeks → give RhoGAM if Rh incompatibility 5. Early 3rd trimester → Hct/Hgb to correct potential anemia and decrease need for transfusion in hemorrhage during delivery 6. 36 weeks → GBSDNA to reduce strep pneumo sepsis in newborn |
|
|
|
QUAD SCREEN:
|
screening test for all pregnant women (but especially if >35y/o, FH of birth defects, hx of radiation, DM, viral illness during pregnancy, harmful medications during pregnancy)
includes BHCG, AFP, estiol, inhibin-A , and mother’s age and ethnicity to assess risk of genetic disorders further tests are indicated if abnormal results (ultrasound, repeat quad screen, amniocentesis) performed at 16-18 weeks performed via venipuncture inaccurate if not performed at appropriate time or inaccurate dating of pregnancy (normally BHCG decrease, AFP increases, estriol increases, and inhibin-A stays constant) BHCG = hormone produced by placenta AFP = protein produced by fetus ESTRIOL = hormone (estrogen) produced by fetus and placenta INHIBIN-A = hormone produced by ovaries and placenta ↑ estriol indicates viable fetus, properly functioning placenta, and maternal well-being ↑AFP may indicate neural tube defect (spina bifida, anencephaly), abdominal wall defects (omphalocele, gastroschisis), multiple fetuses, inaccurate dating of pregnancy ↓AFP and estriol + ↑ BHCG and inhibin-A may indicate down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) |
|
|
|
What is the schedule for prenatal visits?
|
every 4 weeks at 0-32 weeks
every 2 weeks at 32-36 every week at 38-40 several times weekly to daily after EDC |
|
|
|
What is performed at prenatal visits follwoing the 1st prenatal visit?
|
1. BP
2. weight 3. fundal height measurement 4. fetal position determination via Leopold's maneuver 5. fetal heart tones via doppler 6. pregnancy precautions and concerns 7. identify risks using A-F screen 7. urine protein and glucose |
|
|
|
What is the normal rate of fetal heart beat?
|
120-160 bpm
|
|
|
|
What is Leopold's maneuver?
|
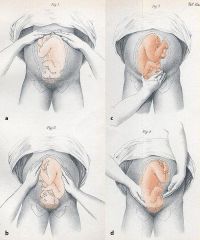
method to determine fetal position inside uterus
|
|
|
|
How do you measure fundal height and what is normal?
|
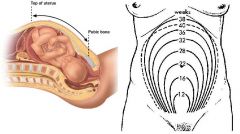
measure from pubic bone to top of uterus
at pubic bone at 8 weeks at umbilicus at ~22 weeks at xiphoid process at ~36 weeks starting at 24 weeks, gestational age should match measurment in cm +/- 3 cm (for example 24 week gestation should measure 21-27cm) |
|
|
|
What is the A-F screen?
|
A → amniotic fluid leak or gush
B → bleeding C → contractions <5-10 minutes apart D → dysuria E → pre-eclampsia or eclampsia (HA, vision changes, epigastric abdominal pain, marked edema) F → fetal movements decreased in frequency or intensity |
|
|
|
What are the indications for genetic counseling?
|
mother >35y/o
FH of genetic disease child with genetic disease abnormal prenatal testing (QUAD screen, amniocentesis) |
|
|
|
How do you assess fetal movement counts and what is a normal count?
|
fetal kicks detectable at 18-25 weeks
time how long it takes to count 10 kicks normally takes <2 hours wait few hours and repeat if abnormal contact provider if repeat abnormal or notice significant change in normal pattern over 3-4 days |
|
|
|
What is the normal weight gain during pregnancy?
|
BMI <20 = 30-40 lbs
BMI 20-25 = 25-35 lbs BMI 25-30 = 15-25 lbs BMI >30 = 15lbs If twins = 35-44 lbs *eat 100-300 extra calories daily |
|
|
|
What are the dietary recommendations during pregnancy?
