![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the Goal of Pharmacokinetics?
|
Develop a dosage regimen
|
|
|
relationship b/w plasma concentration and effect
|
Pharmacodynamics
|
|
|
Relationship b/w dosage regimes Cp. What units of measurements are of interest?
|
Pharmacokinetics
T0., CL, Vd |
|
|
ADMET
|
Absorption
Distribution Metabolism Excretion Xport |
|
|
Constant rate of elimnation, independent of conc. in the body(what type of elimination?)
|
Zero-order elimination
|
|
|
Elimination rate increases and drug concentration increases(what type of elimination?)
|
1st-order elimination
|
|
|
Saturable kinetics is often associated with this...
|
Metabolizing enzymes
|
|
|
What is Vd?
What is the lower and upper limit |
THe volume in which the total amt of drug in the body would be required to be dissolved in order to reflect the drug concentration in the plasma.
Lower limit-Blood volume(5-6L) Upper limit- No upper limit(~400L) |
|
|
Two reasons why Wd is very small
|
1. Drug is very hydrophilic(NM blocking agent, Abx)
2. Highly bound(~100percent) to plasma proteins |
|
|
If Vd for an adult is b/w 10-20L. The drug has entered...
|
Extracellular space
|
|
|
If Vd is 2-0L-Drug has reached...
|
Intracellular space/fluids
|
|
|
If Vd is 40L what happens to drug
|
Drug may be distributed to total body water(40L)
|
|
|
If Vd is very large(>200L). Two outcomes
|
1. Molecule can be very lipophilic
2. Drug is bound tightly in peripheral tissue |
|
|
Vd FOR A 1 COMPARTMENT MODEL:
At time zero following IV bolus dose of drug only, assuming instantaneous distribution throughout the compartment, the following equation can be used to estimate the Vd. |
Cpi=Dose/Vd
Vd=Dose/Cpi |
|
|
1) Which of the following statements is true?
a) Pharmacokinetics relates plasma concentration with dosage regimen. b) Pharmacodynamics relates plasma concentrations with the physiological effect. c) Pharmacokinetic analysis allows one to determine parameters such as t1/2, clearance, volume of distribution by studying the plasma concentration of drugs as a function if time. d) All of the above are true |
d) All of the above are true
|
|
|
2) The abbreviation ADMET stands for:
a) Adherence, Distribution, Marketing, Excretion and Tmax b) Absorption, Disease state, Metabolism , Excretion and Tmax c) Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Tmax d) None of the above are correct |
d) None of the above are correct
|
|
|
3) For a drug described by one compartment model, which of the following statements are true?
a) The whole body is considered as one homogeneous compartment b) Elimination takes place from the central compartment c) Drug input (absorption) is directed into the central compartment. d) All of the above are correct e) None of the above are correct |
d) All of the above are correct
|
|
|
4) For a drug exhibiting first order elimination which of the following statements are true?
a) The first order elimination rate constant increases with increasing drug plasma levels. b) The units of the first order rate constant are 1/time c) The overall drug elimination rate is constant and is not influenced by concentration of drug in the plasma. d) Only a and b are correct e) Only b and c are correct f) None of the above are correct |
b) The units of the first order rate constant are 1/time
|
|
|
5) The volume of distribution for any drug cannot be higher than 400L for a 70kg male.
a) True b) False |
False
|
|
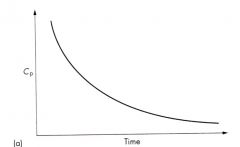
6) From the above plot of concentration of drug in the plasma (Cp) versus time one can definitively say (without taking the logarithm of the Cp) that drug exhibits or can be described by:
a) A one compartment model b) A two compartment model c) A three compartment model d) Non-zero order elimination kinetics e) Both b and d are correct f) None of the above are correct |
d) Non-zero order elimination kinetics
|
|
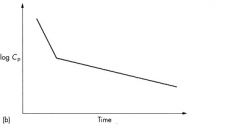
7) From the above plot it would be correct to assume that:
a) The drugs Log Cp versus time plot suggest that it shows two compartment model behavior b) The drugs Log Cp versus time plot suggest that it shows one compartment model behavior c) the drugs Log Cp versus time plot suggest that it shows three compartment model behavior d) All of the above are correct e) None of the above are correct |
a) The drugs Log Cp versus time plot suggest that it shows two compartment model behavior
|
|
|
8) The lower limit for the volume of distribution of a drug is?
a) There is no lower limit. b) 400 L c) Volume of blood and extracellular fluid d) Volume of blood alone |
d) Volume of blood alone
|
|
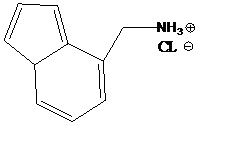
The following new investigational drug shown above is being tested in man for the first time and the following pharmacokinetic data are available. A high fat meal prolongs the Tmax. The drug administered as a solution is much more rapidly absorbed relative to the tablet. The drug has a pKa is 8. The drug has a volume of distribution of 500L and is 90% protein bound. The drug elimination occurs by CYP3A4 metabolism to an inactive metabolite and by renal elimination of the parent compound.
