![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When was the DARK AGE?
|
1200 - 776 BC
|
|
|
When was the ARCHAIC PERIOD?
|
776 - 500 BC
|
|
|
When was the CLASSICAL PERIOD?
|
500 - 323 BC
|
|
|
When was the HELLENISTIC PERIOD?
|
323 - 30 BC
|
|
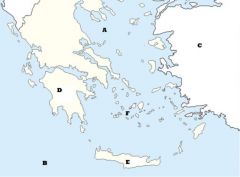
Identify:
- Crete - Asia Minor - Aegean Sea - Cycladic Islands - Peloponnesos - Mediterranean Sea |
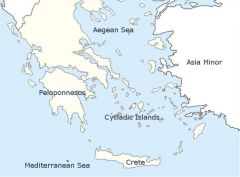
A: Aegean Sea
B: Mediterranean Sea C: Asia Minor D: Peloponnesos E: Crete F: Cycladic Islands |
|
|
Which period does the Late Helladic correspond to?
|
Mycenaean Period
|
|
|
Which period does the Middle Minoan correspond to?
|
Minoan Period
|
|
|
LECTURE #2:
What is a “Bronze Age” and when did the Bronze Age begin in the Aegean? When and why did it end? |
- Bronze Age: bronze was material used for making tools and weapons
- 3000 - 1200 BC - Ended when palace economies collapsed; political issues led to schism with Cyprus, thus no more access to copper. |
|
|
LECTURE #2:
Which periods of Greek history fall in the Bronze Age? What are their dates and their centers of power? |
1) Cycladic Civilization (2700 - 2400 BC)
2) Minoan Period (2000 - 1600 BC) 3) Mycenaean Period (1600 - 1200 BC) |
|
|
LECTURE #2:
Where are the Cyclades? What did archaeologists discover on the Cycladic islands in the early 20th century? |
LOCATION: between Peloponnese and Asia Minor
DISCOVERED: female marble statues - "Fertility figures" - "Mother goddesses" |
|
|
LECTURE #2:
Why do archaeologists refer to Bronze Age civilization on Crete as “Minoan”? Is this what the people of prehistoric Crete called themselves? |
No, MINOAN is a term coined by Sir Arthur Evans because it reminded him of a myth about King Minos (mythical Greek king, although Minoan is pre-Greek)
|
|
|
LECTURE #2:
In what sense are the Cycladic and Minoan civilizations “pre-Greek”? |
Neither civilization spoke Greek.
|
|
|
LECTURE #2:
What myth did Sir Arthur Evans think of when he uncovered the labyrinth-like palace architecture at Cnossus? |
- Poseidon sent King Minos a white bull to prove to Crete that he (Minos) was their true king.
- Minos refused to sacrifice bull back to Poseidon. - In retaliation, Poseidon made Minos’ daughter, Pasiphae, lust for the bull, who impregnated her. - Their child was half man and half bull (aka. Minotaur) |
|
|
LECTURE #2:
What did Greeks of the classical period believe about their Bronze Age past? What were their sources of knowledge? |
- Age of heroes who fought at Troy and Thebes and ruled the seas.
- Their myths and epic poetry about their past are vaguely similar to what archaeologists have discovered. - Sources of knowledge: Hesiod's poetry |
|
|
LECTURE #2:
What do archaeologists mean when they describe the Minoan palaces as “redistributive economies”? |
Their "taxes" were in the form of manufactured goods, produce, and raw materials, and were then redistributed to populace or used for trade.
|
|
|
LECTURE #2:
Explain what Linear A refers to and how it relates to Minoan civilization. |
- Form of writing used by Minoan civilization
- Language of Minoan Crete administration - Never been deciphered, but not Greek - Accident that they survived (fire in palace baked them) |
|
|
LECTURE #2:
Name the archaeologists who excavated at Cnossus and in the Cyclades in the early 1900s. |
1) Sir Arthur Evans
2) Christos Tsountas: discovered Cycladic figurines |
|
|
LECTURE #3:
Explain how archaeologists know that Mycenaeans took over Cnossus ca. 1450BC. How long did they rule on Crete? |
HOW THEY TOOK OVER:
- Definitive proof: Linear B tablets Also: - Artifacts exhibit significant differences from those of immediately preceding period - Evidence of destruction PERIOD OF RULE: ?? |
|
|
LECTURE #3:
What, if anything, did geological events on Thera have to do with the Mycenaean takeover of Crete? |
Volcanoes:
- Destroyed palaces - Weakened economy - Exploded island apart |
|
|
LECTURE #3:
What language does Linear B record? How was it deciphered, and by whom? |
- Linear B = earliest form of Greek
- Deciphered by Michael Ventris; he isolated familiar words from Linear A ?? |
|
|
LECTURE #3:
Who were the “Mycenaeans”? How did they get their name? |
MYCENAEANS: proto-Greeks who arrived in 2000 BC
NAME: came from prominence of Mycenae in story of Troy and other myths. |
|
|
LECTURE #3:
Name the sites of the major Mycenaean palaces. |
- Mycenae
- Pylos - Athens - Thebes - Tiryns |
|
|
LECTURE #3:
In what ways are Mycenaean palaces similar to Minoan? How do they differ? |
SIMILARITIES: manner of centralized authority located in a substantial palace.