|
2500 calories daily (increase by 100-300 extra calories) (though varies by BMI)
60g protein (increase by 20g) never diet prenatal vitamin containing folic acid (especially 1st trimester) possible iron 30-60mg/day and calcium 1-1.5g/day |
|
|
|
During pregnancy, what is the patient education regarding alcohol and smoking?
|
ALCOHOL:
teratogen increases risk of birth defects, death SMOKING: reduces O2 and nutrients supplied to fetus increases risk of low-birth weight, preterm birth, death increases risk of poor growth, learning diabilities, colds, heart disease, lung problems, cancer patch may still affect fetus |
|
|
|
During pregnancy, what is the patient education regarding sex?
|
SEX:
safe unless provider says otherwise may need to alter foreplay and positioning to be comfortable avoid sex if hx of miscarriage or premature birth, presence of STI (including partner), unexplained vaginal discharge or bleeding, placenta previa, incompetent cervix, water broken, dilated cervix |
|
|
|
During pregnancy, what is the patient education for travel?
|
travel is generally safe during entire pregnancy
carry copy of prenatal records LAND TRAVEL: wear seat belt do not disable airbags remain seated (use hand rails if need to use restroom) limit sitting to 5-6 hours stretch and take short walks to keep blood circulating AIR TRAVEL: safe to travel throughout pregnancy airline allows travel through 8th month while written permission from provider is required for 9th month sit in aisle seat hold seats when standing stand and stretch legs avoid small planes (if unpressurized, do not fly above 7000 feet) WATER TRAVEL: make sure provider on board or close by make sure motion sickness medication safe during pregnancy FOREIGN TRAVEL: talk to provider beforehand immunizations avoid diarrhea to prevent dehydration (drink bottled water, avoid unpasteurized milk, avoid fresh fruits and vegetables, avoid undercooked meat) |
|
|
|
During pregnancy, what is the patient education for exercise?
|
OKAY:
low-impact aerobics (unless hx of miscarriage) weight lifting (unless hx of miscarriage) jogging (unless experiencing complications) cycling (unless pavement wet) AVOID: high-impact aerobics contact sports scuba diving any risk for fall |
|
|
|
How do you determine fetal presentation and lie?
|
Leopold's maneuvers
|
|
|
|
What is fetal presentation?
|
1. fetal part most dependent (usually vertex/cephalic AKA head-first)
2. relationship of fetal part to maternal pelvis (usually right occiput anterior AKA fetal occiput lies in contact with right side of maternal iliopubic eminence) |
|
|
|
What is lie?
|
relationship of long axis of fetus to long axis of uterus
either longitudinal or transverse |
|
|
|
What is the most common fetal presentation and lie?
|
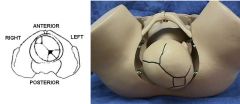
vertex/cephalic (head-first) and longitudinal
right occiput anterior most common left occiput anterior 2nd most common (fetal occiput lies in contact with right or left side of maternal iliopubic eminence) |
|
|
|
Define analgesia.
|
loss or modulation of pain perception
can be local, regional, or systemic |
|
|
|
Define anesthesia.
|
total loss of sensory perception
may include loss of consciousness |
|
|
|
PYSCHOSOCIAL SUPPORT & CHILDBIRTH CLASSES:
|
adjunctive therapy to medications
involves relaxation, suggestion, concentration, and motivation techniques which help reduce anxiety, tension, and fear increases knowledge of process of labor and delivery increases communication between patient and partner effects dependent on provider and patient commitment |
|
|
|
What is regional anesthesia vs general anesthesia?
|
REGIONAL ANESTHESIA:
local analgesia GENERAL ANESTHESIA: requires loss of consciousness |
|
|
|
What are the indications and contraindications for regional analgesia?
|
INDICATIONS:
labor analgesia C-section other OB procedures CONTRAINDICATIONS: infection valvular heart disease progressive neurologic disease coagulopathy hypovolemia patient refusal |
|
|
|
List types of regional analgesia.