9) Which of the following statements are true? a) the drug is basic b) the drug is acidic c) the drug is neutral 10) At what pH would the drug have it highest dissolution rate? a) pH 2 b) pH 8 c) pH 12 11) The fact that the drug in solution is absorbed orally much faster than the tablet supports which of the following conclusions? a) The drug has dissolution rate limited absorption b) The drug has permeation rate limited absorption. 12) During the clinical trials they given too high of a dose and want to clear the drug out of the body as quickly as possible. To limit passive re-absorption back into the blood from the urine the correct action should be to? a) Increase the pH of the urine b) Decrease the pH of the urine 13) Co-administration of this drug with grapefruit juice would likely cause: a) An increase in the bioavailability b) A decrease in the bioavailability c) The bioavailability should stay the same since grapefruit juice inhibits CYP2A1, not CYP3A4 14) A patient is on this drug and starts the atkins diet. (i.e., high protein diet) What would be a likely therapeutic outcome of this? a) increased bioavailability b) decreased AUC c) increased half-life d) all of the above |
9. a) the drug is basic
10. a) pH 2 11. a) The drug has dissolution rate limited absorption 12. b) Decrease the pH of the urine 13. a) An increase in the bioavailability 14. b) decreased AUC |
|
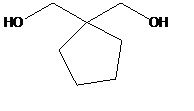
The drug above is administered by IV infusion to a patient (1mg/hour). The drug follows first order elimination kinetics and its kinetics can be described by one compartment model. The volume of distribution is 28 L. It is eliminated entirely unchanged in the urine. The half life of the drug is 32 hours. Please answer the following questions:
15) What is the time to reach steady state? a) 60-90 hrs b) 100-127 hours c) 160 – 190 hours d) 128-160 hours 16) The doctor wants to get the patients blood levels up to steady state levels of 30 mcg/mL immediately. What is the loading dose? a) 0.84 mcg b) 8.4 mcg c) 840 mg d) 840 g 17) Alkalizing the urine would have what effect on the half life of this particular drug? a) increased b) reduced c) no influence 18) A high protein diet will enhance the metabolic clearance of this drug. a) true b) false |
15. d) 128-160 hours
16. c) 840 mg 17.c) no influence 18. b) false |
|
|
22) In class we discussed two separate mechanism how increased drink volume could increase the absorption of drugs. The two reasons are:
a) Increased hepatic blood flow and increased gastric empting rate b) Decreased first pass metabolism and decreased gastric emptying rate c) Increased gastric emptying rate and decreased complexation d) Increased dissolution and increased gastric emptying rate |
d) Increased dissolution and increased gastric emptying rate
|
|
|
23) Increased intake of charbroiled food increases the expression/levels of which of the following?
a) Oxidative metabolizing enzymes b) Aromatic hydrocarbons c) CYP1A2 d) All of the above e) Only a and B |
d) All of the above
|
|
|
24) There are gender related differences in the bioavailability of drugs. These can be specifically attributed to:
a) Differences in CYP3A4 expression and/or activity b) Differences in P-glycoprotein expression and/or activity c) Differences in volume of distribution d) All of the above are correct e) Only a and b are correct |
e) Only a and b are correct
|
|
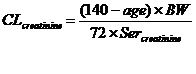
25) The Cockcroft and Gault equation for estimating creatinine clearance is shown above. If this equation is used to estimate the creatinine clearance in a woman the calculated value would likely be:
a) A perfect estimate of the true creatinine clearance. b) An overestimate of the true creatinine clearance. c) An underestimate of the true creatinine clearance. |
b) An overestimate of the true creatinine clearance.
|
|
|
26) Alterations in the pharmacokinetic behavior of drugs occur as person ages. Which of the following statements is/are correct with regard to reasons for changes in the oral absorption of drugs in the elderly?
a) Intestinal blood flow may be reduced. b) Intestinal surface area is usually reduced. c) The residence time in the small intestine may be increased. d) For drugs absorbed by passive diffusion the total area under the curve (AUC) is not usually influenced by age. e) All of the above are correct. f) Only a and b are correct. |
e) All of the above are correct.
|

