![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How long is G1 phase? S phase? G2? M Phase
|
G1: 12 hours (interphase)
S: Duplication G2: 3-4 hours (resting phase) M: 1 hour |
|
|
Anaphase Lag
|
One chromatid does not attach to spindle fiber, creates Monosomy
|
|
|
When does nondisjunction occur?
|
During Anaphase I
|
|
|
Differences in outcomes between Meoisis I and Meoisis II
|
In Meoisis II you have two identical copies of one chromosome
|
|
|
Percent liveborns with anueploidy?
|
0.3%
Leading cause of miscarriage 10-30% of fertilized eggs have a ch abnormality 20-25 % oocytes aneuploid 1-2% sperm aneuploidy |
|
|
4 Mechanisms of UPD
|
1) Trisomy rescue
2) Gamete complementation - sperm missing chromosome, so fert egg is disomic for same chromosome 3) Monosomy rescue - duplication of monosomic ch 4) Somatic crossing over: result in UPD for segment on ch. (ie beckwith) |
|
|
Triploidy
|
3 sets of ch. 1-3% preg
15-20% spont abortions that are ch normal 85% diadric (2 male, 1 female) 15% Digynic (2 female, 1 male) |
|
|
Diandric Triploid
|
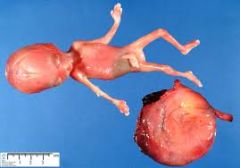
1 egg, 2 sperm
Empty egg fertilized by two sperm None survive well growth fetus normal or small head large placenta w appearance of partial hydatiform mole 3rd and 4th finger syndactyly |
|
|
Digynic triploid
|
2 egg, one sperm
macrocephaly placenta small and fibrotic can survive to term and be liveborn > 1 yr 3rd and 4th finger syndactyly |
|
|
Hydatidiform Moles
|
molar preg placenta has fluid filled sas (1-3 cm) from chorionic villa
|
|
|
Partial Moles
|
Fetus in early stages
Increased placental colume Mixture of normal and hydropic villi: polyploid |
|
|
Complete Mole
|
Fetus never present diffuse hydrops
Karyo is diploid (80% from dad 85% 46XY) Empty egg fertilized by two sperm risk 15-20 % degeneration into choriocarcinoma |
|
|
Benign Ovarian Teratomas
|
46 XY karo usually all mat origin, abnormal development or primary oocyte (tumors have hair teeth etc but unorganized)
|
|
|
Trisomy 21
|
47, XX + 21
1/800 births 3-4% unbalanced Robertsonian (40-60% from Parent) 1-2% mosaics 24% survive to term |
|
|
Trisomy 13
|
1/1200 births
CNS: deafness, seizures, apneic spells, holoproscencephaly microcephaly, micropthalmia, cleft lip,polydactyly 80% patau, 20% 13-14 translocation 55% parent of a carrier derivative 13:14 |
|
|
Robertsonian Translocations
|
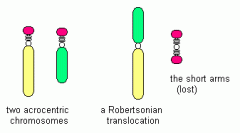
1/1000, 5 acrocentric ch (13-15, 21, 22)
85% der (13, 14)(q 10,q10), 10% der (14, 21)(q10)(q10) carriers at increase risk of infertility, unbalanced offspring, offspring UPD (90% isochromosomes ) 0.6-0.8% if translocation involves non-homologous ch. |
|
|
Reciprocal Translocations
|
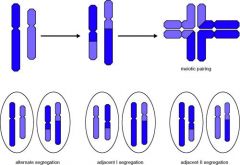
~1/500- 1/1000
70% inherited, unique, risks hard to determine 20-25% parens with liveborn children Size of segments matters: increased break point, smaller inbalance potential Small distal segments : small imbalances, larger risks large distal balances, decreased risks for liveborn abnormal child but increase miscarriage 11:22 common |
|
|
Pericentric Inversion
|
Change at centromere
|
|
|
Paracentric Inversion
|
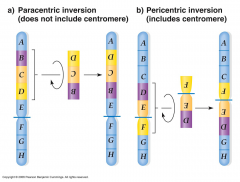
recombination at ends
90% inherited, genetically unstable duplicated or deleted regions almost always lethal |
|
|
Deletion Syndromes
|
4p
5p 18q 18p 18q |
|
|
Marker chromosomes
|
Supernumerary
Associated with abortion phenotype 13-16% 1/4000 newborns 80% from acrocentrics, 80% de novo Isochromosome for p12 = Pallister Killian syndrome: in fibroblasts and not metaphase cells |
|
|
Parental sources of aneuploidy
13-15 16 18 21 XXY XXX monosomy x |
Parental sources of aneuploidy
13:15-87% Maternal, 208 % survive to term 16: 100% maternal, 0 survive 18: 95% maternal, 5.4% survive 21: 93%, 24% survive XXY:55% maternal, 53% survive XXX: 95% maternal, 95% survive monosomy x: 8% PATERNAL, .3% survive |
|
|
Clinical FIndings that Suggest Mosaicsm
|
-mild or variant phenotype
-streaks of pigmentation on the skin -asymmetry |
|
|
Imprinted Chromosomes
|
7: maternal UPD accounts for 10% of russell silver syndrome
11: patUPD 11 associated with beckwidth wiedemman syndrome 14: mat 14 UPD mild-moderate developmental delay, precocious puberty, scoliosis 14: pat 14 more rare, polyhydramnios, low birth weight, blepharophimosis, short palperbral diggures, small ears, small thorax, abnormal ribs, joint contractures, severe MR MatUPD: >100 cases reported, associated with PW, can be hypopigmentations Pat UPD 15: angelman |
|
|
Acrocentric Ch
|
13-15
12, 22 |
|
|
46 XX or XY t(11;22)(q11.2)
|
recurring translocation
usually inherited unbalanced segregants risks for carriers ~3% for males and 5-7% for females |
|
|
Supernumerary RIng Ch
|
1% of non-supernumerary rings are inherited, rest are denovo
most are inherited from Mom |
|
|
Marker Ch
|
1/4000 newborns
80% from derived from acrocentrics, 40% from ch 15 20% familial 80% de novo and associated with maternal age effect |
|
|
XIST
|
X inactivation region on X chromosome
important role in initiating and maintaining X inactivation produces functional RNA and expressed in the inactive X chromosome |
|
|
PARS
|
Pseudoautosomal Regions (PARS)
distal short arm of X and Y contain highly similar DNA sequences Recombination happens often here |
|
|
Female vs Male Meoisis
|
Males: begin puberty, duration of meosis is 60-65 days, 4 spermatids, 100-200 million/ej
|