|
lumbar epidural block
caudal epidural block |
|
|
|
LUMBAR EPIDURAL BLOCK
|
analgesic technique used for labor, vaginal delivery, or C-section
placed once labor established inject 3mL of 1.5% aqueous solution of lidocaine into catheter as test dose (if anesthesia does not occur after 5-10 minutes, inject another 5mL), inject total of 10mL of anesthetic solution (usually Bupivacaine + fentanyl), then continuously infuse 10-12mL/h given via bolus injections or continuous infusion dosing can be altered throughout labor and delivery eradicates pain between T10 and L1 during first stage of labor and between T10 and S5 during 2nd stage of labor supplemented with narcotics prolongs 2nd stage of labor increases use of outlet forceps but does not affect fetal outcomes monitor maternal BP due to predisposition to venous pooling and impaired venous return |
|
|
|
CAUDAL EPIDURAL BLOCK
|
type of epidural block approached through caudal space
can provide selective sacral block for 2nd stage of labor rarely used d/t complications (transfixing rectum, puncturing of fetal skull) lumbar epidural is safer |
|
|
|
SPINAL BLOCK
|
first-line for C-section
performed more quickly than epidural analgesia occurs within 5-10 minutes dense sensory and motor block ideal for surgery give saline beforehand mother remains conscious may cause spinal HA |
|
|
|
Describe the APGAR Score.
|
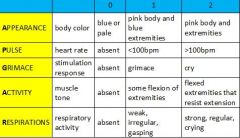
1. evaluation of infant at 1 minute and 5 minutes following birth
2. add scores of five individual observations for score between 0-10 3. continue at 5-minute intervals for ≤ 20 minutes until score ≥7 4. score reflects cardiopulmonary and neurological status 5. score does not determine need for resuscitation 6. 5 minute score of 0-3 associated with increased mortality |
|
|
|
Define spontaneous abortion and list types.
|
AKA miscarriage
pregnancy that ends spontaneously before fetus reaches viable gestational age THREATENED ABORTION: abortion may occur based on symptoms (abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding before 20 weeks) INEVITABLE ABORTION: abortion will occur (ruptured membranes, dilated cervix before 20 weeks) MISSED ABORTION: products of conception retained INCOMPLETE ABORTION: partial expulsion of products of conception SEPTIC ABORTION: incomplete abortion + infection of remaining products of conception, uterus, etc. COMPLETE ABORTION: complete expulsion of products of conception |
|
|
|
What is placenta previa?
|
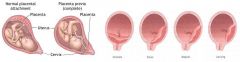
complication of pregnancy where placenta grows in lower part of uterus (may be low-lying, marginal, partially cover cervical canal, or completely cover cervical canal)
|
|
|
|
What is abruptio placentae?
|
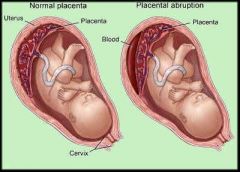
complication of pregnancy where placenta separates from uterine wall before delivery of fetus
|
|
|
|
What are the criteria for recurrent abortion?
|
>2-3 consecutive abortions occuring before 20 weeks with fetus weighing <500g
|
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for premature labor?
|
<16y/o or >35y/o
maternal weight <110 lbs multiple gestation anemia, infection, pneumonia, pyelonephritis incomplete cervix, uterine abnormalities placental abnormalities, premature membrane rupture, abnormal fetal presentation hx of preterm birth poor nutrition smoking alcohol abuse or drug addiction low SE status |
|
|
|
Define teratogen.
|
any substance, agent, or environmental factor that has an adverse effect on the developing fetus
|
|
|
|
What are the most common teratogens?
|
Drugs
Alcohol, antiseizure medications (phenytoin, valproic acid, etc), lithium, mercury, thalidomide, diethylstilbestrol (DES), warfarin (Coumadin), isotretinoin, etc. Infectious Agents Cytomegalovirus, Listeria, rubella, toxoplasmosis, varicella, Mycoplasma, etc. |
|
|
|
What are the risk factors, assessment, and management of Rh isoimmunization?
