![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
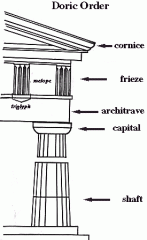
Doric Column
|
Capital - square abacus and a echinus formed by a curved molding.
Column - no base Shaft - tapered slightly, - fluting extended from bottom of the column to the annulets. |
|
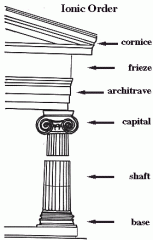
Ionic Column
|
Capital - a thin abacus, a flattened echinus, and a pair of Volutes on the front and the back faces.
Shaft - Tapered much less than did the Doric and small fillets separate the flutes. Attic base Slimmer than doric |
|
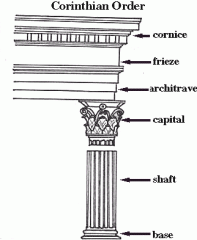
Corinthian Column
|
- Slimmest of columns
-Beneath the abacus were typically 2 rows of 8 curved acanthus leaves. Ionic and corinthian are very similar. Capital is more decorative. |
|
|
What are the 2 key elements in each classical Greek city and what was its function?
|
Acropolis
- Where most important religious structure were built. - Defensive refuge when it was attacked or besieged. Agora - Marketplace, entertainment center and public square. Both were cultural center of the city. |
|
|
What is the most important component of Greek temples and what part of it was used as basic unit of measurement?
|
Column
The diameter of the column as its base, resulting in different units, or diameters, for each building. |
|
|
In which way did classical Greek architecture first use molding extensively?
|
- Separate architectural elements
- Outline and define edges - Divide large areas - Emphasize the functions of components |
|
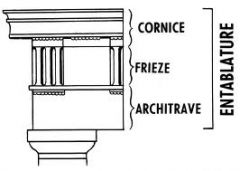
Which three elements form the entablature?
|
- Architrave
- Frieze - Cornice |

