![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Complete fracture |
occurs when the bone is broken to form 2 or more separate pieces |
|
|
Incomplete Fracture |
bone is only partially broken eg) green-stick fracture (shaft of bone is bent tearing the cortical bone on one side but not the other) |
|
|
Open aka compound fracture |
results when the skin is broken bone fragments may be open and protrude from the skin more damage to soft tissue including vessels and nerves, increased risk of infection |
|
|
Closed fracture |
skin is not broken at the fracture site |
|
|
Simple fracture |
a single break in the bone in which the bone ends maintain their alignment and position |
|
|
Comminuted fracture |
there are multiple fracture lines and bone fragments |
|
|
Compression fracture |
common in vertebrae occurring when bone is crushed or collapses into small pieces. |
|
|
Impacted fracture |
one end of the bone is forced or telescoped into the adjacent bone eg: neck of femur is crushed against the pelvis |
|
|
Pathologic fracture |
weakness in the bone structure due to conditions such as tumor or osteoporosis. Break occurs spontaneously or with very little stress on the bone. |
|
|
Stress fracture |
aka fatigue fractures result from repeated or excessive stress common on the tibia, femur, or second or third metatarsals |
|
|
Depressed Fracture |
occurs in the skull when the broken section is forced upward into the brain |
|
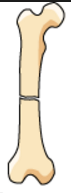
|
transverse fracture fracture across the bone |
|
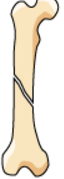
|
oblique fracture break at an angle to the diaphysis |
|
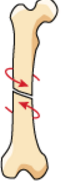
|
spiral fracture usually due to twisting injury |
|
|
Colles' Fracture |
break in the distal radius at the wrist common when a person attempts to break their fall by extending the arm and open hand |
|
|
Pott's fracture |
fracture of the lower fibula due to excessive stress on the ankles (stepping down with too much force) |
|
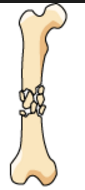
|
comminuted fracture |
|
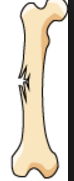
|
greenstick fracture or incomplete fracture |
|
|
Factors affecting healing of bone |
1)time (2 or more months in adults, 1 month kids 2) amount of damage( prolonged inflammation impairs healing 3)approximation of bony ends 4) secondary problems: foreign material, infection 5)systemic factors |
|
|
Systemic factors that influence healing of bone |
advanced age circulatory problems anemia diabetes mellitus nutritional deficits drugs (glucocorticoids) |
|
|
Healing stages of a fracture |
1)Hematoma forms 2)Fibrin mesh and Granulation tissue, increased chondroblasts and osteoblasts 3) Procallus forms 4)Bony callus forms 5) remodelling of bone occurs |
|
|
diaphoresis |
excessive sweating, or sweating to an unusual degree |
|
|
Crepitus |
grating sound created when ends of bones move across one another can be a sign the clavicle is broken in a newborn exam |
|
|
Fracture complications |
1)muscle spasm (may cause deformity of bone pieces 2)infections (tetanus/osteomyelitis) 3)Ischemia 4)compartment sydrome 5)fat emboli-fatty marrow escapes from bone marrow into vein 6)nerve damage 7)failure to heal (nonunion) 8) healing with deformity (malunion) 9) osteoarthritis or stunted growth |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of fracure |
1) crepitus 2)severe pain 3) Pallor 4) diaphoresis 5)hypotension |