|
DEFINITION:
Rh negative mother + Rh positive fetus → causing mother to make anti-Rh antibodies that attack fetus → causing hemolytic anemia of fetus (manifests as jaundice of newborn) RISK FACTORS: previous pregnancy with Rh positive fetus + no RhoGAM given ASSESSMENT: ABORH indirect Coombs → detects antibodies against RBCs in maternal serum MANAGEMENT: if mother Rh negative + no antibodies present → give RhoGAM (300micrograms) at 28 weeks if mother Rh negative + antibodies present → determine type of fetus and monitor closely |
|
|
|
What is gestational diabetes, risk factors, assessment, and management?
|
any degree of glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy
risk factors include obesity, pear-shaped body, hx of gestational diabetes assessed via GTT managed by controlling DM |
|
|
|
What are the outcomes of gestational diabetes?
|
miscarriage, preterm birth, C-section, stillbirth
mother → pre-eclampsia, pyleonephritis fetus → excessive growth, congenital malformations, HR abnormalities, aspiration of meconium in utero |
|
|
|
What are the negative outcomes associated with multiple gestation?
|
pregnancy-induced HTN
preterm birth hemorrhage |
|
|
|
What is large for gestational age?
|
estimated fetal weight (EFW) ≥ 90th percentile for gestational age
|
|
|
|
What is intrauterine growth restriction?
|
estimated fetal weight (EFW) ≤ 10th percentile for gestational age
|
|
|
|
What is pre-eclampsia?
|
pregnancy condition characterized by HTN and protein in urine which develop after 20th week
|
|
|
|
What is eclampsia?
|
pregnancy condition characterized by pre-eclampsia + new-onset of grand mal seizures that cannot attributed to any other cause
|
|
|
|
How long after giving birth can pre-eclampsia remain?
|
2 weeks
if some cases, pre-eclampsia may not show up until labor |
www.preeclampsia.org
|
|
|
Describe the stages of labor and delivery.
|
FIRST STAGE: onset of labor to 10cm dilation (beginning of contractions), longest phase, easiest phase, contractions short, quick, and far apart
1. EARLY → 0-4 cm dilation 2. ACTIVE → 4-7 cm dilation (epidural must be given during this stage) 3. TRANSITION → 8-10 cm dilation SECOND STAGE: 10cm dilation to birth (beginning of pushing) THIRD STAGE: birth to expulsion of placenta 1. uterus contracts down to stop bleeding 2. start nursing to stimulate oxytocin secretion which causes contractions 3. peform fundal massage 4. monitor bleeding 5. deliver placenta 6. repair perineal injuries [FOURTH STAGE: 1st hour following expulsion of placenta (period of highest risk for maternal hemorrhage)] PUERPERIUM: expulsion of placenta to 6 weeks postpartum 1. involution of uterus 2. changes in lochia (postpartal vaginal discharge) which progresses from lochia rubra (reddish discharge for 3-5 days), lochia serosa (pinkish discharge until 10 days), lochia alba (whitish discharge for 10 days to 6 weeks) 3. menstruation and ovulation 4. cardiovascular changes 5. psychosocial changes |
|
|
|
List normal and breech positions.
|
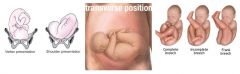
NORMAL:
vertex/cephalic ABNORMAL: face shoulder transverse frank breech (hip flexed, knees extended) incomplete breech AKA footling (one or both legs extended below buttocks) complete breech (hips and knees flexed) |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation and management of malpresentation?
|
detected via palpation and (Leopold's maneuvers) ballottment of uterus, pelvic exam, ultrasound, radiograph
management includes |
|
|
|
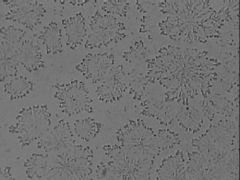
positive fern
|
|

