![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When a normal cell is in a steady state it is called what?
|
Homeostasis
|
|
|
A change in homeostasis due to stimuli can cause what 2 options?
|
1.Cellular Adaption in which the cell adapts to its new environment to survive and is reversible.
2.injury and Cell death (necrosis) which is irreversible |
|
|
Stress affects normal cell function by either 2 ways:
|
1. cellular adaptation to maintain func.
2. fail to func and cause an injury which will lead to maladaptive changes and cell death. |
|
|
What is Cellular Adaptation?
|
Allows the stressed tissue to survive and maintain function.
|
|
|
Name the 5 types of cellular adaptations:
|
1. Atrophy
2. Hypertrophy 3. Hyperplasia 4. Dysplasia 5. Metaplasia |
|
|
What is Pathogenesis?
|
Events that lead to expression of the disease due to response to cell injury. (how the disease process evolved)
*many times the cause is unknown (idiopathic) |
|
|
What is Pathognomonic?
|
characteristic or diagnostic of a specific disease.
you can find signs that resemble a specific disease for diagnosis. |
|
|
7 Causes (mechanisms) of Cell Injury:
|
1. Neoplasia
2. Nutritional Imbalance 3. Hypoxia & Free Radical Injury 4. Physical & Chemical Agents 5. Genetic Derangement 6. Infectious Organisms 7. Immunological Rxns |
|
|
What is a Free Radical?
What 3 things does it to do a cell? |
1.Highly reactive chemicals w/unpaired electron causing high reactivity & unstable.
2. a)lipid peroxidation-damage cell membrane b)damages nucleic acids that make up DNA c)oxidative modification of proteins- free radical attaches to O2 which changes the shape & func of protein. also cause cross links |
|
|
What is Hypoxia?
|
Depletion of oxygen to cell; interrupts production of ATP
|
|
|
Depletion of ATP <5-10% of normal levels causes:
|
Lose control of:
Na/K pump Cell Metabolism Ca metabolism Protein synthesis |
|
|
Impaired Calcium Homeostasis is caused by:
|
ischemia and toxins which increase infux across cell membrane releasing calcium from intracellular stores.
|
|
|
What does an increase in calcium do to the body when it becomes imbalanced?
|
1. release phospholipases which damage the cell membrane
2. ATPase released that damage ATP 3.Endonuclease released that fragment chromatin |
|
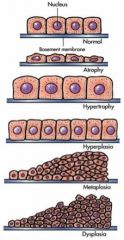
name this types of adaptations
|
normal
atrophy hypertrophy hyperplasia metaplasia dysplasia |
|
|
Review: things that cause membrane damage?
|
1. increased calcium causing imbalance
2. damaged lipids 3. loss of phospholipids 4. reactive oxygen species 5. cytoskeletal damage |
|
|
Reversible Cellular Adaptations include:
|
1. Atrophy
2. Hypertrophy 3. Hyperplasia 4. Dysplasia 5. Metaplasia 6. Accumulations- hydropic changes, fat, amyloid, etc. |
|
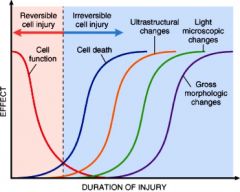
observe changes in function
|
only microscopic changes are seen much longer after death has occured
|
|
|
What is Cellular Atrophy?
|
Shrinkage in the size of the cell by loss of cell substance
|
|
|
What are causes for cell atrophy?
|
1. lack of oxygen
2. decreased workload 3. loss/decreased blood supply 4. inadequate nutrition 5. aging 6. loss of endocrine stimulation |
|
|
Atrophy of the kidneys can be caused by chronic low pressure which send chemicals that do what?
|
raise BP and cause high BP
|
|
|
What is Cellular Hypertrophy?
|
an increase in the size of the cell.
there are NO new cells. |
|
|
what are causes for hypertrophy?
|
an increase in functional demand or specific hormonal.
Example: bodybuilders |
|
|
what is a cause of heart hypertrophy?
|
1.chronic high BP can cause the heart to work harder and the muscle to increase in size.
2.leaky valves also cause the heart to pump harder |
|
|
What is Cellular Hyperplasia?
|
an increase in the number of cells in an organ. the tissue volume is increased.
|
|
|
Examples of Hyperplasia?
Examples of Pathologic Hyperplasia? *caused by excessive hormonal stimulation |
1. Hormonal: uterine and breasts growth in pregnancy
2. Compensatory: liver regeneration 1. Endometrial hyperplasia 2. Benign prostatic hyperplasia |
|
|
What is cellular metaplasia?
|
reversible change in which one cell type is replaced by another that can better withstand that environment.
|
|
|
What is the most common type of cell change in metaplasia?
|
columnar to squamous epithelial tissue
|

