![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hematopoiesis |
The production of blood cells and platelets |
|
|
Whole blood is composed of |
Plasma- fluid portion Cells - RBCs WBCs and thrombocytes (platelets) |
|
|
White Blood Cells are |
Agranulocytes & Granulocytes |
|
|
Agranulocytes include |
No granules present Lymphocytes Monocytes |
|
|
Granulocytes |
Have granules Neutrophils Eosinophils Basophils |
|
|
Blood Cells |
Are constantly produced Finite life span so must be replaced Life span differs by cell type and species Begin in embryonic stages Changes in processes as aging occurs |
|
|
Hematopoietic activity & where it's produced |
Prenatal- produced in liver, spleen, thymus, red bone marrow Adult- primarily produced in red bone marrow or when stressed in the liver and spleen |
|
|
Erythropoiesis |
Production of erythrocytes |
|
|
Leukopoiesis |
Production of leukocytes |
|
|
Thrombopiesis |
Production of thrombocytes (platelets) |
|
|
Pluripotent Hematopoietic Stem Cell (HSC) |
All cells arise from this cell |
|
|
Cells that arise from HSC (Pluripotent Hematopoietic Stem Cell) |
Common Myeloid Progenitor Cells (CMP) -> Lymopcytes & Commom Lymphoid Progenitor Cells (CLP) -> Erythrocytes -Development determined by chemical messengers or cytokine |
|
|
Erythropoietin (EPO); what is it responsible for, where it's produced, what does it do |
-Cytokine responsible for production of RBCs -Produced by the kidneys in response to decrease in oxygen tension in blood -Circulates in the blood to the red bone marrow -Binds to receptors on erythroid precursor cells, causing them to divide and mature |
|
|
Hepatocytes |
Lesser amounts of EPO erythropoietin |
|
|
RBC development includes |
EPO Erythroid precursor cells Rubriblasts Reticulocytes |
|
|
Rubriblasts subdivided into |
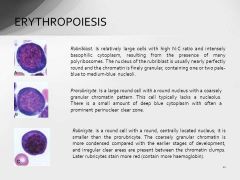
Pro-rubriblasts Rubricytes Metarubricytes |
|
|
Pro-rubriblasts |
Smaller than rubriblasts, slightly more dense basophillic cytoplasm, no visible nucleus |
|
|
Rubricytes |
Basophilic cytoplasm and clumping nucleus but changes ad it matures |
|
|
Metarubricytes |
Smallest cells, condensed nucleus, deep red cytoplasm Cannot divide and hemoglobin formation completed |
|
|
Reticulocytes |
Immature RBCs Lose ribosomal material- small pieces remaining - punctate reticulocytes |