DIFFERENCES: - "Cyclopean" walls - Megaron: ceremonial center of palace (rather than Minoan central court) |
|
|
LECTURE #3:
Who was Heinrich Schliemann and where did he excavate? What was his motivation for digging at these sites? |
- Archaeologist in 19th century who was a strong advocate for the historical reality of places mentioned in Homer's writing.
- Excavated Troy and Mycenae. - Motivated by childhood dream and desire for wealth. |
|
|
LECTURE #3:
What is a “tholos” tomb? Name one example of such a tomb at Mycenae. |
"THOLOS" TOMB: beehive-shaped tomb; statement of overwhelming power and magnificence.
ex. Treasury of Atreus |
|
|
LECTURE #3:
What features of the architecture and material finds at Mycenae have given historians the impression that the Mycenaeans were a warlike people, obsessed with honor and status? |
?
|
|
|
LECTURE #3:
When did the palaces collapse and why? What kinds of theories have been proposed to explain the fall of Mycenaean civilization? |
?
|
|
|
LECTURE #3:
What features of the architecture and material finds at Mycenae have given historians the impression that the Mycenaeans were a warlike people, obsessed with honor and status? |
Cyclopean walls...??
|
|
|
LECTURE #3:
When did the palaces collapse and why? What kinds of theories have been proposed to explain the fall of Mycenaean civilization? |
- All palaces collapsed or were destroyed in 1200 BC.
- Theories: 1) Invasion of "Sea peoples" 2) Natural disasters 3) Better military technology |
|
|
LECTURE #4:
What do we know about Hesiod from his poems? How does the concept of authorship differ when applied to Hesiod than to, say, John Updike? |
- Author of the "Theogeny" and "Works and Days"
- Lived in Ascara (near Thebes) ca. 700 BC - Worked with traditional material |
|
|
LECTURE #4:
What does “Theogony” mean? In what sense is the Theogony an aetiological poem (define “aetiology”)? |
- THEOGENY = "birth of the gods"
- AETIOLOGY = a story that explains the beginning of things - Answers the question of: how did the world come to be the way it is today? |
|
|
LECTURE #4:
What does Ouranos do to his children? How is he eventually dethroned? |
- He stuffs them back into Gaia (wife) for fear he'll be overthrown.
- Kronos overthrows him by cutting off his testicles. - Aphrodite (Venus) grows from severed testicles. |
|
|
IDENTIFY:
- Evans - Tsountas - Ventris - Schliemann - Dorpfeld |
- Sir Arthur Evans: excavated at Cnossus; coined term “Minoan”
- Tsountas: discovered female marble statues - Ventris: deciphered linear B - Schliemann: excavated troy and mcyenae (found “treasure of priam”) - Dorpfeld: excavated at Troy after Schliemann |
|
|
9) What features of the architecture and material finds at Mycenae have given historians the impression that the Mycenaeans were a warlike people, obsessed with honor and status?
|
WARLIKE PEOPLE
- Heavy fortification on high ground: cyclopean walls; in place to deal with sustained and predictable threats. - Tablets at Pylos: records of weaponry and armies - Art was all based around war scenes and hunting - Large amount of weapons in tombs STATUS and HONOR = burial goods and splendid tombs |
|
|
What is the Theogeny?
What is Works and Days? |
Theogeny: origin of gods
Works and Days: origin of human condition |
|
|
Who are Kronos' parents?
Who are Zeus' parents? |
Kronos = Ouranos and Gaia
Zeus = Kronos and Rhea |
|
|
Who was Metis and why is she significant?
|
- First wife of Zeus (who he eats so he won't be overthrown)
- Gets Kronos to throw up his children (for Zeus) |
|
|
Tell me about the ages of man.
|
GOLDEN: humans like gods but can’t reproduce
SILVER: reproduce, but live most of life as children BRONZE: violent, no honor HEROES: half human half divine IRON: present time of Hesiod |
|
|
How is the Hymn to Demeter an aetiological poem?
|
1. Seasons and agricultural year
2. Marriage (female point of view) 3. Eleusinian myths |

