![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
mental status is a crude assessment of:
|
BRAINSTEM
(cerebral cortex and reticular activating center) |
|
|
behavior relates to:
|
FOREBRAIN function
|
|
|
posture reflects function of what 3 things:
|
1. general proprioceptive system
2. vestibular system (special proprioception) 3. cerebellum |
|
|
continuous head tilt to one side suggests:
|
vestibular disease
|
|
|
Abnormal head coordination, bobbing, and tremors result from:
|
cerebellar dysfunction
|
|
|
6 signs of vestibular disease
|
Vestibular Clinical Signs
1. Head tilt - ipsilateral 2. Leaning/falling/tilting - ipsilateral 3. Ataxia 4. Vomiting and salivation -usually more prominent in peripheral disease 5. Nystagmus - labelled according to fast phase that is away from lesion 6. Strabismus - ipsilateral |
|
|
Abnormal posture of the trunk may be caused by:
|
abnormalities of the spine or altered muscle tone from spinal cord or brain lesions
|
|
|
Symmetrical trunkal ataxia is associated with
|
cerebellar lesions
|
|
|
Does maintenance of gait in quadrupeds require control from the cerebral cortex?
|
No.
|
|
|
Limbs are maintained in extension for supporting weight by what?
|
spinal cord reflexes
|
|
|
Gait is initiated where?
|
brainstem
|
|
|
Stepping movement signals are transmitted by what?
|
spinal cord
|
|
|
Do lesions in the forebrain abolish gait?
|
No.
|
|
|
True or false: Lesions in the brainstem cause paresis or paralysis.
|
TRUE
|
|
|
Most brainstem lesions cause paresis/paralysis that is ____________ (ipsilateral or contralateral), but rostral brainstem lesions may be seen ___________.
|
ipsilateral
contralateral |
|
|
Ataxia can be a sign of what 3 things?
|
1. general proprioceptive dysfunction (peripheral nerve and spinal cord pathways)
2. vestibular disease, or 3. cerebellar lesions |
|
|
The motor system is composed of what 2 primary segments?
|
1. upper motor neurons (UMN)
2. lower motor neurons (LMN) |
|
|
The upper motor neuron system includes:
|
1. neurons in the cerebral cortex and brainstem, and
2. their axonal processes (motor long tracts) that synapse on motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord |
|
|
The lower motor neurons are found where? (very general)
|
connecting the central nervous system with muscles
|
|
|
The UMN system is responsible for what?
|
voluntary movement
|
|
|
What are motor long tracts?
|
the axonal processes of upper motor neurons that synapse on motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord
|
|
|
What are the most important lower motor neurons?
|
cranial nerves, brachial plexus, and pelvic plexus
|
|
|
Define monoparesis.
|
paresis of one limb
|
|
|
Define paraparesis.
|
paresis of both pelvic limbs
|
|
|
Define tetraparesis/quadraparesis.
|
paresis of all limbs
|
|
|
Define hemiparesis.
|
paresis of limbs on one side
|
|
|
Ataxia is a sensory sign that results from one of what 3 things?
|
1. proprioceptive dysfunction
2. cerebellar dysfunction, or 3. vestibular dysfunction |
|
|
Define proprioception.
|
sense of position
|
|
|
The general proprioceptive system is composed of what 3 components?
|
1. receptors in joints, tendons and muscles (proproceptors),
2. axons connected to neurons located in the dorsal root ganglion, and 3. axonal processes located in long tracts of the spinal cord and brainstem |
|
|
Do cerebellar lesions cause paresis?
|
NO.
|
|
|
Paresis in vestibular disease indicates what?
|
that it's central vestibular disease
|
|
|
Define dermatomes.
|
the area of skin innervated by a pair of spinal nerves
|
|
|
What does the palpebral reflex check?
|
sensory component is the trigeminal nerve (V)
motor component is the facial nerve (VII) |
|
|
Jaw tone assesses what?
|
Cranial nerve 5 (motor to muscles of mastication)
|
|
|
Tongue placement and movement assesses what?
|
CN 12 – hypoglossal
|
|
|
Gag reflex assesses what?
|
CN 9 (glossopharyngeal) and CN 10 (vagus)
|
|
|
The clinical sign dysphagia may indicate what?
|
Disorders of CN 9 (glossopharyngeal) and CN 10 (vagus) with their origins in the caudal medulla
|
|
|
List the cranial nerves in order.
|
I Olfactory
II Optic III Oculomotor IV Trochlear V Trigeminal VI Abducent VII Facial VIII Acoustic (Vestibulocochlear) IX Glossopharyngeal X Vagus XI Spinal Accessory XII Hypoglossal |
|
|
List the cranial nerves in order.
|
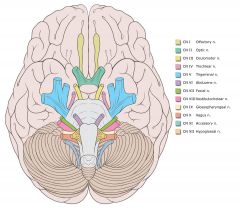
|
|
|
List the cranial nerves in order.
|
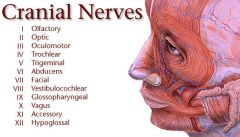
|
|
|
List the cranial nerves and state the function of each.
|
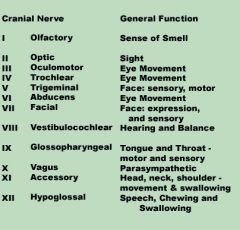
|
|
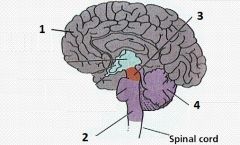
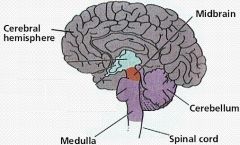
Label the diagram with the following terms: cerebral hemisphere (cerebrum), midbrain, medulla, cerebellum.
|
|

